Compare commits
65 Commits
1ed786139f
...
main
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
a8f567b17a
|
|||
|
917f3bd894
|
|||
|
53d2f55c21
|
|||
|
f01421d2f6
|
|||
|
8e8aba464b
|
|||
|
84648f971e
|
|||
|
f5c97428a3
|
|||
|
633e013f91
|
|||
|
ead3d16257
|
|||
|
bc5d4921ef
|
|||
|
5d70598113
|
|||
|
aa9b672d4f
|
|||
|
86542c0689
|
|||
|
997d8a0ac9
|
|||
|
133b32989c
|
|||
|
4cab80f831
|
|||
|
3c2d75d367
|
|||
|
39fea53675
|
|||
|
8bfc885370
|
|||
|
cb6c797863
|
|||
|
47227f523a
|
|||
|
939c510f21
|
|||
|
8dd4593f58
|
|||
| c2545377f1 | |||
| b5eb1661dc | |||
| ab6d79c94c | |||
|
ad98620120
|
|||
|
3974305e14
|
|||
|
f0fd9a10b4
|
|||
|
0be221d4f8
|
|||
| ace38f0baa | |||
| 4f18a7c2a1 | |||
| 781bfda313 | |||
| fbd4c46e00 | |||
| 5d2ff96026 | |||
| 66fcf7d5e7 | |||
| 720b101c47 | |||
| 947125ebd6 | |||
| ed5eca2f39 | |||
| 643854fd4a | |||
| 75fbf68749 | |||
| 6147ab6705 | |||
| eb21967a49 | |||
| 72c5fd90bd | |||
| 235ebdf748 | |||
| 90ce3a86f6 | |||
| 5371abb806 | |||
|
46c343c1d6
|
|||
|
78612e55a7
|
|||
|
77859f4a53
|
|||
|
59b7e87317
|
|||
|
6066cb4ec6
|
|||
|
9e54ad2ffe
|
|||
|
37056237bb
|
|||
|
111fec0006
|
|||
|
e616e4c1d3
|
|||
|
846a56a368
|
|||
|
fc4d35fd3f
|
|||
|
074b2d3453
|
|||
|
b618ef187d
|
|||
|
cc0e3763be
|
|||
|
b5a4053817
|
|||
|
e472ce9c7a
|
|||
|
cb02a70fcf
|
|||
|
98b3779e63
|
4
.gitattributes
vendored
Normal file
4
.gitattributes
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
*.png filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
||||
*.jpg filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
||||
*.jpge filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
||||
*.webp filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
|
||||
21
FTP mget 批量下载跳过交互.md
Normal file
21
FTP mget 批量下载跳过交互.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
### FTP mget 批量下载跳过交互
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下ftp里面的交互式提示是开启的,平常如果是下载多个文件时,这种提示很让人烦,
|
||||
|
||||
如果是在shell脚本里面要从ftp服务器上一次mget多个文件,写个交互式脚本很麻烦.最好是把这个交互式提示关掉.
|
||||
|
||||
进入ftp命令后,prompt会将交互式提示的配置置反,
|
||||
|
||||
如果原先交互式提示是开着的,
|
||||
|
||||
则使用prompt之后就关闭,如果原先是关闭的,
|
||||
|
||||
则使用prompt后就打开.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
当然也可以直接加参数如prompt on或者prompt off.
|
||||
458
SQL-窗口函数.md
Normal file
458
SQL-窗口函数.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,458 @@
|
||||
# SQL窗口函数
|
||||
|
||||
### 一. 什么是窗口函数
|
||||
|
||||
#### 基本含义
|
||||
|
||||
窗口限定一个范围,它可以理解为满足某些条件的记录集合,窗口函数也就是在窗口范围内执行的函数。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 基本语法
|
||||
|
||||
窗口函数有over关键字,指定函数执行的范围,可分为三部分:分组子句(partition by),排序子句(order by),窗口子句(rows)
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
<函数名> over (partition by <分组的列> order by <排序的列> rows between <起始行> and <终止行>)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**注意Mysql8才支持窗口函数**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 演示表格
|
||||
|
||||
| cid(班级id) | sname(学生姓名) | score(分数) |
|
||||
| ------------ | ----------------- | ------------- |
|
||||
| 001 | 张三 | 78 |
|
||||
| 001 | 李四 | 82 |
|
||||
| 002 | 小明 | 90 |
|
||||
| 001 | 王五 | 67 |
|
||||
| 002 | 小红 | 85 |
|
||||
| 002 | 小刚 | 62 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 演示脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE SQL_5 (
|
||||
cid varchar(4),
|
||||
sname varchar(4),
|
||||
score int
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
insert into SQL_5 (cid, sname, score) values ('001', '张三', 78);
|
||||
insert into SQL_5 (cid, sname, score) values ('001', '李四', 82);
|
||||
insert into SQL_5 (cid, sname, score) values ('002', '小明', 90);
|
||||
insert into SQL_5 (cid, sname, score) values ('001', '王五', 67);
|
||||
insert into SQL_5 (cid, sname, score) values ('002', '小红', 85);
|
||||
insert into SQL_5 (cid, sname, score) values ('002', '小刚', 62);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 二. 窗口的确定
|
||||
|
||||
例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select *, sum(score) over (partition by cid order by score rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) as '班级总分' from SQL_5;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 分组子句(partition by)
|
||||
|
||||
不分组可以写成partition by null或者直接不写
|
||||
|
||||
后面可以跟多个列, 如 partition by cid, sname
|
||||
|
||||
**注意 partition by与group by的区别**
|
||||
|
||||
1)前者不会压缩行数但是后者会
|
||||
|
||||
2)后者只能选取分组的列和聚合的列
|
||||
|
||||
也就是说group by 后生成的结果集与原表的行数和列数都不同
|
||||
|
||||
#### 排序子句(order by)
|
||||
|
||||
不排序可以写成order by null 或者直接不写
|
||||
|
||||
asc或不写表示升序,desc表示降序
|
||||
|
||||
后面可以跟多个列, 如 order by cid, sname
|
||||
|
||||
#### 窗口子句(rows)
|
||||
|
||||
窗口子句的描述
|
||||
|
||||
1) 起始行: N preceding/unbounded preceding
|
||||
|
||||
2) 当前行: current row
|
||||
|
||||
3) 终止行: N following/unbounded following
|
||||
|
||||
举例:
|
||||
|
||||
rows between unbounded preceding and current row 从之前所有的行到当前行
|
||||
|
||||
rows between 2 preceding and current row 从前面两行到当前行
|
||||
|
||||
rows between current row and unbounded following 从当前行到之后所有的行
|
||||
|
||||
rows between current row and 1following 从当前行到后面一行
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:**
|
||||
|
||||
**排序子句后面缺少窗口子句,窗口规范默认是 rows between unbounded preceding and current row**
|
||||
|
||||
**排序子句和窗口子句都缺失,窗口规范默认是 rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following**
|
||||
|
||||
#### 总体流程
|
||||
|
||||
1) 通过partition by 和 order by 子句确定大窗口( 定义出上界unbounded preceding和下界unbounded following)
|
||||
|
||||
2) 通过row 子句针对每一行数据确定小窗口(滑动窗口)
|
||||
|
||||
3) 对每行的小窗口内的数据执行函数并生成新的列
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 三. 函数分类
|
||||
|
||||
#### 排序类
|
||||
|
||||
rank, dense_rank, row_number
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
-- 【排序类】
|
||||
-- 按班级分组后打上序号 不考虑并列
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (partition by cid order by score desc) as '不可并列排名' from SQL_5;
|
||||
-- 按班级分组后作跳跃排名 考虑并列
|
||||
select *, rank() over (partition by cid order by score desc) as '跳跃可并列排名' from SQL_5;
|
||||
-- 按班级分组后作连续排名 考虑并列
|
||||
select *, dense_rank() over (partition by cid order by score desc) as '连续可并列排名' from SQL_5;
|
||||
-- 合并起来对比
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (partition by cid order by score desc) as '不可并列排名' ,
|
||||
rank() over (partition by cid order by score desc) as '跳跃可并列排名',
|
||||
dense_rank() over (partition by cid order by score desc) as '连续可并列排名'
|
||||
from SQL_5;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 聚合类
|
||||
|
||||
sum. avg, count, max, min
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
-- 【聚合类】
|
||||
-- 让同一班级每个学生都知道班级总分是多少
|
||||
select *, sum(score) over (partition by cid) as '班级总分' from SQL_5;
|
||||
-- 或者可以写成
|
||||
select *, sum(score) over (partition by cid rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) as '班级总分' from SQL_5;
|
||||
|
||||
-- 计算同一班级,每个同学和比他分数低的同学的累计总分是多少
|
||||
select *, sum(score) over (partition by cid order by score) '累加分数' from SQL_5;
|
||||
-- 或者可以写成 其中rows between ... and 是规定窗口大小
|
||||
select *, sum(score) over (partition by cid order by score rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as '累加分数' from SQL_5;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 跨行类
|
||||
|
||||
lag, lead
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
-- 【跨行类】
|
||||
-- lag/lead 函数 参数1:比较的列 参数2: 偏移量 参数3:找不到的默认值
|
||||
-- 同一班级内,成绩比自己低一名的分数是多少
|
||||
select *, lag(score, 1) over (partition by cid order by score) as '低一名的分数' from SQL_5;
|
||||
-- 或者写成
|
||||
select *, lag(score, 1, 0) over (partition by cid order by score) as '低一名的分数' from SQL_5;
|
||||
|
||||
-- 同一班级内,成绩比自己高2名的分数是多少
|
||||
select *, lead(score, 2) over (partition by cid order by score) as '高两名的分数' from SQL_5;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 四. 相关题目
|
||||
|
||||
#### 表格
|
||||
|
||||
| cid | sname | course | score |
|
||||
| ---- | ----- | ------ | ----- |
|
||||
| 001 | 张三 | 语文 | 78 |
|
||||
| 002 | 小刚 | 语文 | 71 |
|
||||
| 001 | 李四 | 数学 | 56 |
|
||||
| 002 | 小明 | 数学 | 54 |
|
||||
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE SQL_6 (
|
||||
cid varchar(4),
|
||||
sname varchar(4),
|
||||
course varchar(10),
|
||||
score int
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '张三', '语文', 78);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小刚', '语文', 71);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '李四', '数学', 56);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '王五', '数学', 97);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小明', '数学', 54);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小刚', '数学', 67);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小红', '数学', 82);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '王五', '语文', 80);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '张三', '数学', 77);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小明', '语文', 58);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小红', '语文', 87);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '李四', '语文', 60);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '张三', '英语', 66);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小刚', '英语', 50);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '李四', '地理', 59);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '王五', '地理', 88);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小明', '地理', 45);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小刚', '地理', 66);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小红', '地理', 82);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '王五', '英语', 81);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '张三', '地理', 77);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小明', '英语', 55);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('002', '小红', '英语', 87);
|
||||
insert into SQL_6 (cid, sname, course, score) values ('001', '李四', '英语', 61);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 分组内topN
|
||||
|
||||
问题1:求出每个学生成绩最高的三条记录
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select * from
|
||||
(
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (partition by sname order by score desc) as rn from SQL_6
|
||||
) temp
|
||||
where rn <= 3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
###### 公式:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select * from
|
||||
(
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (partition by 分组列 order by 比较列) as rn from table
|
||||
) as tmp
|
||||
where rn <= N;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 汇总分析
|
||||
|
||||
问题2:找出每门课程都高于班级课程平均分的学生
|
||||
|
||||
可以拆解成以下几个问题:
|
||||
|
||||
1)求出每个班级,每门课程的平均分
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
with
|
||||
-- 1) 求出每个班级,每门课程的平均分
|
||||
t1 as
|
||||
(
|
||||
select *,
|
||||
avg(score) over (partition by cid, course) as 'avg'
|
||||
from SQL_6
|
||||
),
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2)将学生每门课程的成绩与所在班级的对应课程平均分相减,结果大于0就说明该学生的这门成绩高于课程平均分
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
t2 as (
|
||||
select *,
|
||||
score - avg as 'del'
|
||||
from t1
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3)“找出每门课程都高于班级课程平均分的学生”说明对于学生来说,最小的“相减结果”都是大于0的
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select sname from t2
|
||||
group by sname
|
||||
having min(del) > 0;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
合并后的SQL语句
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
with
|
||||
t1 as
|
||||
(
|
||||
select *,
|
||||
avg(score) over (partition by cid, course) as 'avg'
|
||||
from SQL_6
|
||||
),
|
||||
t2 as (
|
||||
select *,
|
||||
score - avg as 'del'
|
||||
from t1
|
||||
)
|
||||
select sname from t2
|
||||
group by sname
|
||||
having min(del) > 0;
|
||||
|
||||
-- 或者
|
||||
select sname from (
|
||||
select *,
|
||||
score - avg as 'del'
|
||||
from (
|
||||
select *,
|
||||
avg(score) over (partition by cid, course) as 'avg'
|
||||
from SQL_6
|
||||
) t1
|
||||
) t2
|
||||
group by sname
|
||||
having min(del) > 0;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 表格
|
||||
|
||||
| empno | ename | hire_date | salary | dept_no |
|
||||
| ----- | ----- | ---------- | ------ | ------- |
|
||||
| 001 | Adam | 2018-03-01 | 1000 | A |
|
||||
| 002 | Bill | 2021-03-01 | 1200 | A |
|
||||
| 003 | Cindy | 2016-03-01 | 1500 | A |
|
||||
| 004 | Danny | 2020-03-01 | 5000 | A |
|
||||
| 005 | Eason | 2020-03-01 | 4000 | B |
|
||||
| 006 | Fred | 2018-03-01 | 3500 | B |
|
||||
| 007 | Gary | 2017-03-01 | 1800 | B |
|
||||
| 008 | Hugo | 2020-03-01 | 2500 | B |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE SQL_7 (
|
||||
empno varchar(4),
|
||||
ename varchar(10),
|
||||
hire_date varchar(10),
|
||||
salary int,
|
||||
dept_no varchar(2)
|
||||
);
|
||||
insert into SQL_7 (empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no) values ('001', 'Adam', '2018-03-01', 1000, 'A');
|
||||
insert into SQL_7 (empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no) values ('002', 'Bill', '2021-03-01', 1200, 'A');
|
||||
insert into SQL_7 (empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no) values ('003', 'Cindy', '2016-03-01', 1500, 'A');
|
||||
insert into SQL_7 (empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no) values ('004', 'Danny', '2020-03-01', 5000, 'A');
|
||||
insert into SQL_7 (empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no) values ('005', 'Eason', '2020-03-01', 4000, 'B');
|
||||
insert into SQL_7 (empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no) values ('006', 'Fred', '2018-03-01', 3500, 'B');
|
||||
insert into SQL_7 (empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no) values ('007', 'Gary', '2017-03-01', 1800, 'B');
|
||||
insert into SQL_7 (empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no) values ('008', 'Hugo', '2020-03-01', 4500, 'B');
|
||||
|
||||
select * from SQL_7;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 分组内topN
|
||||
|
||||
问题一:求出每个部门工资最高的前三名员工
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select * from
|
||||
(
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (partition by dept_no order by salary desc) as rn from SQL_7
|
||||
) as tmp
|
||||
where rn <= 3;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 汇总分析
|
||||
|
||||
问题二:计算这些员工的工资占所属部门总工资的百分比
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
with
|
||||
t1 as (
|
||||
select * , sum(salary) over (partition by dept_no) as 'sum_sal' from SQL_7
|
||||
),
|
||||
t2 as (
|
||||
select *, round(salary*100/sum_sal,2) as 'percentage' from t1
|
||||
)
|
||||
select * from t2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
问题三:对各部门员工的工资进行从小到大排序,排名前30%为低层,30%-80%为中层,高于80%为高层,并打上标签
|
||||
|
||||
```label
|
||||
with
|
||||
t1 as (
|
||||
select * , row_number() over (partition by dept_no order by salary) as cnt,
|
||||
count(empno) over (partition by dept_no) as 'sum' from SQL_7
|
||||
),
|
||||
t2 as (
|
||||
select *, round(cnt/sum,2) as 'percentage' from t1
|
||||
),
|
||||
t3 as (
|
||||
select *, case when percentage <= 0.3 then '低层'
|
||||
when percentage <= 0.8 then '中层'
|
||||
when percentage <= 1 then '高层' end as 'label'
|
||||
from t2
|
||||
)
|
||||
select empno, ename, hire_date, salary, dept_no, label from t3;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
问题四:统计每年入职总数以及截至本年累计入职总人数(本年总入职人数 + 本年之前所有年的总入职人数之和)
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select year(hire_date) as hire_year, count(empno) as cnt
|
||||
from SQL_7
|
||||
group by year(hire_date) order by hire_year;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
with t1 as (
|
||||
select year(hire_date) as hire_year, count(empno) as cnt from SQL_7 group by year(hire_date) order by hire_year
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
select *, sum(cnt) over(partition by null rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as sum from t1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 五. 技巧
|
||||
|
||||
1)分组内topN公式
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select * from
|
||||
(
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (partition by 分组列 order by 比较列) as rn from table
|
||||
) as tmp
|
||||
where rn <= N;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2) 窗口函数 -> 生成辅助列(相当于高级语言的临时变量)
|
||||
|
||||
3) with 语句 -> 生成临时表(相当于高级语言的局部方法)
|
||||
|
||||
把复杂的问题拆分成多个子问题并用临时表去表达
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
324
SQL-行转列与列转行.md
Normal file
324
SQL-行转列与列转行.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,324 @@
|
||||
# SQL 讲解 —— 行转列 与 列转行
|
||||
|
||||
## 行转列
|
||||
|
||||
### 题目1
|
||||
|
||||
#### 描述
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
name subject score
|
||||
张三 语文 78
|
||||
张三 数学 88
|
||||
张三 英语 98
|
||||
李四 语文 89
|
||||
李四 数学 76
|
||||
李四 英语 90
|
||||
王五 语文 99
|
||||
王五 数学 66
|
||||
王五 英语 91
|
||||
|
||||
name 语文 数学 英语
|
||||
张三 78 88 98
|
||||
李四 89 76 90
|
||||
王五 99 66 91
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
create table SQL_1
|
||||
(
|
||||
name varchar(20),
|
||||
subject varchar(20),
|
||||
score float
|
||||
);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('张三', '语文', 78);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('张三', '数学', 88);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('张三', '英语', 98);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('李四', '语文', 89);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('李四', '数学', 76);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('李四', '英语', 90);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('王五', '语文', 99);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('王五', '数学', 66);
|
||||
insert into SQL_1 (name, subject, score) values ('王五', '英语', 91);
|
||||
select * from SQL_1;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 解题步骤
|
||||
|
||||
1) 确定分组列,转换列,数据列
|
||||
|
||||
2) 生成伪列
|
||||
|
||||
3) 做分组查询
|
||||
|
||||
4) 选择合适的聚合函数
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 两步法
|
||||
|
||||
##### 公式:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select 分组列,
|
||||
聚合函数(m1) as 列名1,
|
||||
聚合函数(m2) as 列名2,
|
||||
聚合函数(m3) as 列名3
|
||||
from (select *,
|
||||
case 转换列 when 转换列值1 then 数据列 else ... end as m1,
|
||||
case 转换列 when 转换列值2 then 数据列 else ... end as m2,
|
||||
case 转换列 when 转换列值3 then 数据列 else ... end as m3
|
||||
from 表名) 临时表名
|
||||
group by 分组列;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 解题SQL
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select name,
|
||||
sum(m1) as 语文,
|
||||
sum(m2) as 数学,
|
||||
sum(m3) as 英语
|
||||
from (select *,
|
||||
case subject when '语文' then score else 0 end as m1,
|
||||
case subject when '数学' then score else 0 end as m2,
|
||||
case subject when '英语' then score else 0 end as m3
|
||||
from sql_1) tmp
|
||||
group by name;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 一步法
|
||||
|
||||
##### 公式:
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select 分组列,
|
||||
聚合函数(case 转换列 when 转换列值1 then 数据列 else ... end) as 列名1,
|
||||
聚合函数(case 转换列 when 转换列值2 then 数据列 else ... end) as 列名2,
|
||||
聚合函数(case 转换列 when 转换列值3 then 数据列 else ... end) as 列名3
|
||||
...
|
||||
from 表名
|
||||
group by 分组列;
|
||||
|
||||
select 分组列,
|
||||
聚合函数(case when 转换列=转换列值1 then 数据列 else ... end) as 列名1,
|
||||
聚合函数(case when 转换列=转换列值2 then 数据列 else ... end) as 列名2,
|
||||
聚合函数(case when 转换列=转换列值3 then 数据列 else ... end) as 列名3
|
||||
...
|
||||
from 表名
|
||||
group by 分组列;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 解题SQL
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select name,
|
||||
sum(case subject when '语文' then score else 0 end) as 语文,
|
||||
sum(case subject when '数学' then score else 0 end) as 数学,
|
||||
sum(case subject when '英语' then score else 0 end) as 英语
|
||||
from sql_1
|
||||
group by name;
|
||||
|
||||
select name,
|
||||
sum(case when subject = '语文' then score else 0 end) as 语文,
|
||||
sum(case when subject = '数学' then score else 0 end) as 数学,
|
||||
sum(case when subject = '英语' then score else 0 end) as 英语
|
||||
from sql_1
|
||||
group by name;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题目2
|
||||
|
||||
#### 描述
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
# 日期 结果
|
||||
# 2022-01-01 胜
|
||||
# 2022-01-01 胜
|
||||
# 2022-01-02 负
|
||||
# 2022-01-02 负
|
||||
# 2022-01-01 负
|
||||
# 2022-01-02 负
|
||||
# 2022-01-02 胜
|
||||
|
||||
# 日期 胜 负
|
||||
# 2022-01-01 2 1
|
||||
# 2022-01-02 1 3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
create table SQL_2(
|
||||
ddate varchar(10), result varchar(2)
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
insert into SQL_2 (ddate, result) values('2022-01-01','胜');
|
||||
insert into SQL_2 (ddate, result) values('2022-01-01','胜');
|
||||
insert into SQL_2 (ddate, result) values('2022-01-02','负');
|
||||
insert into SQL_2 (ddate, result) values('2022-01-02','负');
|
||||
insert into SQL_2 (ddate, result) values('2022-01-01','负');
|
||||
insert into SQL_2 (ddate, result) values('2022-01-02','负');
|
||||
insert into SQL_2 (ddate, result) values('2022-01-02','胜');
|
||||
select * from SQL_2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 解题SQL
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select ddate,
|
||||
sum(case when result = '胜' then 1 else 0 end) as 胜,
|
||||
sum(case when result = '负' then 1 else 0 end) as 负
|
||||
from sql_2
|
||||
group by ddate;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 列转行
|
||||
|
||||
### 题目3
|
||||
|
||||
#### 描述
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
name 语文 数学 英语
|
||||
张三 78 88 98
|
||||
李四 89 76 90
|
||||
王五 99 66 91
|
||||
|
||||
name subject score
|
||||
张三 语文 78
|
||||
张三 数学 88
|
||||
张三 英语 98
|
||||
李四 语文 89
|
||||
李四 数学 76
|
||||
李四 英语 90
|
||||
王五 语文 99
|
||||
王五 数学 66
|
||||
王五 英语 91
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE SQL_3 (
|
||||
name varchar(20),
|
||||
语文 float,
|
||||
数学 float,
|
||||
英语 float
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
insert into SQL_3 (name, '语文', '数学', '英语') values ('张三', 78, 88, 98);
|
||||
insert into SQL_3 (name, '语文', '数学', '英语') values ('李四', 89, 76, 90);
|
||||
insert into SQL_3 (name, '语文', '数学', '英语') values ('王五', 99, 66, 91);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 解题步骤
|
||||
|
||||
1) 确定转换列,非转换列
|
||||
|
||||
2) 生成新列
|
||||
|
||||
3) 使用union或union all 进行合并
|
||||
|
||||
4) 根据需要进行order by
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 公式
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SELECT 非转换列, '转换列1' AS 新转换列名, 转换列1 AS 新数据列名 FROM 表名
|
||||
UNION ALL
|
||||
SELECT 非转换列, '转换列2' AS 新转换列名, 转换列2 AS 新数据列名 FROM 表名
|
||||
UNION ALL
|
||||
SELECT 非转换列, '转换列3' AS 新转换列名, 转换列3 AS 新数据列名 FROM 表名
|
||||
ORDER BY ...;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 解题SQL
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SELECT name,'语文' AS subject,语文 AS score FROM SQL_3
|
||||
UNION ALL
|
||||
SELECT name,'数学' AS subject,数学 AS score FROM SQL_3
|
||||
UNION ALL
|
||||
SELECT name,'英语' AS subject,英语 AS score FROM SQL_3
|
||||
ORDER BY name ASC, subject DESC;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题目4
|
||||
|
||||
#### 描述
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
|
||||
1000 2000 3000 4000
|
||||
|
||||
季度 业绩
|
||||
Q1 1000
|
||||
Q2 2000
|
||||
Q3 3000
|
||||
Q4 4000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE SQL_4 (
|
||||
Q1 int, Q2 int, Q3 int, Q4 int
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
insert into SQL_4 values (1000, 2000, 3000, 4000);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 解题SQL
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SELECT 'Q1' AS 季度, Q1 AS 业绩 FROM SQL_4
|
||||
UNION ALL
|
||||
SELECT 'Q2' AS 季度, Q2 AS 业绩 FROM SQL_4
|
||||
UNION ALL
|
||||
SELECT 'Q3' AS 季度, Q3 AS 业绩 FROM SQL_4
|
||||
UNION ALL
|
||||
SELECT 'Q4' AS 季度, Q4 AS 业绩 FROM SQL_4
|
||||
ORDER BY 季度;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 技巧:
|
||||
|
||||
扩展列:select ... as 新列名
|
||||
|
||||
减少列:直接不写
|
||||
|
||||
扩展行:union/ union all
|
||||
|
||||
减少行: 聚合函数
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
231
SQL窗口函数(二).md
Normal file
231
SQL窗口函数(二).md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,231 @@
|
||||
# SQL窗口函数(二)—— 连续问题
|
||||
|
||||
### 题目一
|
||||
|
||||
#### 表格
|
||||
|
||||
| user_id | login_date |
|
||||
| ------- | ---------- |
|
||||
| A | 2022-09-02 |
|
||||
| A | 2022-09-03 |
|
||||
| A | 2022-09-04 |
|
||||
| B | 2021-11-25 |
|
||||
| B | 2021-12-31 |
|
||||
| C | 2022-01-01 |
|
||||
| C | 2022-04-04 |
|
||||
| C | 2022-09-03 |
|
||||
| C | 2022-09-04 |
|
||||
| C | 2022-09-05 |
|
||||
| A | 2022-09-03 |
|
||||
| D | 2022-10-20 |
|
||||
| D | 2022-10-21 |
|
||||
| A | 2022-10-03 |
|
||||
| D | 2022-10-22 |
|
||||
| D | 2022-10-23 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE SQL_8
|
||||
(
|
||||
user_id varchar(2),
|
||||
login_date date
|
||||
);
|
||||
INSERT INTO SQL_8 (user_id,login_date)
|
||||
VALUES ('A', '2022-09-02'), ('A', '2022-09-03'), ('A', '2022-09-04'), ('B', '2021-11-25'),
|
||||
('B', '2021-12-31'), ('C', '2022-01-01'), ('C', '2022-04-04'), ('C', '2022-09-03'),
|
||||
('C', '2022-09-05'), ('C', '2022-09-04'), ('A', '2022-09-03'), ('D', '2022-10-20'),
|
||||
('D', '2022-10-21'), ('A', '2022-10-03'), ('D', '2022-10-22'), ('D', '2022-10-23');
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 问题
|
||||
|
||||
找出这张表中所有的连续3天登录用户
|
||||
|
||||
#### 分析
|
||||
|
||||
连续N天登录用户,要求数据行满足以下条件:
|
||||
|
||||
1) userid 要相同,表示同一用户
|
||||
|
||||
2) 同一用户每行记录以登录时间从小到大排序
|
||||
|
||||
3) 后一行记录比前一行记录的登录时间多一天
|
||||
|
||||
4) 数据行数大于等于N
|
||||
|
||||
#### 解答
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
-- 方法一
|
||||
with t1 as (
|
||||
select distinct user_id, login_date from SQL_8
|
||||
),
|
||||
t2 as (
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (partition by user_id order by login_date) as rn from t1
|
||||
),
|
||||
t3 as (
|
||||
select *, DATE_SUB(login_date, interval rn day) as sub from t2
|
||||
)
|
||||
select distinct user_id from t3 group by user_id, sub having count(user_id) >= 3;
|
||||
|
||||
-- 方法二
|
||||
with t1 as (
|
||||
select distinct user_id, login_date from SQL_8
|
||||
),
|
||||
t2 as (
|
||||
select *, DATEDIFF(login_date, lag(login_date, 1) over (partition by user_id order by login_date)) as diff from t1
|
||||
)
|
||||
select user_id from t2 where diff = 1 group by user_id having count(user_id) >= 2;
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题目二
|
||||
|
||||
#### 表格
|
||||
|
||||
| player_id | score | score_time |
|
||||
| --------- | ----- | ------------------- |
|
||||
| B3 | 1 | 2022-09-20 19:00:14 |
|
||||
| A2 | 1 | 2022-09-20 19:01:04 |
|
||||
| A2 | 3 | 2022-09-20 19:01:16 |
|
||||
| A2 | 3 | 2022-09-20 19:02:05 |
|
||||
| A2 | 2 | 2022-09-20 19:02:25 |
|
||||
| B5 | 2 | 2022-09-20 19:02:54 |
|
||||
| A4 | 3 | 2022-09-20 19:03:10 |
|
||||
| B1 | 2 | 2022-09-20 19:03:34 |
|
||||
| B1 | 2 | 2022-09-20 19:03:58 |
|
||||
| B1 | 3 | 2022-09-20 19:04:07 |
|
||||
| A2 | 1 | 2022-09-20 19:04:19 |
|
||||
| A3 | 2 | 2022-09-20 19:04:31 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE SQL_9
|
||||
(
|
||||
player_id varchar(2),
|
||||
score int,
|
||||
score_time datetime
|
||||
);
|
||||
INSERT INTO SQL_9 (player_id, score, score_time)
|
||||
VALUES ('B3', 1, '2022-09-20 19:00:14'), ('A2', 1, '2022-09-20 19:01:04'),
|
||||
('A2', 3, '2022-09-20 19:01:16'), ('A2', 3, '2022-09-20 19:02:05'),
|
||||
('A2', 2, '2022-09-20 19:02:25'), ('B3', 2, '2022-09-20 19:02:54'),
|
||||
('A4', 3, '2022-09-20 19:03:10'), ('B1', 2, '2022-09-20 19:03:34'),
|
||||
('B1', 2, '2022-09-20 19:03:58'), ('B1', 3, '2022-09-20 19:04:07'),
|
||||
('A2', 1, '2022-09-20 19:04:19'), ('B3', 2, '2022-09-20 19:04:31');
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 问题
|
||||
|
||||
统计出连续三次(及以上)为球队得分的球员名单
|
||||
|
||||
#### 分析
|
||||
|
||||
连续N次以上为球队得分, 要求数据行满足以下条件:
|
||||
|
||||
1) player_id 要相同表示同一球员
|
||||
|
||||
2) 每行记录以得分时间从小到大排序
|
||||
|
||||
3) 数据行数大于等于N
|
||||
|
||||
#### 解答
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
-- 方法一
|
||||
with t1 as (
|
||||
select *, lag(player_id, 1) over (order by score_time) as last_play_id from SQL_9
|
||||
)
|
||||
select distinct player_id from t1 where player_id = last_play_id group by player_id having count(player_id) >= 2;
|
||||
|
||||
-- 方法二
|
||||
with t1 as (
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (order by score_time) as rn from SQL_9
|
||||
),
|
||||
t2 as (
|
||||
select *, row_number() over (order by score_time) + 1 as rn from SQL_9
|
||||
),
|
||||
t3 as (
|
||||
select t1.player_id as player_id from t1 join t2 on t1.rn = t2.rn and t1.player_id = t2.player_id
|
||||
)
|
||||
select distinct player_id from t3 group by player_id having count(player_id) >= 2;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 题目三
|
||||
|
||||
#### 表格
|
||||
|
||||
| log_id |
|
||||
| :----: |
|
||||
| 1 |
|
||||
| 2 |
|
||||
| 3 |
|
||||
| 7 |
|
||||
| 8 |
|
||||
| 10 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
CREATE TABLE SQL_10
|
||||
(
|
||||
log_id int
|
||||
);
|
||||
INSERT INTO SQL_10 (log_id) VALUES (1), (2), (3), (7), (8), (10);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 问题
|
||||
|
||||
编写SQL 查询得到 Logs 表中的连续区间的开始数字和结束数字。按照 start_id 排序。查询结果格式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| start_id | end_id |
|
||||
| -------- | ------ |
|
||||
| 1 | 3 |
|
||||
| 7 | 8 |
|
||||
| 10 | 10 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### 解答
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
-- 方法一
|
||||
with t1 as (
|
||||
select *, log_id - row_number() over (order by log_id) as gr from SQL_10
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
select min(log_id) as start_id, max(log_id) as end_id from t1 group by gr
|
||||
|
||||
-- 方法二
|
||||
with t1 as (
|
||||
select *, log_id - row_number() over (order by log_id) as gr, log_id - lag(log_id,1) over () as diff from SQL_10
|
||||
),
|
||||
t2 as (
|
||||
select log_id, gr from t1 where ifnull(diff,-1) <> 1
|
||||
),
|
||||
t3 as (
|
||||
select *, log_id - row_number() over (order by log_id) as gr, log_id - lead(log_id,1) over () as diff from SQL_10
|
||||
),
|
||||
t4 as (
|
||||
select log_id, gr from t3 where ifnull(diff, 1) <> -1
|
||||
)
|
||||
select t2.log_id as start_id, t4.log_id as end_id from t2, t4 where t2.gr = t4.gr;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 技巧
|
||||
|
||||
如何求连续区间?
|
||||
|
||||
1)行号过滤法
|
||||
|
||||
通过row_number() 生成连续行号,与区间列进行差值运算,得到的临时结果如果相同表示为同一连续区间
|
||||
|
||||
2) 错位比较法
|
||||
|
||||
通过row_number() / row_number() + 1 分别生成原生的和错位的连续行号列,进行连表操作
|
||||
|
||||
也可以通过lag/lead函数直接生成错位列
|
||||
2759
Spark知识体系五万字讲解,学习与面试收藏这篇就够了!.md
Normal file
2759
Spark知识体系五万字讲解,学习与面试收藏这篇就够了!.md
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
300
cdh/CDH部署Kerberos.md
Normal file
300
cdh/CDH部署Kerberos.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,300 @@
|
||||
# CDH部署
|
||||
|
||||
## Kerberos部署
|
||||
|
||||
### 系统环境
|
||||
|
||||
- Centos7.7
|
||||
|
||||
### CDH版本
|
||||
|
||||
- 6.3.2
|
||||
|
||||
### 部署用户权限
|
||||
|
||||
- root权限
|
||||
|
||||
### KDC服务安装及配置
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Cloudera Manager服务器上安装KDC服务
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yum install krb5-server krb5-libs krb5-auth-dialog krb5-workstation openldap-clients -y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 会生成/etc/krb5.conf、/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl、/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf三个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 修改/etc/krb5.conf配置
|
||||
|
||||
```bash\
|
||||
vi /etc/krb5.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 配置文件内容
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Configuration snippets may be placed in this directory as well
|
||||
includedir /etc/krb5.conf.d/
|
||||
|
||||
[logging]
|
||||
default = FILE:/var/log/krb5libs.log
|
||||
kdc = FILE:/var/log/krb5kdc.log
|
||||
admin_server = FILE:/var/log/kadmind.log
|
||||
|
||||
[libdefaults]
|
||||
dns_lookup_realm = false
|
||||
ticket_lifetime = 24h
|
||||
renew_lifetime = 7d
|
||||
forwardable = true
|
||||
rdns = false
|
||||
pkinit_anchors = FILE:/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
|
||||
default_realm = A.COM
|
||||
#default_ccache_name = KEYRING:persistent:%{uid}
|
||||
|
||||
[realms]
|
||||
A.COM = {
|
||||
kdc = node-1
|
||||
admin_server = noe-1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[domain_realm]
|
||||
.a.com = A.COM
|
||||
a.com = A.COM
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 配置参数
|
||||
|
||||
- default_realm: 默认realm,例如当我们使用kinit而不指定principal时使用的就是这里配置的默认realm
|
||||
|
||||
- dns_lookup_realm:是否可以通过DNS查找使用什么样的realm
|
||||
|
||||
- ticket_lifetime: 设定ticket的有效期
|
||||
|
||||
- forwardable: 用于指定ticket是否可以被转发,转发的含义是:如果一个用户已经有了一个TGT,当他登入到另一个远程系统,KDC会为他自动重新创建一个TGT,而不需要让用户重新进行身份认证。
|
||||
|
||||
- 然后是[realms]部分,这一部分会列出所有的realm,kdc和admin_server两个配置是在告诉客户端哪台服务器在运行KDC以及kadmin进程。这两项配置可以在服务器上追加端口,如果不指定,则使用默认端口,KDC是88,admin server是749.
|
||||
|
||||
- 最后一部分[domain_realm]是配置DNS名称和Kerberos Realm映射的。 .http://a.com = A.COM是在说:所有在a.com域下的主机都会被映射到A.COM这个realm下,而a.com = A.COM是说a.com它自己也会映射到A.COM这个realm。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 修改/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl配置
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
vi /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
*/admin@A.COM *
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 修改/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf配置
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
vi /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[kdcdefaults]
|
||||
kdc_ports = 88
|
||||
kdc_tcp_ports = 88
|
||||
|
||||
[realms]
|
||||
A.COM = {
|
||||
#master_key_type = aes256-cts
|
||||
max_renewable_life= 7d 0h 0m 0s
|
||||
acl_file = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.acl
|
||||
dict_file = /usr/share/dict/words
|
||||
admin_keytab = /var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kadm5.keytab
|
||||
supported_enctypes = aes256-cts:normal aes128-cts:normal des3-hmac-sha1:normal arcfour-hmac:normal camellia256-cts:normal camellia128-cts:normal des-hmac-sha1:normal des-cbc-md5:normal des-cbc-crc:normal
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建Kerberos数据库
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kdb5_util create –r http://A.COM -s
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 密码 hadoop
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建Kerberos的管理账号
|
||||
|
||||
admin/admin@A.COM
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kadmin.local
|
||||
addprinc admin/admin@A.COM
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 密码/账号 admin/admin@A.COM
|
||||
|
||||
#### 将Kerberos服务添加到自启动服务,并启动krb5kdc和kadmin服务
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
systemctl enable krb5kdc
|
||||
systemctl enable kadmin
|
||||
systemctl start krb5kdc
|
||||
systemctl start kadmin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 测试Kerberos的管理员账号
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kinit admin/admin@A.COM
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 为集群安装所有Kerberos客户端,包括Cloudera Manager
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yum -y install krb5-libs krb5-workstation
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 将KDC Server上的krb5.conf文件拷贝到所有Kerberos客户端
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
scp /etc/krb5.conf root@node-2:/etc/
|
||||
scp /etc/krb5.conf root@node-3:/etc/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## CDH集群启用Kerberos
|
||||
|
||||
### 在KDC中给Cloudera Manager添加管理员账号
|
||||
|
||||
cloudera-scm/admin@A.COM
|
||||
|
||||
执行命令
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kadmin.local
|
||||
# 添加cloudera-scm 密码admin
|
||||
addprinc cloudera-scm/admin
|
||||
# 查询已有的用户
|
||||
list_principals
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 进入Cloudera Manager的“管理”->“安全”界面
|
||||
|
||||
-
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Kerberos 相关命令
|
||||
|
||||
## 生成kerberos密钥
|
||||
|
||||
- hdfs 账号生成秘钥
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kadmin.local -q "xst -k /tmp/hdfs.keytab hdfs@A.COM -norandkey"
|
||||
kadmin.local -q "xst -k /tmp/hdfs.keytab hdfs@A.COM"
|
||||
#生成密钥文件之后,密码失效,不想密码失效,加 '-norandkey’参数
|
||||
ktadd -k /tmp/hdfs.keytab -norandkey hdfs@A.COM
|
||||
# 或者执行上面的上面命令
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 更新Kerberos票据credentials信息
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 票据过期,无法正常登录,执行命令
|
||||
kinit -R
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 测试Keytable是否可用
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
kinit -k -t /root/admin.keytab admin/admin@A.COM
|
||||
kinit -k -t /tmp/admin.keytab admin/admin@A.COM
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 修改用户的密码
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 修改用户hdfs的密码为‘admin’
|
||||
kadmin.local -q "cpw -pw admin hdfs "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 查询证书状态
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 获取hdfs@A.COM账号的信息
|
||||
getprinc hdfs@A.COM
|
||||
|
||||
modprinc -maxlife 720days -maxrenewlife 1000days +allow_renewable krbtgt/A.COM
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 修改过期参数
|
||||
|
||||
### ticket lifetime
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ticket lifetime取决于以下5项设置中的最小值:
|
||||
Kerberos server上/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf中max_life
|
||||
内置principal krbtgt的maximum ticket life,可在kadmin命令行下用getprinc命令查看
|
||||
principal的maximum ticket life,可在kadmin命令行下用getprinc命令查看
|
||||
Kerberos client上/etc/krb5.conf的ticket_lifetime
|
||||
kinit -l 参数后面指定的时间
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### ticket renew lifetime
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ticket renew lifetime取决于以下5项设置中的最小值:
|
||||
Kerberos server上/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/kdc.conf中max_renewable_life
|
||||
内置principal krbtgt的maximum renewable life,可在kadmin命令行下用getprinc命令查看
|
||||
你的principal的maximum renewable life,可在kadmin命令行下用getprinc命令查看
|
||||
Kerberos client上/etc/krb5.conf的renew_lifetime
|
||||
kinit -r 参数后面指定的时间
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# hive的Ldap配置
|
||||
|
||||
## 无LDAP配置
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
<property>
|
||||
<name>hive.server2.authentication</name>
|
||||
<value>NONE</value>
|
||||
<description>客户端身份认证方式</description>
|
||||
</property>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## LDAP配置
|
||||
|
||||
``` xml
|
||||
<property>
|
||||
<name>hive.server2.authentication</name>
|
||||
<value>LDAP</value>
|
||||
<description>客户端身份认证方式</description>
|
||||
</property>
|
||||
<property>
|
||||
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.url</name>
|
||||
<value>ldaps://ldap.yldev.net:636</value>
|
||||
<description>LDAP Url</description>
|
||||
</property>
|
||||
<property>
|
||||
<name>hive.server2.authentication.ldap.baseDN</name>
|
||||
<value>ou=project,dc=yldev,dc=net</value>
|
||||
<description>LDAP搜索的baseDN</description>
|
||||
</property>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- hive的权限认证的方式 hive.server2.authentication
|
||||
- **NONE**:不做认证;
|
||||
- **LDAP**: 使用基于 LDAP/AD 的用户身份校验;
|
||||
- **KERBEROS**: 使用 Kerberos/GSSAPI 做身份校验;
|
||||
- LDAP认证的服务器URL:hive.server2.authentication.ldap.url
|
||||
- 协议
|
||||
- 未做ssl的ldap协议
|
||||
- **ldap**://ldap.yldev.net
|
||||
- ssl的ldaps协议
|
||||
- **ldaps**://ldap.yldev.net:636
|
||||
- baseDN 登录用户组
|
||||
- project用户组可以登录hive
|
||||
- **ou=project**,dc=yldev,dc=net
|
||||
@ -1,22 +1,45 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Centos 安装 Docker
|
||||
|
||||
# centos 安装 docker
|
||||
|
||||
# Linux 安装 Docker
|
||||
|
||||
## 安装脚本
|
||||
|
||||
一键安装脚本!Linux系统都支持!
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh
|
||||
#国内阿里云镜像
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | bash -s docker --mirror Aliyun
|
||||
#Azure源(中国区azure)
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | bash -s docker --mirror AzureChinaCloud
|
||||
curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## oracle linxu
|
||||
|
||||
1. 执行以下命令,以安装Docker依赖项:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo yum -y install yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 执行以下命令,以添加Docker官方GPG key:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 执行以下命令,以安装Docker CE:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo yum install docker-ce
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. 启动并设置Docker服务为开机自启:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl start docker
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable docker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过`docker --version`命令,您可以检查Docker是否已经安装。如果命令输出了版本信息,说明已经成功安装Docker CE。
|
||||
|
||||
希望这次能给您提供一个更简洁的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动服务
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,8 +64,6 @@
|
||||
systemctl disable docker.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 国内镜像
|
||||
|
||||
为了加速下载镜像文件,国内服务器可以指定国内的镜像!
|
||||
@ -59,26 +80,44 @@ Docker中国:https://registry.docker-cn.com
|
||||
|
||||
腾讯云 https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 写入配置文件 重启服务
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
|
||||
|
||||
sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
|
||||
{
|
||||
"registry-mirrors": ["https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
|
||||
|
||||
#注意EOF前不能有空格
|
||||
sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
|
||||
{
|
||||
"registry-mirrors": ["https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
sudo systemctl restart docker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## docker 配置代理
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d
|
||||
sudo touch /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/proxy.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
Environment="HTTP_PROXY=http://proxy.example.com:8080/"
|
||||
Environment="HTTPS_PROXY=http://proxy.example.com:8080/"
|
||||
Environment="NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1,.example.com"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重启 服务
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
sudo systemctl restart docker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 迁移目录
|
||||
|
||||
@ -118,8 +157,6 @@ Docker中国:https://registry.docker-cn.com
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 常用命令
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -178,7 +215,62 @@ Docker中国:https://registry.docker-cn.com
|
||||
docker inspect -f {{.Config.Hostname}} id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
|
||||
#构建建启动nignx容器
|
||||
docker-compose up -d nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#登录到nginx容器中
|
||||
docker-compose exec nginx bash
|
||||
|
||||
#删除所有nginx容器,镜像
|
||||
docker-compose down
|
||||
|
||||
#显示所有容器
|
||||
docker-compose ps
|
||||
|
||||
#重新启动nginx容器
|
||||
docker-compose restart nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#在php-fpm中不启动关联容器,并容器执行php -v 执行完成后删除容器
|
||||
docker-compose run --no-deps --rm php-fpm php -v
|
||||
|
||||
#构建镜像 。
|
||||
docker-compose build nginx
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#不带缓存的构建。
|
||||
docker-compose build --no-cache nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#查看nginx的日志
|
||||
docker-compose logs nginx
|
||||
|
||||
# 查看nginx的实时日志
|
||||
docker-compose logs -f nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#验证(docker-compose.yml)文件配置,当配置正确时,不输出任何内容,当文件配置错误,输出错误信息。
|
||||
docker-compose config -q
|
||||
|
||||
#以json的形式输出nginx的docker日志
|
||||
docker-compose events --json nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#暂停nignx容器
|
||||
docker-compose pause nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#恢复ningx容器
|
||||
docker-compose unpause nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#删除容器(删除前必须关闭容器)
|
||||
docker-compose rm nginx
|
||||
|
||||
#停止nignx容器
|
||||
docker-compose stop nginx
|
||||
|
||||
# 启动nignx容器
|
||||
docker-compose start nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 开发调试
|
||||
|
||||
@ -198,7 +290,7 @@ Docker中国:https://registry.docker-cn.com
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 容器目录映射
|
||||
## 容器目录映射
|
||||
|
||||
以docker hub的centos:8为研究对象
|
||||
|
||||
@ -214,8 +306,6 @@ Docker中国:https://registry.docker-cn.com
|
||||
|
||||
宿主机映射目录会自动创建,容器映射目录中原来的文件都消失了,在一边操作等同于在另一边操作,且操作的是宿主机目录中的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**4、宿主机映射目录为空,容器映射目录不存在**
|
||||
|
||||
容器映射目录会自动创建,且在一边操作等同于在另一边操作。
|
||||
@ -240,21 +330,12 @@ Docker中国:https://registry.docker-cn.com
|
||||
|
||||
容器映射目录中原来的文件都消失了。在一边操作等同于在另一边操作,且操作的是宿主机目录中的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
容器内没有网 不能解析dns
|
||||
容器内没有网 不能解析dns
|
||||
|
||||
创建时添加以下参数
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
--network=host
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
##### 安装编译环境
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#GCC
|
||||
apt install -y build-essential
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.22.0.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
./configure \
|
||||
--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \
|
||||
--user=www \
|
||||
@ -113,8 +113,20 @@ https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.22.0.tar.gz
|
||||
make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### make 常用命令
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
make #编译
|
||||
|
||||
make install #安装
|
||||
|
||||
make clean #清除上一次make命令生成的文件
|
||||
|
||||
make distclean #清除上一次make以及configure命令生成的文件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 静态编译
|
||||
@ -170,7 +182,7 @@ curl 127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
加到 http 节点中
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
include mime.types;
|
||||
default_type application/octet-stream;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -261,7 +273,7 @@ curl 127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
#### 附1: `systemctl 操作`
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#重载配置文件 添加新的 或者修改都要重载。
|
||||
systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
|
||||
@ -334,7 +346,7 @@ curl 127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
apt 卸载nginx
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
查询 nginx 相关软件
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg --get-selections|grep nginx
|
||||
@ -351,9 +363,8 @@ apt-get --purge remove nginx
|
||||
|
||||
###### nginx.conf
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
worker_processes auto;
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
worker_processes auto;
|
||||
|
||||
worker_rlimit_nofile 51200;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -368,66 +379,54 @@ stream {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
events {
|
||||
use epoll;
|
||||
worker_connections 51200;
|
||||
multi_accept on;
|
||||
}
|
||||
use epoll;
|
||||
worker_connections 51200;
|
||||
multi_accept on;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
http {
|
||||
include mime.types;
|
||||
default_type application/octet-stream;
|
||||
include mime.types;
|
||||
default_type application/octet-stream;
|
||||
|
||||
server_names_hash_bucket_size 512;
|
||||
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
|
||||
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
|
||||
client_max_body_size 50m;
|
||||
server_names_hash_bucket_size 512;
|
||||
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
|
||||
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
|
||||
client_max_body_size 50m;
|
||||
|
||||
sendfile on;
|
||||
tcp_nopush on;
|
||||
sendfile on;
|
||||
tcp_nopush on;
|
||||
|
||||
keepalive_timeout 60;
|
||||
keepalive_timeout 60;
|
||||
|
||||
tcp_nodelay on;
|
||||
tcp_nodelay on;
|
||||
|
||||
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
|
||||
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
|
||||
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
|
||||
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
|
||||
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
|
||||
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
|
||||
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
|
||||
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
|
||||
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
|
||||
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
|
||||
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
|
||||
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
|
||||
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
|
||||
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
|
||||
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
|
||||
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
|
||||
|
||||
gzip on;
|
||||
gzip_min_length 1k;
|
||||
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
|
||||
gzip_http_version 1.1;
|
||||
gzip_comp_level 2;
|
||||
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript application/x-javascript text/javascript text/css application/xml;
|
||||
gzip_vary on;
|
||||
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth;
|
||||
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
|
||||
gzip on;
|
||||
gzip_min_length 1k;
|
||||
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
|
||||
gzip_http_version 1.1;
|
||||
gzip_comp_level 2;
|
||||
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript application/x-javascript text/javascript text/css application/xml;
|
||||
gzip_vary on;
|
||||
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth;
|
||||
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
|
||||
|
||||
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=perip:10m;
|
||||
limit_conn_zone $server_name zone=perserver:10m;
|
||||
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=perip:10m;
|
||||
limit_conn_zone $server_name zone=perserver:10m;
|
||||
|
||||
server_tokens off;
|
||||
access_log off;
|
||||
server_tokens off;
|
||||
access_log off;
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
server_name localhost;
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
root html;
|
||||
index index.html index.htm;
|
||||
}
|
||||
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
|
||||
location = /50x.html {
|
||||
root html;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
include /etc/nginx/site-enable/*.conf;
|
||||
include /etc/nginx/site-enable/*.conf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -436,7 +435,7 @@ include /etc/nginx/site-enable/*.conf;
|
||||
|
||||
###### web-site.conf
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
server_name frp.plugin.dr1997.com;
|
||||
@ -461,7 +460,7 @@ server {
|
||||
|
||||
###### ssl
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
listen 443 ssl http2;
|
||||
@ -501,7 +500,7 @@ server {
|
||||
|
||||
###### 反向代理(http)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
listen 443 ssl http2;
|
||||
@ -544,7 +543,7 @@ server {
|
||||
|
||||
###### 反向代理 tcn
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
upstream tcp {
|
||||
server 127.0.0.1:3306;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
132
debian/debian-preseed.cfg
vendored
Normal file
132
debian/debian-preseed.cfg
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
#_preseed_V1
|
||||
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Preseed configuration for debian 11/bullseye
|
||||
#
|
||||
# ATTENTION: This preseed configuration ERASES the target disks
|
||||
# without any confirmation whatsoever.
|
||||
# https://www.debian.org/releases/stable/amd64/apbs04.zh-cn.html
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
# Locale
|
||||
d-i debian-installer/locale string en_US
|
||||
d-i debian-installer/locale string en_US.UTF-8
|
||||
d-i keyboard-configuration/xkb-keymap select us
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Network
|
||||
d-i hw-detect/load_firmware boolean false
|
||||
d-i netcfg/enable boolean true
|
||||
d-i netcfg/choose_interface select auto
|
||||
d-i netcfg/hostname string unassigned-preseed
|
||||
d-i netcfg/get_hostname string unassigned-preseed
|
||||
d-i netcfg/get_domain string local
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Apt
|
||||
d-i apt-setup/cdrom/set-first boolean false
|
||||
d-i apt-setup/cdrom/set-next boolean false
|
||||
d-i apt-setup/cdrom/set-failed boolean false
|
||||
d-i cdrom-detect/try-again boolean false
|
||||
d-i mirror/country string manual
|
||||
d-i mirror/http/hostname string ftp.cn.debian.org
|
||||
d-i mirror/http/directory string /debian
|
||||
d-i mirror/http/proxy string
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Users/passwords
|
||||
d-i passwd/root-login boolean true
|
||||
d-i passwd/make-user boolean false
|
||||
#使用 密文 mkpasswd -m sha-512
|
||||
d-i passwd/root-password-crypted password $6$XERIk3K43HXcQSmN$UIc6rUH/129Cz5YtN1zQGzU2pleOtl0YbYzyfdIMkeBGzE3qunqBMZtdAIhpIVwsu/cz3CqiL8uJx67spWz810
|
||||
|
||||
#使用明文
|
||||
#d-i passwd/root-password password Xking123456;a
|
||||
#d-i passwd/root-password-again password Xking123456;a
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Clock
|
||||
d-i clock-setup/cst boolean true
|
||||
d-i time/zone string Asia/Shanghai
|
||||
d-i clock-setup/ntp boolean true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Disk partition
|
||||
d-i partman/early_command string \
|
||||
BOOT_DEV=$(list-devices disk | head -1) ; \
|
||||
debconf-set partman-auto/disk $BOOT_DEV
|
||||
|
||||
d-i partman-auto/method string regular
|
||||
d-i partman-auto/choose_recipe select atomic
|
||||
d-i partman-auto/expert_recipe string \
|
||||
50 100 50 fat32 \
|
||||
$primary{ } \
|
||||
method{ efi } \
|
||||
format{ } \
|
||||
. \
|
||||
1000 8000 -1 ext4 \
|
||||
$primary{ } \
|
||||
method{ format } \
|
||||
format{ } \
|
||||
use_filesystem{ } \
|
||||
filesystem{ ext4 } \
|
||||
mountpoint{ / } \
|
||||
. \
|
||||
2048 4096 4096 linux-swap \
|
||||
$primary{ } \
|
||||
method{ swap } \
|
||||
format{ } \
|
||||
.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
d-i partman-lvm/device_remove_lvm boolean true
|
||||
d-i partman-md/device_remove_md boolean true
|
||||
d-i partman/confirm_nooverwrite boolean true
|
||||
d-i partman-efi/non_efi_system boolean true
|
||||
d-i partman/confirm_write_new_label boolean true
|
||||
d-i partman/confirm boolean true
|
||||
d-i partman/choose_partition select Finish partitioning and write changes to disk
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Packages
|
||||
d-i base-installer/install-recommends boolean false
|
||||
d-i base-installer/kernel/image string linux-image-amd64
|
||||
d-i apt-setup/use_mirror boolean true
|
||||
|
||||
#d-i pkgsel/include string openssh-server build-essential
|
||||
|
||||
tasksel tasksel/first multiselect standard, ssh-server
|
||||
|
||||
d-i pkgsel/include string vim sudo
|
||||
d-i pkgsel/upgrade select safe-upgrade
|
||||
popularity-contest popularity-contest/participate boolean true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Boot
|
||||
d-i grub-installer/only_debian boolean true
|
||||
d-i debian-installer/add-kernel-opts string cgroup_enable=memory swapaccount=1
|
||||
d-i grub-installer/with_other_os boolean true
|
||||
d-i grub-installer/force-efi-extra-removable boolean true
|
||||
d-i grub-installer/progress/step_force_efi_removable boolean true
|
||||
d-i grub-installer/bootdev string default
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom late commands
|
||||
d-i preseed/late_command string \
|
||||
HOST_SERIAL="debian-$(head /dev/urandom | tr -dc a-z | head -c10)" ; \
|
||||
sed -i "s/unassigned-preseed/$HOST_SERIAL/g" /target/etc/hostname ; \
|
||||
sed -i "s/unassigned-preseed/$HOST_SERIAL/g" /target/etc/hosts ; \
|
||||
in-target sh -c 'mkdir -pv --mode=0700 /root/.ssh'; \
|
||||
in-target sh -c 'echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABgQD2NB5cURpatXqcEVfr6C6Eg6Tr591eFPwhqkuvifBabDKlzqEkpUgBsbbNv+k8GCgcraFrCL1q90QI+Ou5FNHduPkKNYxxO0oFRc/d4odj5JBuCTYICbTFPrlA7kIV+5ePBw1w8jzgUehwLzq3QDdujC0LmRtn2TOheupz8yl0YCGqxypM4Q49ZU3AgpjxzzETwO6u1XGO7q9VXm1ed39RE4nyIRJ4PxKyFbBxiaeFD3NbPkzviBU2XPI9WrmBEOSfuuwopJGyl7YwT+Jm3flJO7nunVaFbbYhrggfN3JXyaL3EN0nzmeFBHcpwiUsu0avj0OtBLjuTNGnQygz429r8PuBAPaj1XBt+X9lNJElnGjCInon2UHA4Cq3NBJMTw2OhGvejhfPE41E8aJFxeXqyyl8E7nxzQQsUDdqt0k3SxKv4AMV8+NgUQGNHAzY1+7Y6nBecD5o1Cv9u7OniB9IBE6qjbh74gmW1jofOK+Erw9Vgd+Bm20bzdZXyq89oSk= xuwei@Xking" > /root/.ssh/authorized_keys'; \
|
||||
in-target chown --recursive root:root /root/.ssh; \
|
||||
in-target chmod 0600 /root/.ssh/authorized_keys; \
|
||||
in-target update-alternatives --set editor /usr/bin/vim.basic; \
|
||||
in-target sed -i -e 's/^\(PasswordAuthentication\).*/\1 yes/g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config; \
|
||||
# in-target sed -i -e 's/^\(PermitRootLogin\).*/\1 yes/g' /etc/ssh/sshd_config; \
|
||||
in-target sed -i -e '/^GRUB_HIDDEN_TIMEOUT=/d' -e 's/^\(GRUB_HIDDEN_TIMEOUT_QUIET\)=true/\1=false/' /etc/default/grub; \
|
||||
in-target systemctl enable --now sshd; \
|
||||
in-target update-grub
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Finish
|
||||
d-i finish-install/reboot_in_progress note
|
||||
110
debian11编译redis .md
Normal file
110
debian11编译redis .md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
|
||||
### debian 11 安装 编译nginx
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 安装编译环境
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#GCC
|
||||
apt install -y build-essential
|
||||
|
||||
#安装正则库
|
||||
apt install -y libpcre3 libpcre3-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#安装zlib库
|
||||
apt install -y zlib1g-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#openssl
|
||||
apt install -y openssl libssl-dev
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 下载解压源码
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wget https://download.redis.io/redis-stable.tar.gz
|
||||
tar -xzvf redis-stable.tar.gz
|
||||
cd redis-stable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 编译安装
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 修改配置
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 创建配置目录
|
||||
sudo mkdir /etc/redis
|
||||
sudo cp redis.conf /etc/redis/
|
||||
|
||||
# 编辑配置文件
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/redis/redis.conf
|
||||
|
||||
#修改下述配置
|
||||
daemonize yes
|
||||
logfile "/var/log/redis/redis.log"
|
||||
dir /var/lib/redis
|
||||
requirepass your_strong_password_here
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 添加用户
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
useradd redis
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 创建进程守护
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vim /etc/systemd/system/redis.service
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Unit]
|
||||
Description=Redis In-Memory Data Store
|
||||
After=network.target
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
User=redis
|
||||
Group=redis
|
||||
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
|
||||
ExecStop=/usr/local/bin/redis-cli shutdown
|
||||
Type=forking # 改为 forking
|
||||
Restart=on-failure
|
||||
RestartSec=5s # 避免频繁重启
|
||||
|
||||
[Install]
|
||||
WantedBy=multi-user.target
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 启动
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
systemctl enable redis
|
||||
systemctl restart redis
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 验证安装
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
redis-cli ping
|
||||
```
|
||||
430
dolphinscheduler/dolphinscheduler-集群部署.md
Normal file
430
dolphinscheduler/dolphinscheduler-集群部署.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,430 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
gitea: none
|
||||
include_toc: true
|
||||
---
|
||||
# dolphinscheduler 集群部署
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 环境准备
|
||||
|
||||
#### 服务器部署
|
||||
|
||||
准备三台机器,用于安装 dolphinscheduler ,最好部署 在cdh 节点上(非必须)可以公用
|
||||
|
||||
1. hostname 与ip 映射
|
||||
2. 安装好zookeeper(dolphinscheduler 3.0以上版本需要zookeeper3.8) 环境
|
||||
3. spark 环境
|
||||
4. 安装数据库 mysql 或者 postgresql
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 节点免密登录
|
||||
|
||||
1. 创建用户 dolphinscheduler ,切换用户至 dolphinscheduler
|
||||
2. 创建密钥 (三台机器都要dolphinscheduler执行)`ssh-keygen ` 一路回车
|
||||
3. 分发密钥(三台机器都要dolphinscheduler执行)`ssh-copy-id dolphinscheduler@hostname1` `ssh-copy-id dolphinscheduler@hostname2`
|
||||
4. 测试免密登录 `ssh hostname1` `ssh hostname2`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 开始安装
|
||||
|
||||
在三台机器 的 `/opt/` 创建 切换 `dolphinscheduler`目录,并将目录所有者设置为 `dolphinscheduler` 用户
|
||||
|
||||
1. 登录 节点1 dolphinscheduler用户 并切换到 `~` 目录下,下载源码 `https://dlcdn.apache.org/dolphinscheduler/3.2.1/apache-dolphinscheduler-3.2.1-bin.tar.gz`
|
||||
|
||||
2. 解压到文件
|
||||
|
||||
`tar -zxvf https://dlcdn.apache.org/dolphinscheduler/3.2.1/apache-dolphinscheduler-3.2.1-bin.tar.gz`
|
||||
|
||||
`apache-dolphinscheduler-3.2.1-bin` 目录为源目录 不能删除
|
||||
|
||||
3. 配置安装信息
|
||||
|
||||
进入`apache-dolphinscheduler-3.2.1-bin/bin/env`
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 `olphinscheduler_env.sh` 文件,配置数据库信息,时区信息,zookeeper以及各组件路径
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 ` install_env.sh` 文件,分配节点 安装信息, 安装位置,zookeeper节点
|
||||
|
||||
4. 配置全局文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 每个模块的 `common.properties` 文件 找到 `resource.storage.type=HDFS`选择合适存储类型,然后在下面的对应配置项中填写相关配置,
|
||||
|
||||
如果HDFS配置了 kerberos 还需要在 `hadoop.security.authentication.startup.state=false`配置项中配置好,kerberos 用户名证书
|
||||
|
||||
完整配置项
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# if resource.storage.type=HDFS, the user must have the permission to create directories under the HDFS root path
|
||||
resource.hdfs.root.user=hdfs
|
||||
# if resource.storage.type=S3, the value like: s3a://dolphinscheduler; if resource.storage.type=HDFS and namenode HA is enabled, you need to copy core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml to conf dir
|
||||
resource.hdfs.fs.defaultFS=hdfs://cdh-node-2:8020
|
||||
|
||||
# whether to startup kerberos
|
||||
hadoop.security.authentication.startup.state=false
|
||||
|
||||
# java.security.krb5.conf path
|
||||
java.security.krb5.conf.path=/opt/krb5.conf
|
||||
|
||||
# login user from keytab username
|
||||
login.user.keytab.username=hdfs-mycluster@ESZ.COM
|
||||
|
||||
# login user from keytab path
|
||||
login.user.keytab.path=/opt/hdfs.headless.keytab
|
||||
|
||||
# kerberos expire time, the unit is hour
|
||||
kerberos.expire.time=2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. 数据源
|
||||
|
||||
如需要添加数据源,首先将驱动添加至,api-server,worker-server,master-server 的lib 目录下
|
||||
|
||||
- 添加 kerberos 认证的hive,需要在 配置全局文件系统 中配置 conf ,kerberos 用户与证书(默认)
|
||||
|
||||
- 替换 api-server,worker-server,master-server 服务中 hive-* 相关的jar包为 cdh/cdp 中的依赖,
|
||||
|
||||
cdh/cdp 路径
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hive/lib
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 在页面上 的自定义参数中添加
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{"principal":"hive/bigdata57.cua.internal@CUA-KDCSERVER.COM"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 在 kerberos.username 种 填入对应的用户名与keytab `hive@CUA-KDCSERVER.COM`
|
||||
|
||||
6. 配置数据质量校验
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 每个模块的 `common.properties` 确定 `data-quality.jar.name=`配置的名字与模块libs 目录下的jar 名字一样。然后将数据源中的数据类型对应的驱动,以及存储dolphinscheduler 元数据的数据库jdbc驱动 复制到 api-server,worker-server 的libs 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 数据校验包默认不带驱动需要带入驱动,(可以用hdfs 分布式文件系统)
|
||||
2. 校验 kerberos 认证的hive 需要代入
|
||||
|
||||
7. 配置yarn
|
||||
|
||||
将 yarn的hostName 与port 端口进行修改
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# resourcemanager port, the default value is 8088 if not specified
|
||||
resource.manager.httpaddress.port=8088
|
||||
# if resourcemanager HA is enabled, please set the HA IPs; if resourcemanager is single, keep this value empty
|
||||
yarn.resourcemanager.ha.rm.ids=cdh-node-2
|
||||
# if resourcemanager HA is enabled or not use resourcemanager, please keep the default value; If resourcemanager is single, you only need to replace ds1 to actual resourcemanager hostname
|
||||
yarn.application.status.address=http://cdh-node-2:%s/ws/v1/cluster/apps/%s
|
||||
# job history status url when application number threshold is reached(default 10000, maybe it was set to 1000)
|
||||
yarn.job.history.status.address=http://cdh-node-2:19888/ws/v1/history/mapreduce/jobs/%s
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. 开始安装
|
||||
|
||||
执行 bin/ install.sh 进行安装,安装完成后 访问api-server 的hostName:12345/dolphinscheduler/ui/login
|
||||
|
||||
进行登录,使用 admin/dolphinscheduler123 进行登录。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 修改配置
|
||||
|
||||
修改配置 还是在源目录 修改响应的配置 然后执行 bin/ install.sh 进行安装,
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要删除 依赖或者文件,需要在安装目录中删除后,在源目录删除。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 常见问题
|
||||
|
||||
1. 高版本 dolphinscheduler 搭配低版本zookeeper
|
||||
|
||||
将每个模块的zookeeper curator 等依赖,替换成低版本的
|
||||
|
||||
2. hive 数据库链接不上
|
||||
|
||||
将libs 目录相关的 hive 依赖替换成 cdh 中的同名依赖
|
||||
|
||||
3. 多租户 执行数据质量校验任务报错,
|
||||
|
||||
需要在 全局文件系统中的/user/目录下新建 租户主目录并将所有权设置为租户
|
||||
|
||||
4. kerberos 数据源不显示表 测试连接失败
|
||||
|
||||
检查keytab 文件,principal 配置 用户名
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 附录
|
||||
|
||||
1. 3.19 版本的 olphinscheduler_env.sh配置
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Never put sensitive config such as database password here in your production environment,
|
||||
# this file will be sourced everytime a new task is executed.
|
||||
|
||||
# applicationId auto collection related configuration, the following configurations are unnecessary if setting appId.collect=log
|
||||
#export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`hadoop classpath`:${DOLPHINSCHEDULER_HOME}/tools/libs/*
|
||||
#export SPARK_DIST_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:$SPARK_DIST_CLASS_PATH
|
||||
#export HADOOP_CLIENT_OPTS="-javaagent:${DOLPHINSCHEDULER_HOME}/tools/libs/aspectjweaver-1.9.7.jar":$HADOOP_CLIENT_OPTS
|
||||
#export SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS="-javaagent:${DOLPHINSCHEDULER_HOME}/tools/libs/aspectjweaver-1.9.7.jar":$SPARK_SUBMIT_OPTS
|
||||
#export FLINK_ENV_JAVA_OPTS="-javaagent:${DOLPHINSCHEDULER_HOME}/tools/libs/aspectjweaver-1.9.7.jar":$FLINK_ENV_JAVA_OPTS
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
export JAVA_HOME=${JAVA_HOME:-/opt/java/jdk1.8.0_181/}
|
||||
|
||||
export DATABASE=${DATABASE:-mysql}
|
||||
export SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE=${DATABASE}
|
||||
export SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL="jdbc:mysql://cdh-node-1/dolphinscheduler"
|
||||
export SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME=dolphinscheduler
|
||||
export SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD=^Ws#nV4HvrXus*cpyv
|
||||
|
||||
# DolphinScheduler server related configuration
|
||||
export SPRING_CACHE_TYPE=${SPRING_CACHE_TYPE:-none}
|
||||
export SPRING_JACKSON_TIME_ZONE=${SPRING_JACKSON_TIME_ZONE:-GMT+8}
|
||||
export MASTER_FETCH_COMMAND_NUM=${MASTER_FETCH_COMMAND_NUM:-10}
|
||||
|
||||
# Registry center configuration, determines the type and link of the registry center
|
||||
export REGISTRY_TYPE=${REGISTRY_TYPE:-zookeeper}
|
||||
export REGISTRY_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT_STRING=${REGISTRY_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT_STRING:-cdh-node-2:2181}
|
||||
|
||||
# Tasks related configurations, need to change the configuration if you use the related tasks.
|
||||
export HADOOP_HOME=${HADOOP_HOME:-/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-6.3.1-1.cdh6.3.1.p0.1470567/lib/hadoop}
|
||||
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=${HADOOP_CONF_DIR:-/etc/hadoop/conf}
|
||||
export SPARK_HOME=${SPARK_HOME:-/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-6.3.1-1.cdh6.3.1.p0.1470567/lib/spark}
|
||||
export PYTHON_LAUNCHER=${PYTHON_LAUNCHER:-/opt/soft/python}
|
||||
export HIVE_HOME=${HIVE_HOME:-/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH-6.3.1-1.cdh6.3.1.p0.1470567/lib/hive}
|
||||
export FLINK_HOME=${FLINK_HOME:-/opt/soft/flink}
|
||||
export DATAX_LAUNCHER=${DATAX_LAUNCHER:-/opt/soft/datax/bin/python3}
|
||||
|
||||
export PATH=$HADOOP_HOME/bin:$SPARK_HOME/bin:$PYTHON_LAUNCHER:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$HIVE_HOME/bin:$FLINK_HOME/bin:$DATAX_LAUNCHER:$PATH
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 3.19版本的 install_env.sh
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
# INSTALL MACHINE
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
# A comma separated list of machine hostname or IP would be installed DolphinScheduler,
|
||||
# including master, worker, api, alert. If you want to deploy in pseudo-distributed
|
||||
# mode, just write a pseudo-distributed hostname
|
||||
# Example for hostnames: ips="ds1,ds2,ds3,ds4,ds5", Example for IPs: ips="192.168.8.1,192.168.8.2,192.168.8.3,192.168.8.4,192.168.8.5"
|
||||
ips="cdh-node-1,cdh-node-2,cdh-node-3"
|
||||
|
||||
# Port of SSH protocol, default value is 22. For now we only support same port in all `ips` machine
|
||||
# modify it if you use different ssh port
|
||||
sshPort=${sshPort:-"22"}
|
||||
|
||||
# A comma separated list of machine hostname or IP would be installed Master server, it
|
||||
# must be a subset of configuration `ips`.
|
||||
# Example for hostnames: masters="ds1,ds2", Example for IPs: masters="192.168.8.1,192.168.8.2"
|
||||
masters="cdh-node-3"
|
||||
|
||||
# A comma separated list of machine <hostname>:<workerGroup> or <IP>:<workerGroup>.All hostname or IP must be a
|
||||
# subset of configuration `ips`, And workerGroup have default value as `default`, but we recommend you declare behind the hosts
|
||||
# Example for hostnames: workers="ds1:default,ds2:default,ds3:default", Example for IPs: workers="192.168.8.1:default,192.168.8.2:default,192.168.8.3:default"
|
||||
workers="cdh-node-1:default,cdh-node-2:default,cdh-node-3:default"
|
||||
|
||||
# A comma separated list of machine hostname or IP would be installed Alert server, it
|
||||
# must be a subset of configuration `ips`.
|
||||
# Example for hostname: alertServer="ds3", Example for IP: alertServer="192.168.8.3"
|
||||
alertServer="cdh-node-1"
|
||||
|
||||
# A comma separated list of machine hostname or IP would be installed API server, it
|
||||
# must be a subset of configuration `ips`.
|
||||
# Example for hostname: apiServers="ds1", Example for IP: apiServers="192.168.8.1"
|
||||
apiServers="cdh-node-1"
|
||||
|
||||
# The directory to install DolphinScheduler for all machine we config above. It will automatically be created by `install.sh` script if not exists.
|
||||
# Do not set this configuration same as the current path (pwd). Do not add quotes to it if you using related path.
|
||||
installPath="/opt/dolphinscheduler"
|
||||
|
||||
# The user to deploy DolphinScheduler for all machine we config above. For now user must create by yourself before running `install.sh`
|
||||
# script. The user needs to have sudo privileges and permissions to operate hdfs. If hdfs is enabled than the root directory needs
|
||||
# to be created by this user
|
||||
deployUser="dolphinscheduler"
|
||||
|
||||
# The root of zookeeper, for now DolphinScheduler default registry server is zookeeper.
|
||||
# It will delete ${zkRoot} in the zookeeper when you run install.sh, so please keep it same as registry.zookeeper.namespace in yml files.
|
||||
# Similarly, if you want to modify the value, please modify registry.zookeeper.namespace in yml files as well.
|
||||
zkRoot=${zkRoot:-"/dolphinscheduler"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. 3.19 版本的 worker-server 服务 common.properties配置
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
|
||||
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
|
||||
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
|
||||
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
# user data local directory path, please make sure the directory exists and have read write permissions
|
||||
data.basedir.path=/tmp/dolphinscheduler
|
||||
|
||||
# resource view suffixs
|
||||
#resource.view.suffixs=txt,log,sh,bat,conf,cfg,py,java,sql,xml,hql,properties,json,yml,yaml,ini,js
|
||||
|
||||
# resource storage type: HDFS, S3, OSS, NONE
|
||||
resource.storage.type=HDFS
|
||||
# resource store on HDFS/S3 path, resource file will store to this base path, self configuration, please make sure the directory exists on hdfs and have read write permissions. "/dolphinscheduler" is recommended
|
||||
resource.storage.upload.base.path=/dolphinscheduler
|
||||
|
||||
# The AWS access key. if resource.storage.type=S3 or use EMR-Task, This configuration is required
|
||||
resource.aws.access.key.id=minioadmin
|
||||
# The AWS secret access key. if resource.storage.type=S3 or use EMR-Task, This configuration is required
|
||||
resource.aws.secret.access.key=minioadmin
|
||||
# The AWS Region to use. if resource.storage.type=S3 or use EMR-Task, This configuration is required
|
||||
resource.aws.region=cn-north-1
|
||||
# The name of the bucket. You need to create them by yourself. Otherwise, the system cannot start. All buckets in Amazon S3 share a single namespace; ensure the bucket is given a unique name.
|
||||
resource.aws.s3.bucket.name=dolphinscheduler
|
||||
# You need to set this parameter when private cloud s3. If S3 uses public cloud, you only need to set resource.aws.region or set to the endpoint of a public cloud such as S3.cn-north-1.amazonaws.com.cn
|
||||
resource.aws.s3.endpoint=http://localhost:9000
|
||||
|
||||
# alibaba cloud access key id, required if you set resource.storage.type=OSS
|
||||
resource.alibaba.cloud.access.key.id=<your-access-key-id>
|
||||
# alibaba cloud access key secret, required if you set resource.storage.type=OSS
|
||||
resource.alibaba.cloud.access.key.secret=<your-access-key-secret>
|
||||
# alibaba cloud region, required if you set resource.storage.type=OSS
|
||||
resource.alibaba.cloud.region=cn-hangzhou
|
||||
# oss bucket name, required if you set resource.storage.type=OSS
|
||||
resource.alibaba.cloud.oss.bucket.name=dolphinscheduler
|
||||
# oss bucket endpoint, required if you set resource.storage.type=OSS
|
||||
resource.alibaba.cloud.oss.endpoint=https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com
|
||||
|
||||
# if resource.storage.type=HDFS, the user must have the permission to create directories under the HDFS root path
|
||||
resource.hdfs.root.user=hdfs
|
||||
# if resource.storage.type=S3, the value like: s3a://dolphinscheduler; if resource.storage.type=HDFS and namenode HA is enabled, you need to copy core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml to conf dir
|
||||
resource.hdfs.fs.defaultFS=hdfs://cdh-node-2:8020
|
||||
|
||||
# whether to startup kerberos
|
||||
hadoop.security.authentication.startup.state=false
|
||||
|
||||
# java.security.krb5.conf path
|
||||
java.security.krb5.conf.path=/opt/krb5.conf
|
||||
|
||||
# login user from keytab username
|
||||
login.user.keytab.username=hdfs-mycluster@ESZ.COM
|
||||
|
||||
# login user from keytab path
|
||||
login.user.keytab.path=/opt/hdfs.headless.keytab
|
||||
|
||||
# kerberos expire time, the unit is hour
|
||||
kerberos.expire.time=2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# resourcemanager port, the default value is 8088 if not specified
|
||||
resource.manager.httpaddress.port=8088
|
||||
# if resourcemanager HA is enabled, please set the HA IPs; if resourcemanager is single, keep this value empty
|
||||
yarn.resourcemanager.ha.rm.ids=cdh-node-2
|
||||
# if resourcemanager HA is enabled or not use resourcemanager, please keep the default value; If resourcemanager is single, you only need to replace ds1 to actual resourcemanager hostname
|
||||
yarn.application.status.address=http://cdh-node-2:%s/ws/v1/cluster/apps/%s
|
||||
# job history status url when application number threshold is reached(default 10000, maybe it was set to 1000)
|
||||
yarn.job.history.status.address=http://cdh-node-2:19888/ws/v1/history/mapreduce/jobs/%s
|
||||
|
||||
# datasource encryption enable
|
||||
datasource.encryption.enable=false
|
||||
|
||||
# datasource encryption salt
|
||||
datasource.encryption.salt=!@#$%^&*
|
||||
|
||||
# data quality option
|
||||
data-quality.jar.name=dolphinscheduler-data-quality-3.1.9.jar
|
||||
|
||||
#data-quality.error.output.path=/tmp/data-quality-error-data
|
||||
|
||||
# Network IP gets priority, default inner outer
|
||||
|
||||
# Whether hive SQL is executed in the same session
|
||||
support.hive.oneSession=false
|
||||
|
||||
# use sudo or not, if set true, executing user is tenant user and deploy user needs sudo permissions; if set false, executing user is the deploy user and doesn't need sudo permissions
|
||||
sudo.enable=true
|
||||
setTaskDirToTenant.enable=false
|
||||
|
||||
# network interface preferred like eth0, default: empty
|
||||
#dolphin.scheduler.network.interface.preferred=
|
||||
|
||||
# network IP gets priority, default: inner outer
|
||||
#dolphin.scheduler.network.priority.strategy=default
|
||||
|
||||
# system env path
|
||||
#dolphinscheduler.env.path=dolphinscheduler_env.sh
|
||||
|
||||
# development state
|
||||
development.state=false
|
||||
|
||||
# rpc port
|
||||
alert.rpc.port=50052
|
||||
|
||||
# set path of conda.sh
|
||||
conda.path=/opt/anaconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh
|
||||
|
||||
# Task resource limit state
|
||||
task.resource.limit.state=false
|
||||
|
||||
# mlflow task plugin preset repository
|
||||
ml.mlflow.preset_repository=https://github.com/apache/dolphinscheduler-mlflow
|
||||
# mlflow task plugin preset repository version
|
||||
ml.mlflow.preset_repository_version="main"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
159
git/git-bash.md
Normal file
159
git/git-bash.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
|
||||
## git-bash (mingw64)高级操作
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装pacman 包管理器
|
||||
|
||||
依次下载以下包并解压至 Git 安装根目录:
|
||||
|
||||
pacman(需要将usr/bin 中的 pacman.exe 改为 pacman):
|
||||
|
||||
https://packages.msys2.org/package/pacman?repo=msys&variant=x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
pacman-mirrors:
|
||||
|
||||
https://packages.msys2.org/package/pacman-mirrors?repo=msys&variant=x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
msys2-keyring:
|
||||
|
||||
https://packages.msys2.org/package/msys2-keyring?repo=msys&variant=x86_64
|
||||
|
||||
一个是 pacman 主包,一个是源,一个是源秘钥。
|
||||
|
||||
然后改源:清华大学源传送门:https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/help/msys2/ (用 vscode 在 Git 根目录找到文件夹直接改)
|
||||
|
||||
这时候去执行 pacman 不出意外是会不行的,什么签名未信任,无效的数据库,无法锁定数据库之类的,问题不大。
|
||||
|
||||
依次执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
刷新秘钥:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pacman-key --refresh-keys
|
||||
pacman-key --init
|
||||
pacman-key --populat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
清除缓存:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pacman -Sc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
更新系统:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pacman -Syu
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
不出意外应该是不会有报错了,后面该咋用就咋用吧。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### pacman 基本操作
|
||||
|
||||
#### pacman 安装软件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pacman -S 软件名: 安装软件。也可以同时安装多个包,只需以空格分隔包名即可。
|
||||
pacman -S --needed 软件名1 软件名2: 安装软件,但不重新安装已经是最新的软件。
|
||||
pacman -Sy 软件名:安装软件前,先从远程仓库下载软件包数据库(数据库即所有软件列表)。
|
||||
pacman -Sv 软件名:在显示一些操作信息后执行安装。
|
||||
pacman -Sw 软件名: 只下载软件包,不安装。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### pacman 更新软件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pacman -Sy: 从服务器下载新的软件包数据库(实际上就是下载远程仓库最新软件列表到本地)。
|
||||
pacman -Su: 升级所有已安装的软件包。
|
||||
pacman -Syu 结合上面两个操作
|
||||
#在msys2中 pacman -Syu后需要重启一下msys2(关掉shell重新打开即可)。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### pacman 卸载软件
|
||||
|
||||
`# usage: pacman {-R --remove} [options] <package(s)>`
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pacman -R 软件名: 该命令将只删除包,保留其全部已经安装的依赖关系
|
||||
pacman -Rv 软件名: 删除软件,并显示详细的信息
|
||||
pacman -Rs 软件名: 删除软件,同时删除本机上只有该软件依赖的软件。
|
||||
pacman -Rsc 软件名: 删除软件,并删除所有依赖这个软件的程序,慎用
|
||||
pacman -Ru 软件名: 删除软件,同时删除不再被任何软件所需要的依赖
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### pacman 搜索
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pacman -Ss 关键字: 在远端仓库中搜索匹配字符串的软件包(本地已安装的会标记)
|
||||
pacman -Sl <repo>:显示软件仓库中所有软件的列表
|
||||
pacman -Qs 关键字: 在本地已安装包中搜索匹配字符串的软件包
|
||||
pacman -Qu: 列出所有可升级的软件包
|
||||
pacman -Qt: 列出不被任何软件要求的软件包
|
||||
pacman -Q 软件名: 查看软件包是否已安装,已安装则显示软件包名称和版本
|
||||
pacman -Qi 软件名: 查看某个软件包信息,显示较为详细的信息,包括描述、构架、依赖、大小等等
|
||||
pacman -Ql 软件名: 列出软件包内所有文件,包括软件安装的每个文件、文件夹的名称和路径
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### pacman 清理
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pacman -Sc:清理已删除的包文件,从缓存目录( /var/cache/pacman/pkg/)
|
||||
pacman -Scc:清理所有的缓存文件。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 用 pacman 排除常见错误
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
提交事务失败(文件冲突)
|
||||
|
||||
如果你看到以下报错:
|
||||
|
||||
error: could not prepare transaction
|
||||
error: failed to commit transaction (conflicting files)
|
||||
package: /path/to/file exists in filesystem
|
||||
Errors occurred, no packages were upgraded.
|
||||
这是因为 pacman 检测到文件冲突,不会为你覆盖文件。
|
||||
|
||||
解决这个问题的一个安全方法是首先检查另一个包是否拥有这个文件(pacman-Qo 文件路径)。如果该文件属于另一个包,请提交错误报告。如果文件不属于另一个包,请重命名“存在于文件系统中”的文件,然后重新发出更新命令。如果一切顺利,文件可能会被删除。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以显式地运行 pacman -S deepin-movie --overwrite "*" 覆盖与 给模式匹配的文件,而不是手动重命名并在以后删除属于该包的所有文件。
|
||||
|
||||
提交事务失败(包无效或损坏)
|
||||
|
||||
在 /var/cache/pacman/pkg/ 中查找 .part 文件(部分下载的包),并将其删除。这通常是由在 pacman.conf 文件中使用自定义 XferCommand 引起的。
|
||||
|
||||
初始化事务失败(无法锁定数据库)
|
||||
|
||||
当 pacman 要修改包数据库时,例如安装包时,它会在 /var/lib/pacman/db.lck 处创建一个锁文件。这可以防止 pacman 的另一个实例同时尝试更改包数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
如果 pacman 在更改数据库时被中断,这个过时的锁文件可能仍然保留。如果你确定没有 pacman 实例正在运行,那么请删除锁文件。
|
||||
|
||||
检查进程是否持有锁定文件:
|
||||
|
||||
lsof /var/lib/pacman/db.lck
|
||||
如果上述命令未返回任何内容,则可以删除锁文件:
|
||||
|
||||
rm /var/lib/pacman/db.lck
|
||||
如果你发现 lsof 命令输出了使用锁文件的进程的 PID,请先杀死这个进程,然后删除锁文件。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望你喜欢我对 pacman 基础命令的介绍。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
138
git/git基本操作.md
Normal file
138
git/git基本操作.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
|
||||
## git 基本操作
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 配置代理
|
||||
http 协议代理
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
//设置全局代理
|
||||
//http
|
||||
git config --global http.proxy http://127.0.0.1:1080
|
||||
//https
|
||||
git config --global https.proxy http://127.0.0.1:1080
|
||||
//使用socks5代理的 例如ss,ssr 1080是windows下ss的默认代理端口,mac下不同,或者有自定义的,根据自己的改
|
||||
git config --global http.proxy socks5://127.0.0.1:1080
|
||||
git config --global https.proxy socks5://127.0.0.1:1080
|
||||
|
||||
//只对github.com使用代理,其他仓库不走代理
|
||||
git config --global http.https://github.com.proxy socks5://127.0.0.1:1080
|
||||
git config --global https.https://github.com.proxy socks5://127.0.0.1:1080
|
||||
//取消github代理
|
||||
git config --global --unset http.https://github.com.proxy
|
||||
git config --global --unset https.https://github.com.proxy
|
||||
|
||||
//取消全局代理
|
||||
git config --global --unset http.proxy
|
||||
git config --global --unset https.proxy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ssh 协议代理
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
//对于使用git@协议的,可以配置socks5代理
|
||||
//在~/.ssh/config 文件后面添加几行,没有可以新建一个
|
||||
//socks5
|
||||
Host github.com
|
||||
User git
|
||||
ProxyCommand connect -S 127.0.0.1:1080 %h %p
|
||||
|
||||
//http || https
|
||||
Host github.com
|
||||
User git
|
||||
ProxyCommand connect -H 127.0.0.1:1080 %h %p
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 更新git
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git update-git-for-windows
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### git常用命令
|
||||
|
||||
- 取消合并
|
||||
|
||||
当出现推送被拒,本地分支领先 远端分支,远端分支又有别人提交的代码时。
|
||||
需要合并远程分支再提交,如果处理不了 需要先取消本地合并
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git merge --abort
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- git删除文件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1-1.仅删除远程仓库文件,不删除本地
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git rm --cached */src/views/index.vue* # 注意文件路径,加上*号
|
||||
git commit -m "delete remote file filename " # commit提交,无须add
|
||||
git push origin master(此处是当前分支的名字) # 推送即可
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1-2.仅删除远程仓库文件夹!!文件夹,不删除本地
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git rm -r --cached */src/views* # 注意文件路径,加上*号 , 和删除文件区别在于 -r
|
||||
git commit -m "delete remote file filename " # commit提交,无须add
|
||||
git push origin master(此处是当前分支的名字) # 推送即可
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2-1.删除远程仓库文件,同时删除本地文件 (区别在于 --cached)
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git rm */src/views/index.vue* # 注意文件路径,加上*号
|
||||
git commit -m "delete remote file filename " # commit提交,无须add
|
||||
git push origin master(此处是当前分支的名字) # 推送即可
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2-2.删除远程仓库文件夹!!文件夹,同时删除本地
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git rm -r */src/views* #注意文件路径,加上*号 , 和删除文件区别在于 -r
|
||||
git commit -m "delete remote file filename " # commit提交,无须add
|
||||
git push origin master(此处是当前分支的名字) # 推送即可
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- git revert 的用法
|
||||
|
||||
git revert 的作用是通过创建一个新的版本,这个版本的内容与我们要回退到的目标版本一样,但是HEAD指针是指向这个新生成的版本,而不是目标版本。
|
||||
如果我们想恢复之前的某一版本(该版本不是merge类型),但是又想保留该目标版本后面的版本,记录下这整个版本变动流程,就可以用这种方法。
|
||||
我们使用git revert HEAD命令就可以创建一个新的版本,此版本与上一个版本相同。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git revert HEAD :撤销前一次 commit
|
||||
git revert HEAD^ :撤销前前一次 commit
|
||||
git revert commit + (commit id): 撤销指定的版本,撤销也会作为一次提交进行保存。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git reset --soft HEAD^:将最近一次提交节点的提交记录回退到暂存区
|
||||
git reset --mixed HEAD^:将最近一次提交节点的提交记录回退到工作区
|
||||
git reset --hard HEAD^:将最近一次提交节点的提交记录全部清除
|
||||
git revert是用一次新的commit来回滚之前的commit,git reset是直接删除指定的commit。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
59
git/git多环境配置.md
Normal file
59
git/git多环境配置.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
## git 多环境配置
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 多密钥配置
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 ~/.ssh/config 配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# gitee
|
||||
Host gitee.com
|
||||
HostName gitee.com
|
||||
Port 22
|
||||
PreferredAuthentications publickey
|
||||
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_gitee #平台私钥地址
|
||||
|
||||
# github
|
||||
Host github.com
|
||||
HostName github.com
|
||||
Port 22
|
||||
PreferredAuthentications publickey
|
||||
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_github #平台私钥地址
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#低版本 加密兼容
|
||||
Host *
|
||||
HostkeyAlgorithms +ssh-dss,ssh-rsa
|
||||
PubkeyAcceptedKeyTypes +ssh-dss,ssh-rsa
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 提交用户配置
|
||||
|
||||
每个平台建立一个目录 该平台下的所有项目 放在该目录下
|
||||
|
||||
如:d:\work
|
||||
|
||||
在全局配置文件 `~/.gitconfig` 末尾追加配置
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[includeIf "gitdir/i:d:/work/"]
|
||||
path = ~/.gitconfig_work
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在用户目录 `~` 新建 文件 `.gitconfig_work`
|
||||
|
||||
内容如下
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[user]
|
||||
email = xxxx@yilingairdata.com
|
||||
name = xxxx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
18
gitlab/centos搭建gitlab.md
Normal file
18
gitlab/centos搭建gitlab.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
## centos 安装 gitlab
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备工作
|
||||
|
||||
#### 机器信息
|
||||
|
||||
- gitlab 4H8G,IP 192.168.123.131
|
||||
- gitlab-runner 4H4G,IP192.168.123.132
|
||||
- web-server 4H4G,ip 192.168.123.133
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装docker
|
||||
|
||||
参照 [centos 安装 docker.md](..\centos 安装 docker.md) 安装好DOCKER
|
||||
|
||||
85
hive/dataGrip连接hive带kerberos认证.md
Normal file
85
hive/dataGrip连接hive带kerberos认证.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
# dataGrip连接hive带kerberos认证
|
||||
|
||||
### dataGrip 连接带kerberos认证的hive
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先使用 dbeaver 的hive 驱动 ([下载地址](https://github.com/timveil/hive-jdbc-uber-jar/releases/download/v1.9-2.6.5/hive-jdbc-uber-2.6.5.0-292.jar)) 别的驱动测试不成功,
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
准备kerberos的认证信息,
|
||||
|
||||
kerberos 主体、认证密钥 keytab文件,jaas配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
jaas配置文件如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
DataGrip {
|
||||
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
|
||||
useKeyTab=true
|
||||
keyTab="D:\ckw\kn\kn\cuayilinghsd.keytab"
|
||||
principal="cuayilinghsd@CUA-KDCSERVER.COM"
|
||||
doNotPrompt=true
|
||||
useTicketCache=true
|
||||
debug=true;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将上述配置文件中的`keyTab` `principal` 替换成之前准备的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用刚刚下载驱动文件创建一个数据源
|
||||
|
||||
url 如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
jdbc:hive2://bigdata57.cua.internal:10000/;principal=hive/bigdata57.cua.internal@CUA-KDCSERVER.COM
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`hive/bigdata57.cua.internal@CUA-KDCSERVER.COM` 为固定值。
|
||||
|
||||
`bigdata57.cua.internal:10000` hive 地址与端口
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
然后在高级配置里添加
|
||||
|
||||
jvm 参数
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-Djava.security.krb5.conf=C:\ProgramData\MIT\Kerberos5\krb5.ini
|
||||
-Dsun.security.krb5.debug=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`C:\ProgramData\MIT\Kerberos5\krb5.ini` 为kerberos 服务的配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[libdefaults]
|
||||
default_realm = CUA-KDCSERVER.COM
|
||||
|
||||
[realms]
|
||||
CUA-KDCSERVER.COM = {
|
||||
kdc = 10.111.15.61:88
|
||||
admin_server = 10.111.15.61:754
|
||||
default_domain = CUA-KDCSERVER.COM
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[domain_realm]
|
||||
.example.com = CUA-KDCSERVER.COM
|
||||
example.com = CUA-KDCSERVER.COM
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
点击测试连接,完成hive数据源的添加。
|
||||
6
hive/hdfs.md
Normal file
6
hive/hdfs.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
HDFS 集群复制
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
hadoop distcp -D ipc.client.fallback-to-simple-auth-allowed=true hdfs://kn55.cu-air.com:8020/report/ hdfs://bigdata55.cua.internal:8020/travelsky/report/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
54
hive/hive表删除数据的几种方式.md
Normal file
54
hive/hive表删除数据的几种方式.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
## hive 删除数据
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除表
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
-- hive删除表:
|
||||
drop table table_name;
|
||||
-- 永久性删除,不能恢复:
|
||||
drop table table_name purge;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 清空数据
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
-- hive删除表中数据:
|
||||
truncate table table_name;
|
||||
|
||||
-- hive按分区删除数据:
|
||||
alter table table_name drop partition (partition_name='分区名')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 重写数据
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
与删除条件相反,如删除 date=0528 的数据
|
||||
|
||||
那么 重写数 的条件为 date!=0528
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**分区表**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
删除具体partition的部分数据
|
||||
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE table_name PARTITION(year='2021')
|
||||
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE year='2021' and xx;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**非分区表**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE table_name SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE xx;
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
30
hive/impala.md
Normal file
30
hive/impala.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
## impala
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
invalidate metadata; -- 废除所有表的元数据
|
||||
invalidate metadata [table]; -- 废除表table的元数据
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
refresh [table]; -- 刷新表table的元数据
|
||||
refresh [table] partition [partition]; -- 刷新表table的partition分区元数据
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
hive 重建元数据
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
MSCK REPAIR TABLE table_name;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
34
java/CompletableFuture.md
Normal file
34
java/CompletableFuture.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
## CompletableFuture API
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
以下是 `CompletableFuture` API 名字、说明和示例的表格整理:
|
||||
|
||||
| **API 名称** | **说明** | **示例** |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)` | 异步执行任务,返回计算结果。 | `CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100);` |
|
||||
| `runAsync(Runnable runnable)` | 异步执行没有返回值的任务。 | `CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { /* 执行某些任务 */ });` |
|
||||
| `get()` | 阻塞当前线程,直到任务完成并返回计算结果。 | `Integer result = future.get();` |
|
||||
| `get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)` | 阻塞当前线程,最多等待指定时间来获取结果,超时抛出 `TimeoutException`。 | `Integer result = future.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);` |
|
||||
| `thenApply(Function<T, U> fn)` | 在任务完成后应用函数 `fn` 来处理计算结果,并返回一个新的 `CompletableFuture`。 | `CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = future.thenApply(result -> result * 2);` |
|
||||
| `thenAccept(Consumer<T> action)` | 在任务完成后执行 `action`,但不返回任何结果。 | `future.thenAccept(result -> System.out.println("结果是: " + result));` |
|
||||
| `thenRun(Runnable action)` | 在任务完成后执行没有输入输出的 `Runnable` 操作。 | `future.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("任务完成"));` |
|
||||
| `thenCombine(CompletableFuture<U> other, BiFunction<T, U, V> fn)` | 当两个 `CompletableFuture` 都完成时,合并它们的结果,返回一个新的 `CompletableFuture`。 | `CompletableFuture<Integer> combinedFuture = future1.thenCombine(future2, (result1, result2) -> result1 + result2);` |
|
||||
| `thenCompose(Function<T, CompletableFuture<U>> fn)` | 返回一个新的 `CompletableFuture`,执行链式的异步任务。 | `CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = future.thenCompose(result -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> result * 2));` |
|
||||
| `exceptionally(Function<Throwable, T> fn)` | 当任务执行失败时,执行异常处理,并返回一个默认值。 | `future.exceptionally(ex -> { System.out.println("任务异常: " + ex.getMessage()); return -1; });` |
|
||||
| `handle(BiFunction<T, Throwable, T> fn)` | 无论任务成功还是失败,都处理结果或异常,并返回一个新的结果。 | `future.handle((result, ex) -> { if (ex != null) return -1; return result * 2; });` |
|
||||
| ` CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)` | 不改变结果 适合监听日志 处理异常 | future.whenComplete((result, ex) -> { if (ex == null) { System.out.println("结果: " + result); } else { System.err.println("异常: " + ex.getMessage()); }}); |
|
||||
| `allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... futures)` | 等待所有 `CompletableFuture` 完成,返回一个新的 `CompletableFuture<Void>`。 | `CompletableFuture<Void> allOfFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);` |
|
||||
| `anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... futures)` | 等待任意一个 `CompletableFuture` 完成,返回一个新的 `CompletableFuture<Object>`。 | `CompletableFuture<Object> anyOfFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);` |
|
||||
| `cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning)` | 取消任务。如果任务还未开始,取消会返回 `true`;如果任务已开始,`mayInterruptIfRunning` 为 `true` 时可以中断任务。 | `future.cancel(true);` |
|
||||
| `join()` | 阻塞并等待任务完成,类似于 `get()`,但不会抛出 `ExecutionException`,而是抛出 `CompletionException`。 | `Integer result = future.join();` |
|
||||
|
||||
### 简要说明:
|
||||
|
||||
- **`supplyAsync`** 和 **`runAsync`** 用于异步执行任务,分别支持返回结果和无返回值的任务。
|
||||
- **`get()`** 和 **`join()`** 用于等待异步计算结果,`get()` 可能抛出 `ExecutionException`,`join()` 会抛出 `CompletionException`。
|
||||
- **`thenApply`**、**`thenAccept`**、**`thenRun`**、**`thenCombine`** 等方法用于在任务完成后进行链式处理,可以处理计算结果或执行后续任务。
|
||||
- **`exceptionally`** 和 **`handle`** 用于处理任务中的异常。
|
||||
- **`allOf`** 和 **`anyOf`** 用于组合多个 `CompletableFuture`,前者等待所有任务完成,后者等待任意一个完成。
|
||||
|
||||
这种 API 使得异步编程更加简洁,同时避免了传统回调地狱的问题。
|
||||
637
java/Guava中的类型增强.md
Normal file
637
java/Guava中的类型增强.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,637 @@
|
||||
# Guava中的类型增强
|
||||
|
||||
Map - Table、BiMap、Multimap、RangeMap、ClassToInstanceMap
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 简介[#](https://www.cnblogs.com/cao-lei/p/17806222.html#3979976375)
|
||||
|
||||
日常开发中使用Map时经常会遇到很多复杂的处理场景,例如:多个键的Map、不仅可以根据键获取值也可以根据值获取键且不用遍历、重复键的Map、数字等范围内映射相同的值、内存中缓存对象等,Guava提供了以上场景的解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
| 场景 | 解决方案 | 具体实现 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------ | ------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| 多个键的Map | Table | HashBasedTable、TreeBasedTable、ImmutableTable |
|
||||
| 不仅可以根据键获取值也可以根据值获取键且不用遍历 | BiMap | HashBiMap、ImmutableBiMap |
|
||||
| 重复键的Map | Multimap | ArrayListMultimap、LinkedListMultimap、LinkedHashMultimap、ImmutableListMultimap、ImmutableSetMultimap |
|
||||
| 数字等范围内映射相同的值 | RangeMap | TreeRangeMap、ImmutableRangeMap |
|
||||
| 内存中缓存对象 | ClassToInstanceMap | MutableClassToInstanceMap、ImmutableClassToInstanceMap |
|
||||
|
||||
本博客将详细描述具体的示例代码。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 添加依赖[#](https://www.cnblogs.com/cao-lei/p/17806222.html#1443701749)
|
||||
|
||||
Maven项目pom.xml中添加依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
Copy<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>32.0.0-jre</version>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Tbale - 表结构数据[#](https://www.cnblogs.com/cao-lei/p/17806222.html#848306248)
|
||||
|
||||
官方注释翻译:将一对有序键(称为行键和列键)与单个值相关联的集合。
|
||||
示例代码(需求: 记录各个公司每个部门的人数):
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
Copy// HashMap
|
||||
Map<String, Integer> deptMap = new HashMap<>();
|
||||
deptMap.put("A部门", 10);
|
||||
deptMap.put("B部门", 20);
|
||||
Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> companyMap = new HashMap<>();
|
||||
companyMap.put("xx公司", deptMap);
|
||||
// HashMap 获取值
|
||||
Integer val = companyMap.get("xx公司").get("A部门");
|
||||
System.out.println("HashMap 获取值: " + val);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建Hash类型Table, 基于Hash表实现
|
||||
// Table<R, C, V>中三个泛型: R-行, C-列, V-值
|
||||
Table<String, String, Integer> hashTable = HashBasedTable.create();
|
||||
hashTable.put("xx公司", "A部门", 10);
|
||||
hashTable.put("xx公司", "B部门", 20);
|
||||
hashTable.put("xx公司", "C部门", 30);
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nHash Table: " + hashTable);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建Tree类型Table, 基于红黑树实现
|
||||
Table<String, String, Integer> treeTable = TreeBasedTable.create();
|
||||
treeTable.put("xx公司", "C部门", 30);
|
||||
treeTable.put("xx公司", "B部门", 20);
|
||||
treeTable.put("xx公司", "A部门", 10);
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTree Table: " + treeTable);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建不可变Table, 无法新增、更新或删除
|
||||
Table<String, String, Integer> immutableTable = ImmutableTable.<String, String, Integer>builder()
|
||||
.put("xx公司", "C部门", 30)
|
||||
.put("xx公司", "B部门", 20)
|
||||
.put("xx公司", "A部门", 10)
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nImmutable Table: " + immutableTable);
|
||||
|
||||
// Table 获取值
|
||||
Integer val2 = hashTable.get("xx公司", "A部门");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 获取值: " + val2);
|
||||
|
||||
// Table 删除值
|
||||
Integer remove = hashTable.remove("xx公司", "C部门");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 删除值: " + remove);
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据行获取列和值映射
|
||||
Map<String, Integer> columnvalueMap = hashTable.row("xx公司");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 列和值 映射: " + columnvalueMap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据列获取行和值映射
|
||||
Map<String, Integer> rowvalueMap = hashTable.column("A部门");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 行和值 映射: " + rowvalueMap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取key集合
|
||||
Set<String> rowKeySet = hashTable.rowKeySet();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable Row key 集合: " + rowKeySet);
|
||||
Set<String> columnKeySet = hashTable.columnKeySet();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable Column key 集合: " + columnKeySet);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取值集合
|
||||
Collection<Integer> values = hashTable.values();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 值集合: " + values);
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断包含行
|
||||
boolean containsRow = hashTable.containsRow("xx公司");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 包含行: " + containsRow);
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断包含列
|
||||
boolean containsColumn = hashTable.containsColumn("A部门");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 包含列: " + containsColumn);
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断包含行和列
|
||||
boolean contains = hashTable.contains("xx公司", "A部门");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 包含行和列: " + contains);
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断包含值
|
||||
boolean containsValue = hashTable.containsValue(10);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable 包含值: " + containsValue);
|
||||
|
||||
// 行和列转置 - 行 转 列
|
||||
Table<String, String, Integer> transposeTable = Tables.transpose(hashTable);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取所有的行
|
||||
Set<Table.Cell<String, String, Integer>> cells = transposeTable.cellSet();
|
||||
|
||||
// 遍历输出
|
||||
System.out.println("\n遍历输出开始----------------------------");
|
||||
cells.forEach(cell -> System.out.println(cell.getRowKey() + ", " + cell.getColumnKey() + ", " + cell.getValue()));
|
||||
System.out.println("\n遍历输出结束----------------------------");
|
||||
|
||||
// 转换为嵌套的Map
|
||||
Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> rowMap = hashTable.rowMap();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable RowMap: " + rowMap);
|
||||
Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> columnMap = hashTable.columnMap();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nTable ColumnMap: " + columnMap);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
CopyHashMap 获取值: 10
|
||||
|
||||
Hash Table: {xx公司={A部门=10, B部门=20, C部门=30}}
|
||||
|
||||
Tree Table: {xx公司={A部门=10, B部门=20, C部门=30}}
|
||||
|
||||
Immutable Table: {xx公司={C部门=30, B部门=20, A部门=10}}
|
||||
|
||||
Table 获取值: 10
|
||||
|
||||
Table 删除值: 30
|
||||
|
||||
Table 列和值 映射: {A部门=10, B部门=20}
|
||||
|
||||
Table 行和值 映射: {xx公司=10}
|
||||
|
||||
Table Row key 集合: [xx公司]
|
||||
|
||||
Table Column key 集合: [A部门, B部门]
|
||||
|
||||
Table 值集合: [10, 20]
|
||||
|
||||
Table 包含行: true
|
||||
|
||||
Table 包含列: true
|
||||
|
||||
Table 包含行和列: true
|
||||
|
||||
Table 包含值: true
|
||||
|
||||
遍历输出开始----------------------------
|
||||
A部门, xx公司, 10
|
||||
B部门, xx公司, 20
|
||||
|
||||
遍历输出结束----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Table RowMap: {xx公司={A部门=10, B部门=20}}
|
||||
|
||||
Table ColumnMap: {A部门={xx公司=10}, B部门={xx公司=20}}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. BiMap - 双向映射Map[#](https://www.cnblogs.com/cao-lei/p/17806222.html#2347438548)
|
||||
|
||||
官方注释翻译:双映射(或“双向映射”)是一种保留其值及其键的唯一性的映射。此约束使双映射能够支持“反向视图”,即另一个双映射,其中包含与此双映射相同的条目,但具有相反的键和值。
|
||||
示例代码(需求: 数组和英文翻译):
|
||||
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
Copy// 创建BiMap, 底层为两个Hash表的Map
|
||||
BiMap<Integer, String> biMap = HashBiMap.create();
|
||||
biMap.put(1, "one");
|
||||
biMap.put(2, "two");
|
||||
biMap.put(3, "three");
|
||||
biMap.put(4, "four");
|
||||
biMap.put(5, "five");
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("BiMap: " + biMap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建不可变BiMap, 无法新增、更新或删除
|
||||
BiMap<Object, Object> immutableBiMap = ImmutableBiMap.builder()
|
||||
.put(1, "one")
|
||||
.put(2, "two")
|
||||
.put(3, "three")
|
||||
.put(4, "four")
|
||||
.put(5, "five")
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nImmutable BiMap: " + immutableBiMap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 通过key获取value
|
||||
String value = biMap.get(1);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nBiMap 根据key获取value: " + value);
|
||||
|
||||
Integer key = biMap.inverse().get("one");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nBiMap 根据value获取key: " + key);
|
||||
|
||||
// 翻转后修改
|
||||
biMap.inverse().put("six", 6);
|
||||
// 返回双映射的逆视图, 并没有创建新对象, 还是之前的对象, 所以操作翻转后的BiMap会影响之前的BiMap
|
||||
System.out.println("\nBiMap 被影响: " + biMap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 底层是HashMap, key不可重复
|
||||
// value不可重复
|
||||
try {
|
||||
biMap.put(11, "one");
|
||||
} catch (Exception e) {
|
||||
System.err.println("BiMap 替换value异常: " + e.getMessage());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 翻转后key不能重复
|
||||
try {
|
||||
biMap.inverse().put("first", 1);
|
||||
} catch (Exception e) {
|
||||
System.err.println("BiMap 替换key异常: " + e.getMessage());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// key和value可为null
|
||||
biMap.put(null, null);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nBiMap 根据Null key获取Null value: " + biMap.get(null));
|
||||
System.out.println("\nBiMap 根据Null value获取Null key: " + biMap.inverse().get(null));
|
||||
|
||||
// 强制替换key
|
||||
biMap.forcePut(11, "one");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nBiMap 获取新key: " + biMap.inverse().get("one"));
|
||||
|
||||
// values为Set集合
|
||||
Set<String> values = biMap.values();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nBiMap 不重复的value: " + values);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```mipsasm
|
||||
CopyBiMap: {1=one, 2=two, 3=three, 4=four, 5=five}
|
||||
|
||||
Immutable BiMap: {1=one, 2=two, 3=three, 4=four, 5=five}
|
||||
|
||||
BiMap 根据key获取value: one
|
||||
|
||||
BiMap 根据value获取key: 1
|
||||
|
||||
BiMap 被影响: {1=one, 2=two, 3=three, 4=four, 5=five, 6=six}
|
||||
BiMap 替换value异常: value already present: one
|
||||
BiMap 替换key异常: key already present: 1
|
||||
|
||||
BiMap 根据Null key获取Null value: null
|
||||
|
||||
BiMap 根据Null value获取Null key: null
|
||||
|
||||
BiMap 获取新key: 11
|
||||
|
||||
BiMap 不重复的value: [two, three, four, five, six, null, one]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. Multimap - 多重映射Map[#](https://www.cnblogs.com/cao-lei/p/17806222.html#819077997)
|
||||
|
||||
官方注释翻译将键映射到值的集合,类似于 Map,但其中每个键可能与 多个 值相关联。
|
||||
示例代码(需求: 学生和各科选修课成绩):
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
Copy// 创建Multimap, key为HashMap, value为ArrayList
|
||||
Multimap<String, Integer> arrayListMultimap = ArrayListMultimap.create();
|
||||
arrayListMultimap.put("张三", 90);
|
||||
arrayListMultimap.put("张三", 80);
|
||||
arrayListMultimap.put("张三", 100);
|
||||
arrayListMultimap.put("李四", 88);
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("Multimap key为HashMap, value为ArrayList: " + arrayListMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建Multimap, key为HashMap, value为HashSet
|
||||
Multimap<String, Integer> hashMultimap = HashMultimap.create();
|
||||
hashMultimap.put("张三", 90);
|
||||
hashMultimap.put("张三", 80);
|
||||
hashMultimap.put("张三", 100);
|
||||
hashMultimap.put("李四", 88);
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap key为HashMap, value为HashSet: " + hashMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建Multimap, key为LinkedHashMap, value为LinkedList
|
||||
Multimap<String, Integer> linkedListMultimap = LinkedListMultimap.create();
|
||||
linkedListMultimap.put("张三", 90);
|
||||
linkedListMultimap.put("张三", 80);
|
||||
linkedListMultimap.put("张三", 100);
|
||||
linkedListMultimap.put("李四", 88);
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap key为LinkedHashMap, value为LinkedList: " + linkedListMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建Multimap, key为LinkedHashMap, value为LinkedHashMap
|
||||
Multimap<String, Integer> linkedHashMultimap = LinkedHashMultimap.create();
|
||||
linkedHashMultimap.put("张三", 90);
|
||||
linkedHashMultimap.put("张三", 80);
|
||||
linkedHashMultimap.put("张三", 100);
|
||||
linkedHashMultimap.put("李四", 88);
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap key为LinkedHashMap, value为LinkedHashMap: " + linkedHashMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建Multimap, key为TreeMap, value为TreeSet
|
||||
Multimap<String, Integer> treeMultimap = TreeMultimap.create();
|
||||
treeMultimap.put("张三", 90);
|
||||
treeMultimap.put("张三", 80);
|
||||
treeMultimap.put("张三", 100);
|
||||
treeMultimap.put("李四", 88);
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap key为TreeMap, value为TreeSet: " + treeMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建不可变Multimap, 无法新增、更新或删除, key为ImmutableMap, value为ImmutableList
|
||||
Multimap<String, Integer> immutableListMultimap = ImmutableListMultimap.<String, Integer>builder()
|
||||
.put("张三", 90)
|
||||
.put("张三", 80)
|
||||
.put("张三", 100)
|
||||
.put("李四", 88)
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap key为ImmutableMap, value为ImmutableList: " + immutableListMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建不可变Multimap, 无法新增、更新或删除, key为ImmutableMap, value为ImmutableSet
|
||||
Multimap<String, Integer> immutableSetMultimap = ImmutableSetMultimap.<String, Integer>builder()
|
||||
.put("张三", 90)
|
||||
.put("张三", 80)
|
||||
.put("张三", 100)
|
||||
.put("李四", 88)
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap key为ImmutableMap, value为ImmutableSet: " + immutableSetMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取值
|
||||
Collection<Integer> values = arrayListMultimap.get("张三");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 获取值集合: " + values);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取不存在key的值, 返回的是空集合, 而不是null
|
||||
Collection<Integer> valuesByNotExistsKey = arrayListMultimap.get("王五");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 获取不存在的Key值集合: " + valuesByNotExistsKey);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取值集合添加值
|
||||
// 返回的是多重映射中关联的值的视图集合, 并没有创建新对象, 还是之前的对象, 所以操作值集合会影响之前的Multimap
|
||||
values.add(60);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 被影响: " + arrayListMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取大小
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 大小:" + arrayListMultimap.size());
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断是否为空
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 是否为空: " + arrayListMultimap.isEmpty());
|
||||
|
||||
// 包含key
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 包含key: " + arrayListMultimap.containsKey("张三"));
|
||||
|
||||
// 包含value
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 包含value: " + arrayListMultimap.containsValue(60));
|
||||
|
||||
// 包含key-value键值对
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 包含key-value对: " + arrayListMultimap.containsEntry("张三", 60));
|
||||
|
||||
// 替换value
|
||||
arrayListMultimap.replaceValues("张三", Arrays.asList(10, 20, 30));
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 替换value: " + arrayListMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据key-value删除
|
||||
arrayListMultimap.remove("张三", 10);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 根据key-value删除: " + arrayListMultimap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 根据key删除
|
||||
Collection<Integer> removeAll = arrayListMultimap.removeAll("张三");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 根据key删除: " + removeAll);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取key集合
|
||||
Set<String> keySet = arrayListMultimap.keySet();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 获取key集合(HashSet): " + keySet);
|
||||
Multiset<String> keys = arrayListMultimap.keys();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 获取key集合(MultiSet): " + keys);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取所有的key-value
|
||||
Collection<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = arrayListMultimap.entries();
|
||||
System.out.println("\n遍历key-value开始--------------------------");
|
||||
entries.forEach(entry -> System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue()));
|
||||
System.out.println("\n遍历key-value结束--------------------------");
|
||||
|
||||
// 转换为Map<K, Collection<V>>
|
||||
Map<String, Collection<Integer>> collectionMap = arrayListMultimap.asMap();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nMultimap 转换为Map<K, Collection<V>>: " + collectionMap);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```mipsasm
|
||||
CopyMultimap key为HashMap, value为ArrayList: {李四=[88], 张三=[90, 80, 100]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap key为HashMap, value为HashSet: {李四=[88], 张三=[80, 100, 90]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap key为LinkedHashMap, value为LinkedList: {张三=[90, 80, 100], 李四=[88]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap key为LinkedHashMap, value为LinkedHashMap: {张三=[90, 80, 100], 李四=[88]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap key为TreeMap, value为TreeSet: {张三=[80, 90, 100], 李四=[88]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap key为ImmutableMap, value为ImmutableList: {张三=[90, 80, 100], 李四=[88]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap key为ImmutableMap, value为ImmutableSet: {张三=[90, 80, 100], 李四=[88]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 获取值集合: [90, 80, 100]
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 获取不存在的Key值集合: []
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 被影响: {李四=[88], 张三=[90, 80, 100, 60]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 大小:5
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 是否为空: false
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 包含key: true
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 包含value: true
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 包含key-value对: true
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 替换value: {李四=[88], 张三=[10, 20, 30]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 根据key-value删除: {李四=[88], 张三=[20, 30]}
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 根据key删除: [20, 30]
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 获取key集合(HashSet): [李四]
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 获取key集合(MultiSet): [李四]
|
||||
|
||||
遍历key-value开始--------------------------
|
||||
李四 : 88
|
||||
|
||||
遍历key-value结束--------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Multimap 转换为Map<K, Collection<V>>: {李四=[88]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. RangeMap - 范围映射Map[#](https://www.cnblogs.com/cao-lei/p/17806222.html#684335507)
|
||||
|
||||
官方注释翻译:从不相交的非空范围到非 null 值的映射。查询查找与包含指定键的范围(如果有)关联的值。
|
||||
示例代码(需求:考试成绩分类):
|
||||
|
||||
```swift
|
||||
Copy// if-else
|
||||
int score = 88;
|
||||
String rank;
|
||||
if (0 <= score && score < 60) {
|
||||
rank = "不及格";
|
||||
} else if (60 <= score && score <= 84) {
|
||||
rank = "及格";
|
||||
} else if (84 < score && score <= 100) {
|
||||
rank = "优秀";
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
rank = "无效";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("if-else 获取值: " + rank);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建RangeMap, 基于TreeMap(红黑树)实现
|
||||
RangeMap<Integer, String> treeRangeMap = TreeRangeMap.create();
|
||||
treeRangeMap.put(Range.closedOpen(0, 60), "不及格");
|
||||
treeRangeMap.put(Range.closed(60, 84), "及格");
|
||||
treeRangeMap.put(Range.openClosed(84, 100), "优秀");
|
||||
treeRangeMap.put(Range.lessThan(0), "无效");
|
||||
treeRangeMap.put(Range.greaterThan(100), "无效");
|
||||
|
||||
rank = treeRangeMap.get(score);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 获取值: " + rank);
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建不可变RangeMap, 无法新增、更新或删除
|
||||
ImmutableRangeMap<Integer, String> immutableRangeMap = ImmutableRangeMap.<Integer, String>builder()
|
||||
.put(Range.closedOpen(0, 60), "不及格")
|
||||
.put(Range.closed(60, 84), "及格")
|
||||
.put(Range.openClosed(84, 100), "优秀")
|
||||
.put(Range.lessThan(0), "无效")
|
||||
.put(Range.greaterThan(100), "无效")
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
|
||||
rank = immutableRangeMap.get(score);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nImmutableRangeMap 获取值: " + rank);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取key-value对
|
||||
Map.Entry<Range<Integer>, String> entry = treeRangeMap.getEntry(88);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 获取key-value对: " + entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
|
||||
|
||||
// 返回不可变的升序的Map
|
||||
Map<Range<Integer>, String> asMapOfRanges = treeRangeMap.asMapOfRanges();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 不可变的升序的Map: " + asMapOfRanges);
|
||||
|
||||
// 返回不可变的降序的Map
|
||||
Map<Range<Integer>, String> asDescendingMapOfRanges = treeRangeMap.asDescendingMapOfRanges();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 不可变的降序的Map: " + asDescendingMapOfRanges);
|
||||
|
||||
// 相连范围合并
|
||||
RangeMap<Integer, String> treeRangeMap2 = TreeRangeMap.create();
|
||||
treeRangeMap2.putCoalescing(Range.closedOpen(0, 60), "不及格");
|
||||
treeRangeMap2.putCoalescing(Range.closed(60, 84), "及格");
|
||||
treeRangeMap2.putCoalescing(Range.openClosed(84, 100), "及格"); // 或者 [60..84]范围合并
|
||||
treeRangeMap2.putCoalescing(Range.lessThan(0), "无效");
|
||||
treeRangeMap2.putCoalescing(Range.greaterThan(100), "无效");
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 不合并相连范围: " + treeRangeMap.asMapOfRanges());
|
||||
System.out.println("RangeMap 合并相连范围: " + treeRangeMap2.asMapOfRanges());
|
||||
|
||||
// 最小范围
|
||||
Range<Integer> span = treeRangeMap.span();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 最小范围: " + span);
|
||||
|
||||
// 子范围Map
|
||||
RangeMap<Integer, String> subRangeMap = treeRangeMap.subRangeMap(Range.closed(70, 90));
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 子范围Map: " + subRangeMap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 合并范围
|
||||
treeRangeMap.merge(Range.closed(60, 100), "及格", (s, s2) -> s2);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 合并Map: " + treeRangeMap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 移除范围
|
||||
treeRangeMap.remove(Range.open(90, 95));
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 移除范围: " + treeRangeMap);
|
||||
|
||||
// 清除所有范围
|
||||
treeRangeMap.clear();
|
||||
System.out.println("\nRangeMap 清除所有范围: " + treeRangeMap);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
Copyif-else 获取值: 优秀
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 获取值: 优秀
|
||||
|
||||
ImmutableRangeMap 获取值: 优秀
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 获取key-value对: (84..100] : 优秀
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 不可变的升序的Map: {(-∞..0)=无效, [0..60)=不及格, [60..84]=及格, (84..100]=优秀, (100..+∞)=无效}
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 不可变的降序的Map: {(100..+∞)=无效, (84..100]=优秀, [60..84]=及格, [0..60)=不及格, (-∞..0)=无效}
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 不合并相连范围: {(-∞..0)=无效, [0..60)=不及格, [60..84]=及格, (84..100]=优秀, (100..+∞)=无效}
|
||||
RangeMap 合并相连范围: {(-∞..0)=无效, [0..60)=不及格, [60..100]=及格, (100..+∞)=无效}
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 最小范围: (-∞..+∞)
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 子范围Map: {[70..84]=及格, (84..90]=优秀}
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 合并Map: [(-∞..0)=无效, [0..60)=不及格, [60..84]=及格, (84..100]=及格, (100..+∞)=无效]
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 移除范围: [(-∞..0)=无效, [0..60)=不及格, [60..84]=及格, (84..90]=及格, [95..100]=及格, (100..+∞)=无效]
|
||||
|
||||
RangeMap 清除所有范围: []
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. ClassToInstanceMap - 类型映射到实例Map[#](https://www.cnblogs.com/cao-lei/p/17806222.html#85873049)
|
||||
|
||||
官方注释翻译:映射,其每个条目将一个 Java 原始类型 映射到该类型的实例。除了实现 Map之外,还提供额外的类型安全操作 putInstance 和 getInstance 。与任何其他 Map<Class, Object>映射一样,此映射可能包含基元类型的条目,并且基元类型及其相应的包装器类型可以映射到不同的值。
|
||||
示例代码(需求:缓存Bean(不交给Spring管理,自己管理Bean)):
|
||||
|
||||
```csharp
|
||||
Copyclass UserBean {
|
||||
private final Integer id;
|
||||
private final String username;
|
||||
|
||||
public UserBean(Integer id, String username) {
|
||||
this.id = id;
|
||||
this.username = username;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@Override
|
||||
public String toString() {
|
||||
return "UserBean{" + "id=" + id + ", username='" + username + '\'' + '}';
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 创建Bean
|
||||
UserBean userBean = new UserBean(1, "张三");
|
||||
|
||||
// HashMap
|
||||
HashMap<Class, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
|
||||
hashMap.put(UserBean.class, userBean);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取值,需要强转
|
||||
UserBean value = (UserBean) hashMap.get(UserBean.class);
|
||||
System.out.println("HashMap 获取对象实例: " + value);
|
||||
System.out.println("HashMap 获取对象实例等于创建的Bean: " + (value == userBean));
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建ClassToInstanceMap
|
||||
ClassToInstanceMap<Object> classToInstanceMap = MutableClassToInstanceMap.create();
|
||||
classToInstanceMap.putInstance(UserBean.class, userBean);
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取值,无需强转
|
||||
UserBean value2 = classToInstanceMap.getInstance(UserBean.class);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nClassToInstanceMap 获取对象实例: " + value2);
|
||||
System.out.println("ClassToInstanceMap 获取对象实例等于创建的Bean: " + (value2 == userBean));
|
||||
|
||||
// 创建不可变ClassToInstanceMap, 无法新增、更新或删除
|
||||
ClassToInstanceMap<UserBean> immutableClassToInstanceMap = ImmutableClassToInstanceMap.<UserBean>builder()
|
||||
.put(UserBean.class, userBean)
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取值,无需强转
|
||||
UserBean value3 = immutableClassToInstanceMap.getInstance(UserBean.class);
|
||||
System.out.println("\nImmutableClassToInstanceMap 获取对象实例: " + value3);
|
||||
System.out.println("ImmutableClassToInstanceMap 获取对象实例等于创建的Bean: " + (value3 == userBean));
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// 限制类型,避免使用HashMap存储对象时,因为使用Object值类型而在添加缓存时需要今天类型校验
|
||||
ClassToInstanceMap<Collection> classToInstanceMap1 = MutableClassToInstanceMap.create();
|
||||
classToInstanceMap1.put(ArrayList.class, new ArrayList());
|
||||
classToInstanceMap1.put(HashSet.class, new HashSet());
|
||||
// 编译保存: 'put(java.lang.Class<? extends java.util.@org.checkerframework.checker.nullness.qual.NonNull Collection>, java.util.Collection)' in 'com.google.common.collect.MutableClassToInstanceMap' cannot be applied to '(java.lang.Class<java.util.HashMap>, java.util.HashMap)'
|
||||
// classToInstanceMap1.put(HashMap.class, new HashMap());
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行结果:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
CopyHashMap 获取对象实例: UserBean{id=1, username='张三'}
|
||||
HashMap 获取对象实例等于创建的Bean: true
|
||||
|
||||
ClassToInstanceMap 获取对象实例: UserBean{id=1, username='张三'}
|
||||
ClassToInstanceMap 获取对象实例等于创建的Bean: true
|
||||
|
||||
ImmutableClassToInstanceMap 获取对象实例: UserBean{id=1, username='张三'}
|
||||
ImmutableClassToInstanceMap 获取对象实例等于创建的Bean: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
137
java/Jsr303校验.md
Normal file
137
java/Jsr303校验.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
|
||||
# JSR303数据校验
|
||||
|
||||
JSR303是Java为Bean数据合法性校验提供给的标准框架,已经包含在 JavaEE6.0 中、JSR303通过在Bean 属性中标注类似 @NotNull @Max 等标准的注解指定校验规则并通过标准的验证接口对 Bean进行验证
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### JSR303中含有的注解
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@Null 被注释的元素必须为 null
|
||||
@NotNull 被注释的元素必须不为 null
|
||||
@AssertTrue 被注释的元素必须为 true
|
||||
@AssertFalse 被注释的元素必须为 false
|
||||
@Min(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
|
||||
@Max(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
|
||||
@DecimalMin(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值
|
||||
@DecimalMax(value) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值
|
||||
@Size(max=, min=) 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内
|
||||
@Digits (integer, fraction) 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内
|
||||
@Past 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期
|
||||
@Future 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期
|
||||
@Pattern(regex=,flag=) 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Hibernate Validator 附加的注解
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@NotBlank(message =) 验证字符串非null,且长度必须大于0
|
||||
@Email 被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址
|
||||
@Length(min=,max=) 被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内
|
||||
@NotEmpty 被注释的字符串的必须非空
|
||||
@Range(min=,max=,message=) 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内
|
||||
|
||||
注:HIbernate Validator是JSR303的一个参考实现,除了支持所有标准的校验注解外,另外HIbernate Validator还有JSR-380的实现
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### @Validated @Valid 有什么区别
|
||||
|
||||
`@Validated` 是spring 中提供的注解用于在添加该注解的方法、类上触发bean 校验。
|
||||
|
||||
`@Valid` java自身的注解 用于校验嵌套对象(在spring 环境中,添加该注解同样会触发bean 校验)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### @Validated @Valid 注解的位置
|
||||
|
||||
@Valid 注解在对象上用于嵌套注解
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@Validated 注解在类上 启用全局的方法校验 (对@RequestBody **不生效**)
|
||||
|
||||
@Validated 注解在方法上 启用该方法方法校验 覆盖类全局(对@RsequestBody **不生效**)
|
||||
|
||||
@Validated 注解在参数上 启用该参数校验 (对@RequestBody **生效**)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 对象嵌套校验
|
||||
|
||||
@Valid 校验嵌套对象
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
|
||||
public class Project {
|
||||
|
||||
@NotBlank(message = "Project title must be present")
|
||||
@Size(min = 3, max = 20, message = "Project title size not valid")
|
||||
private String title;
|
||||
@Valid // 校验嵌套的对象
|
||||
private User owner;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public class User {
|
||||
// 校验规则
|
||||
@NotBlank(message = "User name must be present")
|
||||
@Size(min = 3, max = 50, message = "User name size not valid")
|
||||
private String name;
|
||||
|
||||
// 校验规则
|
||||
@NotBlank(message = "User email must be present")
|
||||
@Email(message = "User email format is incorrect")
|
||||
private String email;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@Valid 校验可迭代对象
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
// @Valid 定义在容器对象上
|
||||
@Valid
|
||||
private List<Task> tasks;
|
||||
|
||||
// @Valid (JSR303注解也可以)定义在泛型参数上
|
||||
private List<@Valid Task> tasks;
|
||||
|
||||
private Map<@Valid User, @Valid Task> assignedTasks;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Validator Api 手动校验BEAN
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
ValidatorFactory factory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
|
||||
Validator validator = factory.getValidator();
|
||||
|
||||
AirportDTO dto = new AirportDTO();
|
||||
dto.setIataCode("PKX");
|
||||
dto.setThroughput("-1"); // 符合条件
|
||||
// data.setValue(1234567.789); // 不符合条件,整数部分超过6位
|
||||
// data.setValue(123456.78901); // 不符合条件,小数部分超过4位
|
||||
// data.setValue(-123.45); // 不符合条件,小于0
|
||||
|
||||
Set<ConstraintViolation<AirportDTO>> validate = validator.validate(dto,Update.class);
|
||||
for (ConstraintViolation<AirportDTO> violation : validate) {
|
||||
System.out.println(violation.getMessage());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
###
|
||||
38
java/Springboot配置文件与参数加载优先级.md
Normal file
38
java/Springboot配置文件与参数加载优先级.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
## Springboot 配置文件 与参数加载优先级
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 加载顺序
|
||||
|
||||
在 Spring Boot 中,配置文件的加载顺序是按照以下规则:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **bootstrap.yml 或 bootstrap.properties**: 这是最先加载的配置文件,用于配置应用程序上下文的基础设施,例如外部配置源和加密/解密。
|
||||
2. **application.yml 或 application.properties**: 这是主配置文件,包含应用程序的常规配置。
|
||||
3. **application-{profile}.yml 或 application-{profile}.properties**: 针对不同的环境(profile)加载相应的配置文件。例如,`application-dev.yml` 用于开发环境,`application-prod.yml` 用于生产环境。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置文件目录
|
||||
|
||||
SpringBoot配置文件可以放置在多种路径下,不同路径下的配置优先级有所不同。
|
||||
可放置目录**(优先级从高到低)**
|
||||
|
||||
- **file:./config/** (当前项目路径config目录下);
|
||||
- **file:./** (当前项目路径下);
|
||||
- **classpath:/config/** (类路径config目录下);
|
||||
- **classpath:/** (类路径config下).
|
||||
|
||||
优先级由高到底,高优先级的配置会覆盖低优先级的配置;
|
||||
SpringBoot会从这四个位置全部加载配置文件并互补配置;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 命令行参数、环境变量
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 的配置加载顺序(**后者覆盖前者**):
|
||||
|
||||
1. **`application.yml` / `application.properties`**(默认配置)
|
||||
2. **`-D` JVM 参数**(如 `-Dserver.port=8080`)
|
||||
3. **`--` 命令行参数**(如 `--server.port=8081`)
|
||||
4. **环境变量**(如 `SERVER_PORT=8082`)
|
||||
|
||||
340
java/date.md
Normal file
340
java/date.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,340 @@
|
||||
# Java 中的日期和时间处理类:从传统到现代
|
||||
|
||||
2024-11-07
|
||||
|
||||
## 1、概览
|
||||
|
||||
处理 `Date`(日期)和 `Time`(时间)是许多 Java 应用程序的基本组成部分。多年来,Java 在处理日期方面不断发展,引入了更好的解决方案来简化开发者的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
## 2、传统的日期和时间处理类
|
||||
|
||||
在 `java.time` 包出现之前,Java 主要使用 `Date` 和 `Calendar` 类来处理日期。尽管它们现在也可以使用,但是有一些缺陷。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.1、java.util.Date 类
|
||||
|
||||
`java.util.Date` 类是 Java 最初处理日期的解决方案,但它有一些缺点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 它是可变的,这意味着可能会遇到 **线程安全** 问题。
|
||||
- 不支持时区。
|
||||
- 它使用了令人困惑的方法名称和返回值,比如 `getYear()`,它返回的是自 *1900* 年以来的年数。
|
||||
- 许多方法已废弃。
|
||||
|
||||
使用无参数构造函数创建 `Date` 对象,表示当前日期和时间(对象创建时)。
|
||||
|
||||
如下,实例化一个 `Date` 对象并打印其值:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
Date now = new Date();
|
||||
logger.info("Current date and time: {}", now);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这将输出当前日期和时间,如 *Wed Sep 24 10:30:45 PDT 2024*。虽然该构造函数仍然有效,但由于上述原因,这里不再建议新项目使用该构造函数。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2、java.util.Calendar 类
|
||||
|
||||
由于 `Date` 的局限性,Java 引入了 `Calendar` 类,对其进行了改进:
|
||||
|
||||
- 支持各种日历系统。
|
||||
- 时区管理。
|
||||
- 更加直观的日期操作方法。
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以使用 `Calendar` 操作日期。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
|
||||
cal.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 5);
|
||||
Date fiveDaysLater = cal.getTime();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如上,我们计算当前日期 5 天后的日期,并将其存储在 `Date` 对象中。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,`Calendar` 也有缺陷:
|
||||
|
||||
- 和 `Date` 一样,它仍然是可变的,所以不是线程安全的。
|
||||
- 其 API 既混乱又复杂,比如月份是从 *0* 开始的。
|
||||
|
||||
## 3、现代的日期和时间处理类:java.time 包
|
||||
|
||||
Java 8 引入了 `java.time` 包,为处理日期和时间提供了一个现代、强大的 API。它旨在解决旧版 `Date` 和 `Calendar` 类的许多问题,使日期和时间操作更加直观和友好。
|
||||
|
||||
受到流行的 [Joda-Time](https://www.joda.org/joda-time/) 库的启发,`java.time` 现在已成为处理日期和时间的核心 Java 解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1、java.time 包下的关键类
|
||||
|
||||
`java.time` 包提供了几个在实际应用中经常使用的重要类。这些类可分为三大类:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 时间容器
|
||||
|
||||
- `LocalDate`:代表日期,不包含时间或时区。
|
||||
- `LocalTime`:代表时间,不包含日期或时区。
|
||||
- `LocalDateTime`:包括了日期和时间,但不包括时区。
|
||||
- `ZonedDateTime`:包括了日期和时间以及时区。
|
||||
- `Instant`:代表时间轴上的一个特定点,类似于时间戳。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 时间操作
|
||||
|
||||
- `Duration`:表示基于时间的时间量(例如 “5 小时” 或 “30 秒”)。
|
||||
- `Period`:代表基于日期的时间量(如 “2 年 3 个月”)。
|
||||
- `TemporalAdjusters`:提供调整日期的方法(如查找下一个星期一)。
|
||||
- `Clock`:使用时区提供当前日期时间,并可进行时间控制。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 格式化和输出
|
||||
|
||||
- `DateTimeFormatter`:用于格式化和解析日期时间对象。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2、java.time 包的优点
|
||||
|
||||
与旧的日期和时间类相比,`java.time` 包带来了多项改进:
|
||||
|
||||
- **不可变**:所有类都不可变,确保线程安全。
|
||||
- **清晰的 API**:方法一致,使 API 更容易理解。
|
||||
- **专注的类**:每个类都有特定的作用,无论是处理日期存储、操作还是格式化。
|
||||
- **格式化和解析**:内置方法可轻松格式化和解析日期。
|
||||
|
||||
## 4、java.time 的使用示例
|
||||
|
||||
首先从使用 `java.time` 包创建日期和时间表示的基础知识开始。有了基础后,再了解如何调整日期以及如何格式化和解析日期。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.1、创建日期表示
|
||||
|
||||
`java.time` 包提供了多个类来表示日期和时间的不同方面。
|
||||
|
||||
代码如下,使用 `LocalDate`、`LocalTime` 和 `LocalDateTime` 创建一个基本日期:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenCurrentDateTime_whenUsingLocalDateTime_thenCorrect() {
|
||||
LocalDate currentDate = LocalDate.now(); // 当前日期
|
||||
LocalTime currentTime = LocalTime.now(); // 当前时间
|
||||
LocalDateTime currentDateTime = LocalDateTime.now(); // 当前日期和时间
|
||||
|
||||
assertThat(currentDate).isBeforeOrEqualTo(LocalDate.now());
|
||||
assertThat(currentTime).isBeforeOrEqualTo(LocalTime.now());
|
||||
assertThat(currentDateTime).isBeforeOrEqualTo(LocalDateTime.now());
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
还可以通过传递所需的参数来创建特定的日期和时间:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenSpecificDateTime_whenUsingLocalDateTime_thenCorrect() {
|
||||
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2024, Month.SEPTEMBER, 18);
|
||||
LocalTime time = LocalTime.of(10, 30);
|
||||
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.of(date, time);
|
||||
|
||||
assertEquals("2024-09-18", date.toString());
|
||||
assertEquals("10:30", time.toString());
|
||||
assertEquals("2024-09-18T10:30", dateTime.toString());
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.2、用 TemporalAdjusters 调整日期
|
||||
|
||||
有了日期表示后,我们就可以使用 `TemporalAdjusters` 对其进行调整。
|
||||
|
||||
`TemporalAdjusters` 类提供了一组预定义的方法来操作日期:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenTodaysDate_whenUsingVariousTemporalAdjusters_thenReturnCorrectAdjustedDates() {
|
||||
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
|
||||
|
||||
LocalDate nextMonday = today.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.MONDAY)); // 调整日期为下周一
|
||||
assertThat(nextMonday.getDayOfWeek())
|
||||
.as("Next Monday should be correctly identified")
|
||||
.isEqualTo(DayOfWeek.MONDAY);
|
||||
|
||||
LocalDate firstDayOfMonth = today.with(TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfMonth()); // 整日期为月初第一天
|
||||
assertThat(firstDayOfMonth.getDayOfMonth())
|
||||
.as("First day of the month should be 1")
|
||||
.isEqualTo(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
除了预定义的 *Adjuster*(调整器)外,我们还可以根据特定需求创建自定义 *Adjuster*:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenCustomTemporalAdjuster_whenAddingTenDays_thenCorrect() {
|
||||
LocalDate specificDate = LocalDate.of(2024, Month.SEPTEMBER, 18);
|
||||
TemporalAdjuster addTenDays = temporal -> temporal.plus(10, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
|
||||
LocalDate adjustedDate = specificDate.with(addTenDays);
|
||||
|
||||
assertEquals(
|
||||
today.plusDays(10),
|
||||
adjustedDate,
|
||||
"The adjusted date should be 10 days later than September 18, 2024"
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.3、格式化日期
|
||||
|
||||
`java.time.format` 包中的 `DateTimeFormatter` 类允许我们以线程安全的方式格式化和解析日期时间对象:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenDateTimeFormat_whenFormatting_thenVerifyResults() {
|
||||
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm");
|
||||
LocalDateTime specificDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2024, 9, 18, 10, 30);
|
||||
|
||||
String formattedDate = specificDateTime.format(formatter);
|
||||
LocalDateTime parsedDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse("18-09-2024 10:30", formatter);
|
||||
|
||||
assertThat(formattedDate).isNotEmpty().isEqualTo("18-09-2024 10:30");
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以根据需要使用预定义的格式或自定义的格式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.4、解析日期
|
||||
|
||||
同样,`DateTimeFormatter` 可以将字符串解析为日期或时间对象:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenDateTimeFormat_whenParsing_thenVerifyResults() {
|
||||
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("dd-MM-yyyy HH:mm");
|
||||
|
||||
LocalDateTime parsedDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse("18-09-2024 10:30", formatter);
|
||||
|
||||
assertThat(parsedDateTime)
|
||||
.isNotNull()
|
||||
.satisfies(time -> {
|
||||
assertThat(time.getYear()).isEqualTo(2024);
|
||||
assertThat(time.getMonth()).isEqualTo(Month.SEPTEMBER);
|
||||
assertThat(time.getDayOfMonth()).isEqualTo(18);
|
||||
assertThat(time.getHour()).isEqualTo(10);
|
||||
assertThat(time.getMinute()).isEqualTo(30);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.5、通过 OffsetDateTime 和 OffsetTime 处理时区
|
||||
|
||||
在处理不同时区时,`OffsetDateTime` 和 `OffsetTime` 类对于处理日期和时间或与 UTC 的偏移量非常有用:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenVariousTimeZones_whenCreatingOffsetDateTime_thenVerifyOffsets() {
|
||||
// 巴黎时区
|
||||
ZoneId parisZone = ZoneId.of("Europe/Paris");
|
||||
// 纽约时区
|
||||
ZoneId nyZone = ZoneId.of("America/New_York");
|
||||
|
||||
OffsetDateTime parisTime = OffsetDateTime.now(parisZone);
|
||||
OffsetDateTime nyTime = OffsetDateTime.now(nyZone);
|
||||
|
||||
assertThat(parisTime)
|
||||
.isNotNull()
|
||||
.satisfies(time -> {
|
||||
assertThat(time.getOffset().getTotalSeconds())
|
||||
.isEqualTo(parisZone.getRules().getOffset(Instant.now()).getTotalSeconds());
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 验证不同地区之间的时差
|
||||
assertThat(ChronoUnit.HOURS.between(nyTime, parisTime) % 24)
|
||||
.isGreaterThanOrEqualTo(5) // 纽约一般比巴黎晚 5-6 个小时
|
||||
.isLessThanOrEqualTo(7);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
代码如上,演示了如何为不同时区创建 `OffsetDateTime` 实例并验证其偏移量。首先,使用 `ZoneId` 定义巴黎和纽约的时区。然后,使用 `OffsetDateTime.now()` 创建这两个时区的当前时间。
|
||||
|
||||
该测试检查巴黎时间的偏移量是否与巴黎时区的预期偏移量相匹配。最后,验证纽约和巴黎之间的时间差,确保它在典型的 *5* 到 *7* 小时范围内,反映了标准时区差异。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4.6、高级用例:Clock
|
||||
|
||||
`java.time` 软件包中的 `Clock` 类提供了一种灵活的方式来访问当前日期和时间,同时考虑到特定的时区。
|
||||
|
||||
在我们需要对时间进行更多控制或测试基于时间的逻辑时,该类非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
与使用 `LocalDateTime.now()` 获取系统当前时间不同,`Clock` 允许我们获取相对于特定时区的时间,甚至为测试目的模拟时间。通过向 `Clock.system()` 方法传递 `ZoneId`,我们可以获得任何地区的当前时间。例如,在下面的测试用例中,我们使用 `Clock` 类获取 `America/New_York`(美国/纽约)时区的当前时间:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenSystemClock_whenComparingDifferentTimeZones_thenVerifyRelationships() {
|
||||
Clock nyClock = Clock.system(ZoneId.of("America/New_York"));
|
||||
|
||||
LocalDateTime nyTime = LocalDateTime.now(nyClock);
|
||||
|
||||
assertThat(nyTime)
|
||||
.isNotNull()
|
||||
.satisfies(time -> {
|
||||
assertThat(time.getHour()).isBetween(0, 23);
|
||||
assertThat(time.getMinute()).isBetween(0, 59);
|
||||
// 验证是否在最后一分钟内(最近)
|
||||
assertThat(time).isCloseTo(
|
||||
LocalDateTime.now(),
|
||||
within(1, ChronoUnit.MINUTES)
|
||||
);
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这也使得 `Clock` 对于管理多个时区或控制时间流一致的应用非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 5、从传统类到现代类的迁移
|
||||
|
||||
我们可能仍然需要处理使用 `Date` 或 `Calendar` 的遗留代码或库。幸运的是,我们可以轻松地从旧的日期时间类迁移到新的日期时间类。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.1、转换 Date 为 Instant
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `toInstant()` 方法可以轻松地将传统的 `Date` 类转换为 `Instant`。这对我们迁移到 `java.time` 包中的类很有帮助,因为 `Instant` 表示时间轴上的一个点(纪元):
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenSameEpochMillis_whenConvertingDateAndInstant_thenCorrect() {
|
||||
long epochMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
|
||||
Date legacyDate = new Date(epochMillis);
|
||||
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(epochMillis);
|
||||
|
||||
assertEquals(
|
||||
legacyDate.toInstant(),
|
||||
instant,
|
||||
"Date and Instant should represent the same moment in time"
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以将传统的 `Date` 转换为 `Instant`,并通过从相同的毫秒纪元创建两者来确保它们代表相同的时间点。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.2、迁移 Calendar 到 ZonedDateTime
|
||||
|
||||
在使用 `Calendar` 时,我们可以迁移到更现代的 `ZonedDateTime`,它可以同时处理日期和时间以及时区信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Test
|
||||
void givenCalendar_whenConvertingToZonedDateTime_thenCorrect() {
|
||||
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
|
||||
calendar.set(2024, Calendar.SEPTEMBER, 18, 10, 30);
|
||||
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(
|
||||
calendar.toInstant(),
|
||||
calendar.getTimeZone().toZoneId()
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
assertEquals(LocalDate.of(2024, 9, 18), zonedDateTime.toLocalDate());
|
||||
assertEquals(LocalTime.of(10, 30), zonedDateTime.toLocalTime());
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如上,我们将 `Calendar` 实例转换为 `ZonedDateTime`,并验证它们是否代表相同的日期时间。
|
||||
|
||||
## 6、最佳实践
|
||||
|
||||
有一些使用 `java.time` 类的最佳实践,你可以参考:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 任何新项目都应使用 `java.time` 类。
|
||||
2. 当不需要时区时,可以使用 `LocalDate`、`LocalTime` 或 `LocalDateTime`。
|
||||
3. 处理时区或时间戳时,请使用 `ZonedDateTime` 或 `Instant` 代替。
|
||||
4. 使用 `DateTimeFormatter` 来解析和格式化日期。
|
||||
5. 为避免混淆,应始终明确指定时区。
|
||||
|
||||
这些最佳实践为在 Java 中处理日期和时间奠定了坚实的基础,确保我们可以在应用程序中高效、准确地处理它们。
|
||||
|
||||
## 7、总结
|
||||
|
||||
Java 8 中引入的 `java.time` 包极大地改进了我们处理日期和时间的方式。此外,采用该 API 还能确保代码更简洁、更易于维护。
|
||||
|
||||
对于旧项目中遗留的 `Date` 或 `Calendar`,我们也可以轻松地迁移到新的 `java.time` API。
|
||||
10
java/mybatis-plus.md
Normal file
10
java/mybatis-plus.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
### mybtais-plus
|
||||
|
||||
mybtais-plus 默认空字段 不插入 导致生成的sql 字段不完整,
|
||||
|
||||
在批量插入时, 因为每个po 空值不确定 导致 sql 重写失效,
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
&reWriteBatchedInserts=true
|
||||
403
java/oauth-server.md
Normal file
403
java/oauth-server.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,403 @@
|
||||
# 在 Spring Authorization Server 中动态注册客户端
|
||||
|
||||
2024-08-27
|
||||
|
||||
[教程](https://springdoc.cn/categories/教程/)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1、简介
|
||||
|
||||
[Spring Authorization Server](https://springdoc.cn/spring-authorization-server/)(授权服务器)自带一系列合理的默认设置,开箱即用。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,它还有一个功能,默认下没有启动:**态客户端注册**。本文将带你了解如何在客户端应用中启用和使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
## 2、为什么使用动态注册?
|
||||
|
||||
当基于 OAuth2 的客户端应用(在 OIDC 术语中称为依赖方)启动认证流程时,它将自己的客户端标识符发送给身份提供者(Provider)。
|
||||
|
||||
一般情况下,这个标识符是通过外部流程(如邮件发送等其他手段)发放给客户端的,客户端随后将其添加到配置中,并在需要时使用。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,在使用 Azure 的 EntraID 或 Auth0 等流行的身份提供商(Identity Provider)解决方案时,我们可以使用管理控制台或 API 来配置新客户端。在此过程中,我们需要告知应用名称、授权回调 URL、支持的作用域等信息。
|
||||
|
||||
提供所需信息后,我们会得到一个新的客户端标识符,对于所谓的 “secret” 客户端,还将得到一个 *client secret*。然后,我们将这些信息添加到应用的配置中,就可以开始部署了。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,当我们应用不多,或者总是使用单一的一个身份供应商时(Identity Provider),这种方式就能正常工作。但对于更复杂的情况,注册过程需要是动态的,这就是 [OpenID Connect 动态客户端注册规范](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-registration-1_0.html) 的用武之地。
|
||||
|
||||
在现实世界中,英国的 [OpenBanking](https://www.openbanking.org.uk/) 标准就是一个很好的例子,该标准将动态客户注册作为其核心协议之一。
|
||||
|
||||
## 3、动态注册是如何实现的?
|
||||
|
||||
OpenID Connect 标准使用一个注册 URL,客户端使用该 URL 注册自己。注册是通过 POST 请求完成的,该请求包含一个 JSON 对象,其中有执行注册所需的客户端元数据。
|
||||
|
||||
**重要的是,访问注册端点需要身份认证,通常是一个 \*Bearer Token\*。当然,这就引出了一个问题:想成为客户端的人如何获得用于此操作的 Token?**
|
||||
|
||||
遗憾的是,答案并不明确。一方面,规范指出端点是受保护的资源,因此需要某种形式的身份认证。另一方面,它也提到了开放注册端点的可能性。
|
||||
|
||||
对于 Spring 授权服务器来说,注册需要一个具有 `client.create` scope 的 *Bearer Token*。要创建该令牌,我们需要使用常规 OAuth2 的 Token 端点和基本凭证。
|
||||
|
||||
动态注册的流程如下:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
客户端注册成功后,就可以使用返回的客户端 ID 和 secret *secret* 执行任何标准授权流程。
|
||||
|
||||
## 4、实现动态注册
|
||||
|
||||
了解了所需的步骤后,让我们使用两个 Spring Boot 应用创建一个测试场景。一个托管 Spring 授权服务器,另一个是一个简单的 WebMVC 应用程序,它使用 Spring Security Outh2 Login Starter 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
我们先从服务器开始。
|
||||
|
||||
## 5、授权服务器的实现
|
||||
|
||||
首先添加所需的 Maven 依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-authorization-server</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>1.3.1</version>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
最新版本可从 [Maven Central](https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.security/spring-security-oauth2-authorization-server) 获取。
|
||||
|
||||
对于普通的 *Spring Authorization Server* 来说,只需要这个依赖。
|
||||
|
||||
出于安全考虑,默认情况下不会启用动态注册。此外,截至本文撰写时,还 **无法通过配置属性来启用动态注册**,这意味着我们要通过一些代码来进行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.1、启用动态注册
|
||||
|
||||
`OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer` 是配置授权服务器所有方面的入口,包括注册端点。这个配置应该作为创建 `SecurityFilterChain` Bean 的一部分完成:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Configuration
|
||||
@EnableConfigurationProperties(SecurityConfig.RegistrationProperties.class)
|
||||
public class SecurityConfig {
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
@Order(1)
|
||||
public SecurityFilterChain authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
|
||||
OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration.applyDefaultSecurity(http);
|
||||
http.getConfigurer(OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer.class)
|
||||
.oidc(oidc -> {
|
||||
oidc.clientRegistrationEndpoint(Customizer.withDefaults());
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
http.exceptionHandling((exceptions) -> exceptions
|
||||
.defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor(
|
||||
new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login"),
|
||||
new MediaTypeRequestMatcher(MediaType.TEXT_HTML)
|
||||
)
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
http.oauth2ResourceServer((resourceServer) -> resourceServer
|
||||
.jwt(Customizer.withDefaults()));
|
||||
|
||||
return http.build();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 。。。 其他 Bean
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如上,我们使用 `OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer` 的 `oidc()` 方法来访问 `OidConfigurer` 实例,该方法允许我们控制与 OpenID Connect 标准相关的端点。要启用注册端点,我们使用带有默认配置的 `clientRegistrationEndpoint()` 方法。这将在 `/connect/register` 路径下启用注册端点,并使用 Bearer Token 授权。其他配置选项包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 定义自定义认证
|
||||
- 对收到的注册数据进行自定义处理
|
||||
- 对发送给客户端的响应进行自定义处理
|
||||
|
||||
现在,由于我们提供的是自定义的 `SecurityFilterChain`,Spring Boot 默认的自动配置将不会生效,我们需要负责向配置中添加一些额外的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
尤其需要添加设置表单登录身份认证的逻辑:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
@Order(2)
|
||||
SecurityFilterChain loginFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
|
||||
return http.authorizeHttpRequests(r -> r.anyRequest().authenticated())
|
||||
.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults())
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.2、注册客户端配置
|
||||
|
||||
如上所述,注册机制本身要求客户端发送一个 Bearer Token。Spring 授权服务器要求客户端使用客户端凭证流(Client Credentials Flow)来生成该 Token,从而解决了这个先有鸡还是先有蛋的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
此 Token 请求所需的 scope 是 `client.create`,客户端必须使用服务器支持的认证方案之一。在这里,我们使用 [Basic 凭证](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7617),但在实际场景中,我们也可以使用其他方法。
|
||||
|
||||
从授权服务器的角度来看,这个注册客户端只是另一个客户端。因此,我们使用 `RegisteredClient` Fluent API 来创建它:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
public RegisteredClientRepository registeredClientRepository(RegistrationProperties props) {
|
||||
RegisteredClient registrarClient = RegisteredClient.withId(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
|
||||
.clientId(props.getRegistrarClientId())
|
||||
.clientSecret(props.getRegistrarClientSecret())
|
||||
.clientAuthenticationMethod(ClientAuthenticationMethod.CLIENT_SECRET_BASIC)
|
||||
.authorizationGrantType(AuthorizationGrantType.CLIENT_CREDENTIALS)
|
||||
.clientSettings(ClientSettings.builder()
|
||||
.requireProofKey(false)
|
||||
.requireAuthorizationConsent(false)
|
||||
.build())
|
||||
.scope("client.create")
|
||||
.scope("client.read")
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
|
||||
RegisteredClientRepository delegate = new InMemoryRegisteredClientRepository(registrarClient);
|
||||
return new CustomRegisteredClientRepository(delegate);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用 `@ConfigurationProperties` 类允许使用 Spring 的 `Environment` 来配置 *client ID* 和 *secret* 属性。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.3、自定义 RegisteredClientRepository
|
||||
|
||||
Spring 授权服务器使用配置的 `RegisteredClientRepository` 实现将所有注册客户端存储在服务器中。开箱即用的是基于内存和 JDBC 的实现,涵盖了基本用例。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,这些实现在保存注册信息之前并没有提供任何自定义的能力。在我们的案例中,我们希望修改默认的 `ClientProperties` 设置,这样在授权用户时就不需要 *Consent* 或 [PKCE](https://www.baeldung.com/spring-security-pkce-secret-clients)。
|
||||
|
||||
我们的实现将大多数方法委托给构建时传递的实际 Repository。重要的例外是 `save()` 方法:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Override
|
||||
public void save(RegisteredClient registeredClient) {
|
||||
Set<String> scopes = ( registeredClient.getScopes() == null || registeredClient.getScopes().isEmpty())?
|
||||
Set.of("openid","email","profile"):
|
||||
registeredClient.getScopes();
|
||||
|
||||
// 禁用 PKCE 和 Consent
|
||||
RegisteredClient modifiedClient = RegisteredClient.from(registeredClient)
|
||||
.scopes(s -> s.addAll(scopes))
|
||||
.clientSettings(ClientSettings
|
||||
.withSettings(registeredClient.getClientSettings().getSettings())
|
||||
.requireAuthorizationConsent(false)
|
||||
.requireProofKey(false)
|
||||
.build())
|
||||
.build();
|
||||
|
||||
delegate.save(modifiedClient);
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如上,我们根据接收到的 `RegisteredClient` 创建一个新的 `RegisteredClient`,并根据需要更改客户端设置。然后,新注册的客户端将被传递到后台,并在需要时存储起来。
|
||||
|
||||
至此,服务器的实现就结束了。现在,开始客户端部分。
|
||||
|
||||
## 6、动态注册客户端的实现
|
||||
|
||||
我们的客户端也是一个标准的 Spring Web MVC 应用,只有一个页面显示当前用户信息。
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Security,或者更具体地说,其 *OAuth2* Login 模块,将处理所有安全方面的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
从所需的 Maven 依赖开始:
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>3.3.2</version>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>3.3.2</version>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>3.3.2</version>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这些依赖的最新版本可从 Maven Central 获取:
|
||||
|
||||
- *[spring-boot-starter-web](https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-web)*
|
||||
- *[spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf](https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf)*
|
||||
- *[spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client](https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client)*
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.1、Security 配置
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Spring Boot 的自动配置机制使用来自可用 `PropertySources` 的信息来收集所需数据,以创建一个或多个 `ClientRegistration` 实例,然后将其存储在基于内存的 `ClientRegistrationRepository` 中。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,给定的 `application.yaml` 如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
spring:
|
||||
security:
|
||||
oauth2:
|
||||
client:
|
||||
provider:
|
||||
spring-auth-server:
|
||||
issuer-uri: http://localhost:8080
|
||||
registration:
|
||||
test-client:
|
||||
provider: spring-auth-server
|
||||
client-name: test-client
|
||||
client-id: xxxxx
|
||||
client-secret: yyyy
|
||||
authorization-grant-type:
|
||||
- authorization_code
|
||||
- refresh_token
|
||||
- client_credentials
|
||||
scope:
|
||||
- openid
|
||||
- email
|
||||
- profile
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Spring 将创建名为 `test-client` 的 `ClientRegistration` 并将其传递给 Repository。
|
||||
|
||||
之后,当需要启动身份认证流程时,OAuth2 引擎就会查询该 Repository,并根据其注册标识符(在我们的例子中为 `test-client`)恢复注册信息。
|
||||
|
||||
这里的关键点是,授权服务器应该已经知道此时返回的 `ClientRegistration`。这意味着,为了支持动态客户端,我们必须实现一个替代 Repository,并将其作为 `@Bean` 暴露。
|
||||
|
||||
这样,Spring Boot 的自动配置就会自动使用它,而不是默认配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.2、动态 ClientRegistration Repository
|
||||
|
||||
我们必须实现 `ClientRegistration` 接口,而该接口只包含一个方法:`findByRegistrationId()`。这就有一个问题: OAuth2 引擎如何知道哪些注册信息是可用的?毕竟,它可以在默认登录页面上列出这些注册信息。
|
||||
|
||||
事实证明,Spring Security 也希望 Repository 也能实现 `Iterable<ClientRegistration>`,这样它就能枚举可用的客户端:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class DynamicClientRegistrationRepository implements ClientRegistrationRepository, Iterable<ClientRegistration> {
|
||||
private final RegistrationDetails registrationDetails;
|
||||
private final Map<String, ClientRegistration> staticClients;
|
||||
private final RegistrationRestTemplate registrationClient;
|
||||
private final Map<String, ClientRegistration> registrations = new HashMap<>();
|
||||
|
||||
// 实现省略。。。
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该类需要一些关键属性才可以运行:
|
||||
|
||||
- 一个 `RegistrationDetails`,其中包含执行动态注册所需的所有参数
|
||||
- 存储动态注册的 `ClientRegistration` 的 `Map`。
|
||||
- 用于访问授权服务器的 `RestTemplate`。
|
||||
|
||||
注意,在本例中,我们假设所有客户端都在同一授权服务器上进行注册。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个重要的设计决策是定义何时进行动态注册。这里,我们采取一种简单的方法,公开 `doRegistrations()` 方法,该方法将注册所有已知客户端,并保存返回的客户端标识符和 *secret*,以供以后使用:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public void doRegistrations() {
|
||||
staticClients.forEach((key, value) -> findByRegistrationId(key));
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
对于传递给构造函数的每个 *staticClients*,实现过程都会调用 `findByRegistrationId()`。该方法会检查给定标识符是否存在有效注册,如果没有,则会触发实际注册流程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.3、动态注册
|
||||
|
||||
`doRegistration()` 函数才是真正发挥作用的地方:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
private ClientRegistration doRegistration(String registrationId) {
|
||||
String token = createRegistrationToken();
|
||||
var staticRegistration = staticClients.get(registrationId);
|
||||
|
||||
var body = Map.of(
|
||||
"client_name", staticRegistration.getClientName(),
|
||||
"grant_types", List.of(staticRegistration.getAuthorizationGrantType()),
|
||||
"scope", String.join(" ", staticRegistration.getScopes()),
|
||||
"redirect_uris", List.of(resolveCallbackUri(staticRegistration)));
|
||||
|
||||
var headers = new HttpHeaders();
|
||||
headers.setBearerAuth(token);
|
||||
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
|
||||
|
||||
var request = new RequestEntity<>(
|
||||
body,
|
||||
headers,
|
||||
HttpMethod.POST,
|
||||
registrationDetails.registrationEndpoint());
|
||||
|
||||
var response = registrationClient.exchange(request, ObjectNode.class);
|
||||
// ... 省略异常处理
|
||||
return createClientRegistration(staticRegistration, response.getBody());
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们必须获取调用注册端点所需的注册 Token。注意,我们必须为每次注册尝试获取一个新 Token,因为正如 Spring Authorization 的服务器文档所述,我们只能使用该 Token 一次。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,使用静态注册对象中的数据构建注册 Payload,添加所需的 `authorization` 和 `content-type` Header,然后将请求发送到注册端点。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,使用响应数据创建最终的 `ClientRegistration`,并将其保存在 Repository 的缓存中,然后返回给 *OAuth2* 引擎。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.4、注册 ClientRegistrationRepository @Bean
|
||||
|
||||
完成客户端的最后一步是将 `DynamicClientRegistrationRepository` 作为 `@Bean` 公开。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个 `@Configuration` 类:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
ClientRegistrationRepository dynamicClientRegistrationRepository( DynamicClientRegistrationRepository.RegistrationRestTemplate restTemplate) {
|
||||
var registrationDetails = new DynamicClientRegistrationRepository.RegistrationDetails(
|
||||
registrationProperties.getRegistrationEndpoint(),
|
||||
registrationProperties.getRegistrationUsername(),
|
||||
registrationProperties.getRegistrationPassword(),
|
||||
registrationProperties.getRegistrationScopes(),
|
||||
registrationProperties.getGrantTypes(),
|
||||
registrationProperties.getRedirectUris(),
|
||||
registrationProperties.getTokenEndpoint());
|
||||
|
||||
Map<String,ClientRegistration> staticClients = (new OAuth2ClientPropertiesMapper(clientProperties)).asClientRegistrations();
|
||||
var repo = new DynamicClientRegistrationRepository(registrationDetails, staticClients, restTemplate);
|
||||
repo.doRegistrations();
|
||||
return repo;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`@Bean` 注解的 `dynamicClientRegistrationRepository()` 方法首先会根据可用属性填充 `RegistrationDetails` 记录,从而创建 Repository。
|
||||
|
||||
其次,它利用 Spring Boot 自动配置模块中的 `OAuth2ClientPropertiesMapper` 类创建 *staticClient* map。由于两者的配置结构相同,因此这种方法能让我们以最小的工作量快速从静态客户端(*staticClients*)切换到动态客户端,然后再切换回来。
|
||||
|
||||
## 7、测试
|
||||
|
||||
最后,进行一些集成测试。首先,启动服务器应用,将其配置为监听 *8080* 端口:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
[ server ] $ mvn spring-boot:run
|
||||
... lots of messages omitted
|
||||
[ main] c.b.s.s.a.AuthorizationServerApplication : Started AuthorizationServerApplication in 2.222 seconds (process running for 2.454)
|
||||
[ main] o.s.b.a.ApplicationAvailabilityBean : Application availability state LivenessState changed to CORRECT
|
||||
[ main] o.s.b.a.ApplicationAvailabilityBean : Application availability state ReadinessState changed to ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,在另一个 shell 中启动客户端:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
[client] $ mvn spring-boot:run
|
||||
// ... 省略其他消息
|
||||
[ restartedMain] o.s.b.d.a.OptionalLiveReloadServer : LiveReload server is running on port 35729
|
||||
[ restartedMain] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8090 (http) with context path ''
|
||||
[ restartedMain] d.c.DynamicRegistrationClientApplication : Started DynamicRegistrationClientApplication in 2.063 seconds (process running for 2.425)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这两个应用在运行时都设置了 *debug* 属性,因此会产生大量日志信息。重点是,我们可以看到对授权服务器 `/connect/register` 端点的调用:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
[nio-8080-exec-3] o.s.security.web.FilterChainProxy : Securing POST /connect/register
|
||||
// ... lots of messages omitted
|
||||
[nio-8080-exec-3] ClientRegistrationAuthenticationProvider : Retrieved authorization with initial access token
|
||||
[nio-8080-exec-3] ClientRegistrationAuthenticationProvider : Validated client registration request parameters
|
||||
[nio-8080-exec-3] s.s.a.r.CustomRegisteredClientRepository : Saving registered client: id=30OTlhO1Fb7UF110YdXULEDbFva4Uc8hPBGMfi60Wik, name=test-client
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在客户端,我们可以看到一条包含注册标识符(*test-client*)和相应 `client_id` 的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
[ restartedMain] s.d.c.c.OAuth2DynamicClientConfiguration : Creating a dynamic client registration repository
|
||||
[ restartedMain] .c.s.DynamicClientRegistrationRepository : findByRegistrationId: test-client
|
||||
[ restartedMain] .c.s.DynamicClientRegistrationRepository : doRegistration: registrationId=test-client
|
||||
[ restartedMain] .c.s.DynamicClientRegistrationRepository : creating ClientRegistration: registrationId=test-client, client_id=30OTlhO1Fb7UF110YdXULEDbFva4Uc8hPBGMfi60Wik
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们打开浏览器并访问 *`http://localhost:8090`*,就会被重定向到登录页面。注意,地址栏中的 URL 变成了 *`http://localhost:8080`*,这表明该页面来自授权服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
测试凭证为 `user1/password`。将其填入表单并发送后,就会返回客户端主页。由于我们现在已通过身份认证,我们可以看到一个页面,其中包含从 Authorization Token 中提取的一些详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
## 8、总结
|
||||
|
||||
本文介绍了如何启用 *Spring Authorization Server* 的动态注册功能,并在基于 Spring Security 的客户端应用中使用该功能。
|
||||
97
java/spring-security.md
Normal file
97
java/spring-security.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
在Spring Security中,`SecurityFilterChain`和`WebSecurityCustomizer`分别用于不同的配置场景,以下是它们的核心区别和使用场景:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. **SecurityFilterChain**
|
||||
|
||||
- **作用**:配置`HttpSecurity`,定义请求级别的安全规则(如URL访问控制、认证机制、CSRF、CORS等)。
|
||||
|
||||
- **适用场景**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 需要为特定URL路径设置访问权限(如`permitAll()`、`authenticated()`)。
|
||||
- 配置登录/注销行为、表单登录、OAuth2、JWT等认证机制。
|
||||
- 启用或禁用安全特性(如CSRF保护、Session管理)。
|
||||
|
||||
- **特点**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 请求会经过完整的Spring Security过滤器链。
|
||||
- 即使路径设置为`permitAll()`,请求仍会被安全过滤器处理(如记录日志、CSRF验证等)。
|
||||
|
||||
- **示例**:
|
||||
|
||||
java
|
||||
|
||||
复制
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
|
||||
http
|
||||
.authorizeRequests()
|
||||
.antMatchers("/public/**").permitAll() // 允许匿名访问
|
||||
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 其他请求需认证
|
||||
.and()
|
||||
.formLogin() // 启用表单登录
|
||||
.loginPage("/login")
|
||||
.permitAll();
|
||||
return http.build();
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. **WebSecurityCustomizer**
|
||||
|
||||
- **作用**:配置`WebSecurity`,**全局忽略**某些路径,使其完全绕过Spring Security过滤器链。
|
||||
|
||||
- **适用场景**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 忽略静态资源(如CSS、JS、图片)或公开API路径。
|
||||
- 提升性能,避免不必要的安全处理。
|
||||
|
||||
- **特点**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 被忽略的路径不会经过任何安全过滤器。
|
||||
- 无法在此处配置细粒度的安全规则(如角色权限、认证方式)。
|
||||
|
||||
- **示例**:
|
||||
|
||||
java
|
||||
|
||||
复制
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
public WebSecurityCustomizer webSecurityCustomizer() {
|
||||
return (web) -> web.ignoring()
|
||||
.antMatchers("/static/**", "/resources/**"); // 完全绕过安全过滤器
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
### **关键区别**
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | SecurityFilterChain | WebSecurityCustomizer |
|
||||
| :--------------- | :------------------------------------ | :----------------------------------- |
|
||||
| **配置对象** | `HttpSecurity`(请求级安全) | `WebSecurity`(全局Web安全) |
|
||||
| **请求处理** | 经过安全过滤器链 | 完全绕过安全过滤器链 |
|
||||
| **适用场景** | 细粒度权限控制、认证机制配置 | 忽略静态资源或无安全需求的路径 |
|
||||
| **性能影响** | 请求会经过过滤器链(可能有开销) | 无开销,直接跳过安全处理 |
|
||||
| **配置方法示例** | `.antMatchers("/api/**").permitAll()` | `.ignoring().antMatchers("/css/**")` |
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
### **何时选择?**
|
||||
|
||||
- **使用 `SecurityFilterChain`**:
|
||||
- 需要对路径应用安全规则(如允许匿名访问但仍需CSRF保护)。
|
||||
- 需要配置登录页、OAuth2、权限验证等复杂逻辑。
|
||||
- **使用 `WebSecurityCustomizer`**:
|
||||
- 静态资源(如`/css/**`, `/js/**`)完全无需安全处理。
|
||||
- 公开API(如健康检查`/actuator/health`)无需任何安全机制。
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
### **最佳实践**
|
||||
|
||||
- **优先用 `SecurityFilterChain`**:除非明确需要完全绕过安全,否则用`permitAll()`替代`ignoring()`,以确保安全特性(如CSRF)仍生效。
|
||||
- **谨慎使用 `ignoring()`**:被忽略的路径可能暴露敏感信息或成为安全漏洞。
|
||||
94
java/spring.md
Normal file
94
java/spring.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
# 通过 Spring 5 中 Supplier 来获取 Bean
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Spring5 中开始提供了 `Supplier`,可以通过接口回调获取到一个 Bean 的实例,这种方式显然性能更好一些。
|
||||
|
||||
如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
|
||||
GenericBeanDefinition definition = new GenericBeanDefinition();
|
||||
definition.setBeanClass(Book.class);
|
||||
definition.setInstanceSupplier((Supplier<Book>) () -> {
|
||||
Book book = new Book();
|
||||
book.setName("深入浅出 Spring Security");
|
||||
book.setAuthor("江南一点雨");
|
||||
return book;
|
||||
});
|
||||
ctx.registerBeanDefinition("b1", definition);
|
||||
ctx.refresh();
|
||||
Book b = ctx.getBean("b1", Book.class);
|
||||
System.out.println("b = " + b);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
关键就是通过调用 `BeanDefinition` 的 `setInstanceSupplier` 方法去设置回调。当然,上面这段代码还可以通过 *Lambda* 进一步简化:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class BookSupplier {
|
||||
public Book getBook() {
|
||||
Book book = new Book();
|
||||
book.setName("深入浅出 Spring Security");
|
||||
book.setAuthor("江南一点雨");
|
||||
return book;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后调用这个方法即可:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
|
||||
GenericBeanDefinition definition = new GenericBeanDefinition();
|
||||
definition.setBeanClass(Book.class);
|
||||
BookSupplier bookSupplier = new BookSupplier();
|
||||
definition.setInstanceSupplier(bookSupplier::getBook);
|
||||
ctx.registerBeanDefinition("b1", definition);
|
||||
ctx.refresh();
|
||||
Book b = ctx.getBean("b1", Book.class);
|
||||
System.out.println("b = " + b);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这是不是更有一点 *Lambda* 的感觉了?
|
||||
|
||||
在 Spring 源码中,处理获取 Bean 实例的时候,有如下一个分支,就是处理 `Supplier` 这种情况的:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance
|
||||
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
|
||||
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
|
||||
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
|
||||
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
|
||||
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
|
||||
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
|
||||
}
|
||||
Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier();
|
||||
if (instanceSupplier != null) {
|
||||
return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
|
||||
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
//...
|
||||
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@Nullable
|
||||
private Object obtainInstanceFromSupplier(Supplier<?> supplier, String beanName) {
|
||||
String outerBean = this.currentlyCreatedBean.get();
|
||||
this.currentlyCreatedBean.set(beanName);
|
||||
try {
|
||||
if (supplier instanceof InstanceSupplier<?> instanceSupplier) {
|
||||
return instanceSupplier.get(RegisteredBean.of((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this, beanName));
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (supplier instanceof ThrowingSupplier<?> throwableSupplier) {
|
||||
return throwableSupplier.getWithException();
|
||||
}
|
||||
return supplier.get();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面 `obtainFromSupplier` 这个方法,最终会调用到第二个方法。第二个方法中的 `supplier.get();` 其实最终就调用到我们自己写的 `getBook` 方法了。
|
||||
|
||||
如上,这是从 Spring5 开始结合 Lamdba 的一种 Bean 注入方式。
|
||||
113
java/springboot-事件.md
Normal file
113
java/springboot-事件.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
## springboot事件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 事务本身
|
||||
|
||||
实现 ApplicationEvent 类
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Getter
|
||||
public static class SchSyncToUpcomingEndEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
|
||||
public SchSyncToUpcomingEndEvent(Object source) {
|
||||
super(source);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 事务发布
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent()
|
||||
applicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 注解接收事件
|
||||
|
||||
默认同步处理 需要异步处理 添加@Async 注解
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* 监听 SCH 同步至航班计划完成事件。
|
||||
* 开始 航班计划同步至算法
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @param event
|
||||
*/
|
||||
@Async
|
||||
@EventListener(FlightPlanEvent.SchSyncToUpcomingEndEvent.class)
|
||||
public void syncCurrentStatusToAlgListener(FlightPlanEvent.SchSyncToUpcomingEndEvent event) {
|
||||
XxlJobHelper.log("同步当前航班状态至算法 开始");
|
||||
XxlJobHelper.log("同步当前航班状态至算法 结束");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 编程式接收事务
|
||||
|
||||
监听器
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@Component
|
||||
@Slf4j
|
||||
public class EventListener implements ApplicationListener<CustomEvent>{
|
||||
|
||||
@Override
|
||||
public void onApplicationEvent(CustomEvent event) {
|
||||
//这里也可以监听所有事件 使用 ApplicationEvent 类即可
|
||||
//这里仅仅监听自定义事件 CustomEvent
|
||||
log.info("ApplicationListener方式监听事件:{}", event);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
注册监听器
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@SpringBootApplication
|
||||
public class Application {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args){
|
||||
SpringApplication app =new SpringApplication(Application.class);
|
||||
app.addListeners(new MyApplicationStartingEventListener());//加入自定义的监听类
|
||||
app.run(args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 事务事件
|
||||
|
||||
需要等 事务发布者的事务完成提交 才能接收到事件
|
||||
|
||||
事务事件 只能接收一次
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@Async
|
||||
@TransactionalEventListener(value = FlightPlanEvent.SchSyncToUpcomingEndEvent.class, phase = TransactionPhase.AFTER_COMMIT)
|
||||
public void syncBaseDataUpdateListener(FlightPlanEvent.SchSyncToUpcomingEndEvent event) {
|
||||
syncBaseData();
|
||||
syncSchRouteToRedis();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
764
java/在 Java 中优雅地操纵时间.md
Normal file
764
java/在 Java 中优雅地操纵时间.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,764 @@
|
||||
# 在 Java 中优雅地操纵时间
|
||||
|
||||
2024-11-11
|
||||
|
||||
[教程](https://springdoc.cn/categories/教程/)
|
||||
|
||||
在开发时候,发现有很多需要用到时间的地方,例如记录操作的时间、比较时间判断产品是否有效等。总而言之,时间是我们业务开发必须关注、时刻注意的点。但目前工程的代码中使用了非常多时间的工具类,一会儿用 `java.util.Date` 记录时间,一会用 `java.time.LocalDateTime` 记录时间,怎么才能在 Java 中优雅的操纵时间呢,我整理了相关的概念和工具类,希望帮助大家在代码开发的过程中对对时间的使用更加优雅。
|
||||
|
||||
这里先写一个结论:
|
||||
|
||||
- 建议使用 java8 的时间 API,在安全性和易用性上都远高于 `java.util.Date`。
|
||||
- 目前比较流行的封装 java API 的时间工具类大都基于 `java.util.Date`,建议在开发过程中根据业务需要基于 `java.time.*` 的方法封装工具类(文末给出了一个简单的实现)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 时间在计算机中的存储和展示
|
||||
|
||||
时间以整数的方式进行存储:时间在计算机中存储的本质是一个整数,称为 Epoch Time(时间戳),计算从 1970 年 1 月 1 日零点(格林威治时间/GMT+00:00)到现在所经历的秒数。
|
||||
|
||||
在 java 程序中,时间戳通常使用 `long` 表示毫秒数,通过 `System.currentTimeMillis()` 可以获取时间戳。时间戳对我们人来说是不易理解的,因此需要将其转换为易读的时间,例如,*2024-10-7 20:21:59*(实际上说的是本地时间),而同一时刻不同时区的人看到的本地时间是不一样,所以在时间展示的时候需要加上时区的信息,才能精准的找到对应的时刻。
|
||||
|
||||
时区与世界时间标准相关:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
世界时间的标准在 1972 年发生了变化,但我们在开发程序的时候可以忽略 **GMT** 和 **UTC** 的差异, 因为计算机的时钟在联网的时候会自动与时间服务器同步时间。 本地时间等于我们所在(或者所使用)时区内的当地时间,它由与世界标准时间(UTC)之间的偏移量来定义。这个偏移量可以表示为 *UTC-* 或 *UTC+*,后面接上偏移的小时和分钟数。 例如:*GMT+08:00* 或者 *UTC+08:00* 表示东八区,*2024-10-7 20:21:59 UTC+08:00* 便可以精准的定位一个时刻。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 时间容器
|
||||
|
||||
- `LocalDate`:代表日期,不包含时间或时区。
|
||||
- `LocalTime`:代表时间,不包含日期或时区。
|
||||
- `LocalDateTime`:包括了日期和时间,但不包括时区。
|
||||
- `ZonedDateTime`:包括了日期和时间以及时区。
|
||||
- `Instant`:代表时间轴上的一个特定点,类似于时间戳。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 时间操作
|
||||
|
||||
- `Duration`:表示基于时间的时间量(例如 “5 小时” 或 “30 秒”)。
|
||||
- `Period`:代表基于日期的时间量(如 “2 年 3 个月”)。
|
||||
- `TemporalAdjusters`:提供调整日期的方法(如查找下一个星期一)。
|
||||
- `Clock`:使用时区提供当前日期时间,并可进行时间控制。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 格式化和输出
|
||||
|
||||
- `DateTimeFormatter`:用于格式化和解析日期时间对象。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 日期 API
|
||||
|
||||
JDK 以版本 8 为界,有两套处理日期/时间的 API。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
简单的比较如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | java.util.Date | java.util.Date.Calendar | java.time.LocalDateTime |
|
||||
| -------- | --------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------- | -------------------------- |
|
||||
| 线程安全 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| 时间运算 | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| 可读性 | Tue Oct 08 00:11:16 CST 2024 易读性较低 | ❌不易读 | ✅ yyyy-MM-dd’T’HH:mm:ss |
|
||||
| 常量设计 | 需要对获取的年份(+1900)月份(0-11)进行处理 | 需要对获月份(0-11)进行处理 | ✅ 不需要额外处理,符合常识 |
|
||||
| 时间精度 | 精确到毫秒 | 精确到毫秒 | 精确到纳秒 |
|
||||
| 时区 | 具体的时间调用 | 不 | - |
|
||||
|
||||
| 特性 | java.text.SimpleDateFormat | java.time.DateTimeFormatter |
|
||||
| -------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| 线程安全 | ❌ 在多线程环境下每个线程独立维护一份 SimpleDateFormat 对象实例,或者将 `SimpleDateFormat` 放到 `ThreadLocal` 中 | ✅ 不变对象,线程安全,可以使用单例存储 |
|
||||
| 使用场景 | `Date` | `LocalDateTime` |
|
||||
|
||||
### java.util
|
||||
|
||||
在 jdk8 之前,Java 使用 `java.util` 中的 API 对处理时间。 在获取年月日的时候,`Date` 和 `Calendar` 需要进行不同的转换 => 规则不统一。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Date
|
||||
|
||||
`java.util.Date` 用于表示一个日期和时间的对象,其实现很简单,实际上存储了一个 `long` 类型的以毫秒表示的时间戳,在通过 `new Date()` 获取当前时间的时候,实际上是通过 `System.currentTimeMillis()` 获取时间戳进行赋值。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class Date {
|
||||
long fastTime;
|
||||
|
||||
public Date(long date) {
|
||||
fastTime = date;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public long getTime() {
|
||||
return fastTime;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`java.util.Date` 承载的功能有限,且在利用 `Date` 类获取具体年/月/日的时候需要注意:`getYear()` 返回的年份必须加上 `1900`,`getMonth()` 返回的月份是 *0-11* 分别表示 *1-12* 月,所以要加 *1*,而 `getDate()` 返回的日期范围是 *1~31*,又不能加 *1*。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Calendar
|
||||
|
||||
`Calendar` 可以用于获取并设置年、月、日、时、分、秒,它和 `Date` 比,主要多了一个可以做简单的日期和时间运算的功能,但代码粗糙,API 不好用,性能也不好。
|
||||
|
||||
`Calendar` 对象 `getTime()` 可以获得 `Date` 对象:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
// 获取当前时间:
|
||||
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
|
||||
int y = c.get(Calendar.YEAR);//返回年份不用转换
|
||||
int m = 1 + c.get(Calendar.MONTH);//返回月份需要加1
|
||||
int d = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
|
||||
int w = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);//返回的
|
||||
int hh = c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
|
||||
int mm = c.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
|
||||
int ss = c.get(Calendar.SECOND);
|
||||
int ms = c.get(Calendar.MILLISECOND);
|
||||
System.out.println(y + "-" + m + "-" + d + " " + w + " " + hh + ":" + mm + ":" + ss + "." + ms);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
import java.text.*;
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
// 当前时间:
|
||||
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
|
||||
// 清除所有:
|
||||
c.clear();
|
||||
// 设置年月日时分秒:
|
||||
c.set(2019, 10 /* 11月 */, 20, 8, 15, 0);
|
||||
// 加5天并减去2小时:
|
||||
c.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 5);
|
||||
c.add(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, -2);
|
||||
// 显示时间:
|
||||
var sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
|
||||
Date d = c.getTime();
|
||||
System.out.println(sdf.format(d));
|
||||
// 2019-11-25 6:15:00
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### TimeZone
|
||||
|
||||
`Calendar` 和 `Date` 相比,它提供了时区转换的功能。时区用 `TimeZone` 对象表示。
|
||||
|
||||
时区的唯一标识是以字符串表示的 *ID*。获取指定 `TimeZone` 对象也是以这个 *ID* 为参数获取,*GMT+09:00*、*Asia/Shanghai* 都是有效的时区 *ID*。可以通过 `TimeZone.getAvailableIDs()` 获取系统支持的所有 *ID*。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.text.*;
|
||||
import java.util.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class learnTime {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
// 当前时间:
|
||||
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
|
||||
// 清除所有字段:
|
||||
c.clear();
|
||||
// 设置为北京时区:
|
||||
c.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("Asia/Shanghai"));
|
||||
// 设置年月日时分秒:
|
||||
c.set(2024, 9 /* 10月 */, 10, 8, 15, 0);
|
||||
// 显示时间:
|
||||
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
|
||||
sdf.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("America/New_York"));
|
||||
System.out.println(sdf.format(c.getTime()));
|
||||
// 2024-10-09 20:15:00
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### java.text.SimpleDateFormat
|
||||
|
||||
`Date` 使用 `SimpleDateFormat` 解析和格式化时间:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
// SimpleDateFormat线程不安全,每次使用都要构造新的,在初始的时候定义解析的字符串格式
|
||||
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
|
||||
|
||||
// 将指定字符串String解析为Date
|
||||
Date date = format.parse("2024-10-07 16:10:22");
|
||||
|
||||
// 将Date格式化为String
|
||||
String str = format.format(date);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
由于 `SimpleDateFormat` 线程不安全,为了提升性能,可以使用 `ThreadLocalCache`。
|
||||
|
||||
如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
static final ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT_LOCAL
|
||||
= ThreadLocal.withInitial(
|
||||
() -> new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
|
||||
);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Java.time.*
|
||||
|
||||
> 开源社区开发了一个日期库 [Joda](https://www.joda.org/joda-time/),API 清晰,性能较好,提交了 *JSR-310*,在 java8 中称为 JDK 基础类库。
|
||||
|
||||
- 本地日期和时间:`LocalDateTime`(日期和时间),`LocalDate`(日期),`LocalTime`(时间)(因为没有时区,所以无法与时间戳转换);
|
||||
- 带时区的日期和时间:`ZonedDateTime`;
|
||||
- 时刻:`Instant`;
|
||||
- 时区:`ZoneId`,`ZoneOffset`;
|
||||
- 时间间隔:`Duration`。
|
||||
|
||||
以及一套新的用于取代 `SimpleDateFormat` 的格式化类型 `DateTimeFormatter`。
|
||||
|
||||
#### LocalDate/LocalTime/LocalDateTime
|
||||
|
||||
- 默认严格按照 *ISO 8601* 规定日期和时间格式进行打印(日期和时间的分隔符是 `T`)。
|
||||
|
||||
- 日期:`yyyy-MM-dd`; 时间 `HH:mm:ss`;
|
||||
- 日期和时间:`yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss`;
|
||||
|
||||
- 可以解析简单格式获取类型:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
LocalDateTime localDayTime=LocalDateTime.of(2024, 10, 07, 8, 15, 0);
|
||||
LocalDate localDay=LocalDate.of(2024, 10, 07);
|
||||
LocalTime localTime=LocalTime.parse("08:15:07");
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 有对日期和时间进行加减的非常简单的链式调用,通过 `plusXxx()`/`minusXxx()` 对时间进行变换:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class learnTime {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.of(2024, 10, 10, 20, 30, 59);
|
||||
System.out.println(dt);
|
||||
// 加5天减3小时:2024-10-10T20:30:59
|
||||
LocalDateTime dt2 = dt.plusDays(5).minusHours(3);
|
||||
System.out.println(dt2); // 2024-10-15T17:30:59
|
||||
// 减1月:
|
||||
LocalDateTime dt3 = dt2.minusMonths(1); //2024-09-15T17:30:59
|
||||
System.out.println(dt3); // 2019-09-30T17:30:59
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 对日期和时间进行调整使用 `withXxx()`,例如将月份调整为 9月: `dataLocalTime.withMonth(9)`;
|
||||
|
||||
- 复杂的操作:获取特殊时间
|
||||
|
||||
- `with` 和 `TemporalAdjusters` 配合使用找到特殊时间(当月的第一天)。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取本月第一天0:00时刻:
|
||||
System.out.println("当月第一天0:00时刻"+now.withDayOfMonth(1).atStartOfDay());
|
||||
//获取当月第一天
|
||||
System.out.println("当月第一天:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfMonth()));
|
||||
//获取下月第一天
|
||||
System.out.println("下月第一天:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfNextMonth()));
|
||||
//获取明年第一天
|
||||
System.out.println("明年第一天:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfNextYear()));
|
||||
//获取本年第一天
|
||||
System.out.println("本年第一天:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfYear()));
|
||||
//获取当月最后一天
|
||||
System.out.println("当月最后一天:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfMonth()));
|
||||
//获取本年最后一天
|
||||
System.out.println("本年最后一天:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfYear()));
|
||||
//获取当月第三周星期五
|
||||
System.out.println("当月第三周星期五:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.dayOfWeekInMonth(3, DayOfWeek.FRIDAY)));
|
||||
//获取上周一
|
||||
System.out.println("上周一:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.previous(DayOfWeek.MONDAY)));
|
||||
//获取下周日
|
||||
System.out.println("下周日:"+now.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY)));
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 比较可以使用 `isBefore()` 和 `isAfter()`。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Duration 和 Period
|
||||
|
||||
- Duration: 基于时间值(
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Instant
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
/
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
LocalDateTime
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
),表示两个时刻时间的时间间隔,适合处理较短的时间,需要更高的精确性。
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用 `between()` 方法比较两个瞬间的差;
|
||||
- 使用 `getSeconds()` 或 `getNanosecends()` 方法获取时间单元的值;
|
||||
- 获得具体的粒度的间隔:`ofDays()`、`ofHours()`、`ofMillis()`、`ofMinutes()`、`ofNanos()`、`ofSeconds()`;
|
||||
- 通过文本创建 `Duration` 对象,格式为 “PnDTnHnMn.nS”,`Duration.parse("P1DT1H10M10.5S")`;
|
||||
- 使用 `toDays()`、`toHours()`、`toMillis()`、`toMinutes()` 方法把 `Duration` 对象可以转成其他时间单元;
|
||||
- 通过 `plusX()`、`minusX()` 方法增加或减少 `Duration` 对象,其中 X 表示 *days*, *hours*, *millis*, *minutes*, *nanos* 或 *seconds*。
|
||||
|
||||
- ```
|
||||
Period
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
基于日期值,表示一段时间的年、月、日:
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用 `between()` 方法比较两个日期的差;
|
||||
- 使用 `getYears()`、`getMonhs()`、`getDays()` 方法获取具体粒度差距(返回的类型是 `int`);
|
||||
- 通过文本创建 `Period` 对象,格式为 “PnYnMnD”:`Period.parse("P2Y3M5D")`;
|
||||
- 可以通过 `plusX()`、`minusX()` 方法进行增加或减少,其中 `X` 表示日期单元;
|
||||
|
||||
#### ZonedDateTime
|
||||
|
||||
`ZonedDateTime` 是 `LocalDateTime` 加 `ZoneId`。
|
||||
|
||||
- `ZonedDateTime` 带时区时间的常见方法:
|
||||
|
||||
- `now()`:获取当前时区的ZonedDateTime对象。
|
||||
- `now(ZoneId zone)`:获取指定时区的 `ZonedDateTime` 对象。
|
||||
- `getYear`、`getMonthValue`、`getDayOfMonth` 等:获取年月日、时分秒、纳秒等。
|
||||
- `withXxx(时间)`:修改时间系列的方法。
|
||||
- `minusXxx(时间)`:减少时间系列的方法。
|
||||
- `plusXxx(时间)`:增加时间系列的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
- 时区转换
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.time.*;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
// 以中国时区获取当前时间:
|
||||
ZonedDateTime zbj = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
|
||||
// 转换为纽约时间:
|
||||
ZonedDateTime zny = zbj.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.of("America/New_York"));
|
||||
System.out.println(zbj);
|
||||
System.out.println(zny);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### ZoneId
|
||||
|
||||
时区类,功能和 `java.util.TimeZone` 类似。
|
||||
|
||||
`ZoneId` 支持两种类型格式初始化,一种是时区偏移的格式(基于 UTC/Greenwich 时),一种是地域时区的格式(eg:*Europe/Paris*)。`ZoneId` 是抽象类,具体的逻辑实现由来子类完成,`ZoneOffset` 处理时区偏移类型的格式,`ZoneRegion` 处理基于地域时区的格式:
|
||||
|
||||
- `getAvailableZoneIds()`:获取Java中支持的所有时区。
|
||||
- `systemDefault()`:获取系统默认时区。
|
||||
- `of(String zoneId)`:获取一个指定时区。
|
||||
|
||||
| 格式 | 描述 | 示例 |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ----------------------------- |
|
||||
| Z, GMT, UTC, UT | 格林尼治标准时间,和中国相差8个小时 | `ZoneId.of("Z");` |
|
||||
| +h +hh +hh:mm -hh:mm +hhmm -hhmm +hh:mm:ss -hh:mm:ss +hhmmss -hhmmss | 表示从格林尼治标准时间偏移时间,中国用+8表示 | `ZoneId.of("+8");` |
|
||||
| 前缀:UTC+, UTC-, GMT+, GMT-, UT+ UT-, 后缀:-h +hh +hh:mm -hh:mm… | 表示从格林尼治标准时间偏移时间 | `ZoneId.of("UTC+8");` |
|
||||
| Asia/Aden, America/Cuiaba, Etc/GMT+9, Etc/GMT+8, Africa/Nairobi, America/Marigot… | 地区表示法,这些ID必须包含在getAvailableZoneIds集合中,否则会抛出异常 | `ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai");` |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Instant
|
||||
|
||||
> 时间线上的某个时刻/时间戳
|
||||
|
||||
通过获取 `Instant` 的对象可以拿到此刻的时间,该时间由两部分组成:从 *1970-01-01 00:00:00* 开始走到此刻的总秒数+不够 1 秒的纳秒数。
|
||||
|
||||
- 作用:可以用来记录代码的执行时间,或用于记录用户操作某个事件的时间点。
|
||||
- 传统的 `Date` 类,只能精确到毫秒,并且是可变对象。
|
||||
- 新增的 `Instant` 类,可以精确到纳秒,并且是不可变对象,推荐用 `Instant` 代替 `Date`。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
//1、创建Instant的对象,获取此刻时间信息
|
||||
Instant now = Instant.now(); //不可变对象
|
||||
//2、获取总秒数
|
||||
long second = now.getEpochSecond();
|
||||
system.out.println(second) ;
|
||||
//3、不够1秒的纳秒数
|
||||
int nano = now.getNano();
|
||||
system.out.println(nano) ;
|
||||
|
||||
system.out.println(now);
|
||||
//可以进行加减法
|
||||
Instant instant = now.plusNanos(111);//将纳秒加111
|
||||
|
||||
// Instant对象的作用:做代码的性能分析,或者记录用户的操作时间点
|
||||
Instant now1 = Instant.now();
|
||||
//代码执行...
|
||||
Instant now2 = Instant.now();
|
||||
//用这两个时间点相减就可以知道这段代码运行了多少时间
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### DateTimeFormatter
|
||||
|
||||
使用方式,传入格式化字符串,可以指定 `local`。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.time.*;
|
||||
import java.time.format.*;
|
||||
import java.util.Locale;
|
||||
|
||||
public class Main {
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
ZonedDateTime zdt = ZonedDateTime.now();
|
||||
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm ZZZZ");
|
||||
System.out.println(formatter.format(zdt));
|
||||
|
||||
DateTimeFormatter zhFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy MMM dd EE HH:mm", Locale.CHINA);
|
||||
System.out.println(zhFormatter.format(zdt));
|
||||
|
||||
DateTimeFormatter usFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("E, MMMM/dd/yyyy HH:mm", Locale.US);
|
||||
System.out.println(usFormatter.format(zdt));
|
||||
|
||||
//2024-10-08T00:25 GMT+08:00
|
||||
//2024 十月 08 星期二 00:25
|
||||
//Tue, October/08/2024 00:25
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 转换
|
||||
|
||||
#### `LocalTimeTime` 和 `Date` 的相互转换
|
||||
|
||||
`LocalDateTime` 不包括时区,而 `Date` 代表一个具体的时间瞬间,精度为毫秒。
|
||||
|
||||
为了从 `LocalDateTime` 转换到 `Date` 需要提供时区。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
// LocalDateTime 转换为 Date
|
||||
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
|
||||
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = localDateTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
|
||||
Date date = Date.from(zonedDateTime.toInstant());
|
||||
// Date 转换为 LocalDateTime
|
||||
Date date = new Date();
|
||||
Instant instant = date.toInstant();
|
||||
LocalDateTime localDateTime = instant.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toLocalDateTime();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 数据库映射变化
|
||||
|
||||
- `java.util.Date` 和数据库映射
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<arg column="gmt_create" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" javaType="java.util.Date"/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `java.time.*` 和数据库映射
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<arg column="gmt_create" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP" javaType="java.time.LocalDateTime"/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- *mybatis 3.5.0* 以后已经支持,有 `LocalDateTimeTypeHandler` 等类型处理器支持,不需要额外操作。
|
||||
|
||||
- 比较老的 *mybatis* 版本可能会报错,需要添加相关的依赖。
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>mybatis-typehandlers-jsr310</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>1.0.2</version>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
*Mybatis* 中和时间相关的 `jdbcType` 和 j`avaType`、`typeHandler` 的对照关系如下:
|
||||
|
||||
| TypeHandler | Java类型 | JDBC类型 |
|
||||
| ------------------------- | ----------------------------- | ---------------------- |
|
||||
| DateTypeHandler | java.util.Date | TIMESTAMP |
|
||||
| DateOnlyTypeHandler | java.util.Date | DATE |
|
||||
| TimeOnlyTypeHandler | java.util.Date | TIME |
|
||||
| InstantTypeHandler | java.time.Instant | TIMESTAMP |
|
||||
| LocalDateTimeTypeHandler | java.time.LocalDateTime | TIMESTAMP |
|
||||
| LocalDateTypeHandler | java.time.LocalDate | DATE |
|
||||
| LocalTimeTypeHandler | java.time.LocalTime | TIME |
|
||||
| OffsetDateTimeTypeHandler | java.time.OffsetDateTime | TIMESTAMP |
|
||||
| OffsetTimeTypeHandler | java.time.OffsetTime | TIME |
|
||||
| ZonedDateTimeTypeHandler | java.time.ZonedDateTime | TIMESTAMP |
|
||||
| YearTypeHandler | java.time.Year | INTEGER |
|
||||
| MonthTypeHandler | java.time.Month | INTEGER |
|
||||
| YearMonthTypeHandler | java.time.YearMonth | VARCHAR 或 LONGVARCHAR |
|
||||
| JapaneseDateTypeHandler | java.time.chrono.JapaneseDate | DATE |
|
||||
|
||||
### 操作时间相关的工具
|
||||
|
||||
有一些对基础的API进行了封装便于我们在开发中有效的处理时间。
|
||||
|
||||
- 蚂蚁时间工具类:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
com.iwallet.biz.common.util.DateUtil
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 基于 `java.Util.Date`,提供了广泛的日期/时间处理方法,可满足绝大部分需求。
|
||||
|
||||
- ```
|
||||
org.apache.commons.lang3.time
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 包括多种基于 `java.util.Date` 封装的工具类,提供了很多方便操作日期和时间的算法。
|
||||
|
||||
目前暂时没有发现基于 `java.time*` 封装的公共的时间工具类。
|
||||
|
||||
在很多情况下,因为已有的工具类不能满足当下的业务需求,工程内部需要自己实现类似 `DateUtil` 的工具类,建议基于 `java.time*` 实现相关的工具类。
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
import java.time.*;
|
||||
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
|
||||
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
|
||||
|
||||
public class DateUtils {
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取当前日期
|
||||
public static LocalDate getCurrentDate() {
|
||||
return LocalDate.now();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取当前时间
|
||||
public static LocalTime getCurrentTime() {
|
||||
return LocalTime.now();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取当前日期时间
|
||||
public static LocalDateTime getCurrentDateTime() {
|
||||
return LocalDateTime.now();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 格式化日期为字符串
|
||||
public static String formatLocalDate(LocalDate date, String pattern) {
|
||||
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(pattern);
|
||||
return date.format(formatter);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 解析字符串为LocalDate
|
||||
public static LocalDate parseLocalDate(String dateStr, String pattern) {
|
||||
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(pattern);
|
||||
return LocalDate.parse(dateStr, formatter);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 增加指定天数
|
||||
public static LocalDate addDays(LocalDate date, long days) {
|
||||
return date.plusDays(days);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 减少指定天数
|
||||
public static LocalDate minusDays(LocalDate date, long days) {
|
||||
return date.minusDays(days);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 计算两个日期之间的天数差
|
||||
public static long getDaysBetween(LocalDate startDate, LocalDate endDate) {
|
||||
return ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(startDate, endDate);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在月份的第一天
|
||||
public static LocalDate getFirstDayOfMonth(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.withDayOfMonth(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在月份的最后一天
|
||||
public static LocalDate getLastDayOfMonth(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.withDayOfMonth(date.lengthOfMonth());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断两个日期是否相等
|
||||
public static boolean isSameDate(LocalDate date1, LocalDate date2) {
|
||||
return date1.isEqual(date2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断日期是否在指定范围内
|
||||
public static boolean isDateInRange(LocalDate date, LocalDate startDate, LocalDate endDate) {
|
||||
return date.isAfter(startDate) && date.isBefore(endDate);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的星期几
|
||||
public static DayOfWeek getDayOfWeek(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.getDayOfWeek();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断是否为闰年
|
||||
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
|
||||
return Year.of(year).isLeap();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定月份的天数
|
||||
public static int getDaysInMonth(int year, int month) {
|
||||
return YearMonth.of(year, month).lengthOfMonth();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的年份
|
||||
public static int getYear(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.getYear();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的月份
|
||||
public static int getMonth(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.getMonthValue();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的天数
|
||||
public static int getDayOfMonth(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.getDayOfMonth();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的小时数
|
||||
public static int getHour(LocalDateTime dateTime) {
|
||||
return dateTime.getHour();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的分钟数
|
||||
public static int getMinute(LocalDateTime dateTime) {
|
||||
return dateTime.getMinute();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的秒数
|
||||
public static int getSecond(LocalDateTime dateTime) {
|
||||
return dateTime.getSecond();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断指定日期是否在当前日期之前
|
||||
public static boolean isBefore(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.isBefore(LocalDate.now());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断指定日期是否在当前日期之后
|
||||
public static boolean isAfter(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.isAfter(LocalDate.now());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断指定日期是否在当前日期之前或相等
|
||||
public static boolean isBeforeOrEqual(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.isBefore(LocalDate.now()) || date.isEqual(LocalDate.now());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断指定日期是否在当前日期之后或相等
|
||||
public static boolean isAfterOrEqual(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.isAfter(LocalDate.now()) || date.isEqual(LocalDate.now());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的年龄
|
||||
public static int getAge(LocalDate birthDate) {
|
||||
LocalDate currentDate = LocalDate.now();
|
||||
return Period.between(birthDate, currentDate).getYears();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的季度
|
||||
public static int getQuarter(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return (date.getMonthValue() - 1) / 3 + 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的下一个工作日
|
||||
public static LocalDate getNextWorkingDay(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
do {
|
||||
date = date.plusDays(1);
|
||||
} while (date.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || date.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY);
|
||||
return date;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期的上一个工作日
|
||||
public static LocalDate getPreviousWorkingDay(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
do {
|
||||
date = date.minusDays(1);
|
||||
} while (date.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || date.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY);
|
||||
return date;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在周的第一天(周一)
|
||||
public static LocalDate getFirstDayOfWeek(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.with(DayOfWeek.MONDAY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在周的最后一天(周日)
|
||||
public static LocalDate getLastDayOfWeek(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.with(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在年的第一天
|
||||
public static LocalDate getFirstDayOfYear(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.withDayOfYear(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在年的最后一天
|
||||
public static LocalDate getLastDayOfYear(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.withDayOfYear(date.lengthOfYear());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在季度的第一天
|
||||
public static LocalDate getFirstDayOfQuarter(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
int month = (date.getMonthValue() - 1) / 3 * 3 + 1;
|
||||
return LocalDate.of(date.getYear(), month, 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在季度的最后一天
|
||||
public static LocalDate getLastDayOfQuarter(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
int month = (date.getMonthValue() - 1) / 3 * 3 + 3;
|
||||
return LocalDate.of(date.getYear(), month, Month.of(month).maxLength());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断指定日期是否为工作日(周一至周五)
|
||||
public static boolean isWeekday(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.getDayOfWeek() != DayOfWeek.SATURDAY && date.getDayOfWeek() != DayOfWeek.SUNDAY;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 判断指定日期是否为周末(周六或周日)
|
||||
public static boolean isWeekend(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
return date.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SATURDAY || date.getDayOfWeek() == DayOfWeek.SUNDAY;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在月份的工作日天数
|
||||
public static int getWeekdayCountOfMonth(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
int weekdayCount = 0;
|
||||
LocalDate firstDayOfMonth = getFirstDayOfMonth(date);
|
||||
LocalDate lastDayOfMonth = getLastDayOfMonth(date);
|
||||
|
||||
while (!firstDayOfMonth.isAfter(lastDayOfMonth)) {
|
||||
if (isWeekday(firstDayOfMonth)) {
|
||||
weekdayCount++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
firstDayOfMonth = firstDayOfMonth.plusDays(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return weekdayCount;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在月份的周末天数
|
||||
public static int getWeekendCountOfMonth(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
int weekendCount = 0;
|
||||
LocalDate firstDayOfMonth = getFirstDayOfMonth(date);
|
||||
LocalDate lastDayOfMonth = getLastDayOfMonth(date);
|
||||
|
||||
while (!firstDayOfMonth.isAfter(lastDayOfMonth)) {
|
||||
if (isWeekend(firstDayOfMonth)) {
|
||||
weekendCount++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
firstDayOfMonth = firstDayOfMonth.plusDays(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return weekendCount;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 获取指定日期所在年份的工作日天数
|
||||
public static int getWeekdayCountOfYear(LocalDate date) {
|
||||
int weekdayCount = 0;
|
||||
LocalDate firstDayOfYear = getFirstDayOfYear(date);
|
||||
LocalDate lastDayOfYear = getLastDayOfYear(date);
|
||||
|
||||
while (!firstDayOfYear.isAfter(lastDayOfYear)) {
|
||||
if (isWeekday(firstDayOfYear)) {
|
||||
weekdayCount++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
firstDayOfYear = firstDayOfYear.plusDays(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return weekdayCount;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
Ref:`https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIzOTU0NTQ0MA==&mid=2247542060&idx=1&sn=ebde870557f2f3002dacef8a43e04bfd`
|
||||
|
||||
70
java/线程.md
Normal file
70
java/线程.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
|
||||
|
||||
public class AlternatePrint {
|
||||
// 使用原子整数作为共享变量,初始值为1表示轮到线程1打印第一个数字
|
||||
private static AtomicInteger turn = new AtomicInteger(1);
|
||||
// 当前要打印的数字
|
||||
private static int currentNumber = 1;
|
||||
// 定义终止条件
|
||||
private static final int MAX_NUMBER = 100;
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
// 创建两个线程
|
||||
Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> {
|
||||
while (currentNumber <= MAX_NUMBER) {
|
||||
// 线程1检查是否轮到自己
|
||||
if (turn.get() == 1) {
|
||||
System.out.println("线程1: " + currentNumber);
|
||||
// 切换到线程2
|
||||
turn.set(2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 短暂休眠以避免CPU过度使用
|
||||
try {
|
||||
Thread.sleep(10);
|
||||
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
|
||||
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> {
|
||||
while (currentNumber <= MAX_NUMBER) {
|
||||
// 线程2检查是否轮到自己
|
||||
if (turn.get() == 2) {
|
||||
System.out.println("线程2: " + currentNumber);
|
||||
// 增加当前数字
|
||||
currentNumber++;
|
||||
// 切换回线程1
|
||||
turn.set(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 短暂休眠
|
||||
try {
|
||||
Thread.sleep(10);
|
||||
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
|
||||
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 启动线程
|
||||
thread1.start();
|
||||
thread2.start();
|
||||
|
||||
// 等待线程结束
|
||||
try {
|
||||
thread1.join();
|
||||
thread2.join();
|
||||
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
|
||||
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
System.out.println("所有数字打印完毕");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
132
linux/fdisk磁盘分区.md
Normal file
132
linux/fdisk磁盘分区.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
||||
# fdisk磁盘分区
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Fdisk 命令
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
fdisk [必要参数][选择参数]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
必要参数
|
||||
|
||||
- -l 列出素所有分区表
|
||||
- -u 与 **-l** 搭配使用,显示分区数目
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
选择参数
|
||||
|
||||
- -s<分区编号> 指定分区
|
||||
- -v 版本信息
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
菜单操作说明
|
||||
|
||||
- m :显示菜单和帮助信息
|
||||
- a :活动分区标记/引导分区
|
||||
- d :删除分区
|
||||
- l :显示分区类型
|
||||
- n :新建分区
|
||||
- p :显示分区信息
|
||||
- q :退出不保存
|
||||
- t :设置分区号
|
||||
- v :进行分区检查
|
||||
- w :保存修改
|
||||
- x :扩展应用,高级功能
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
实例
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||
Disk /dev/sda: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes
|
||||
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1305 cylinders
|
||||
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
|
||||
|
||||
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
|
||||
/dev/sda1 * 1 13 104391 83 Linux
|
||||
/dev/sda2 14 1305 10377990 8e Linux LVM
|
||||
|
||||
Disk /dev/sdb: 5368 MB, 5368709120 bytes
|
||||
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 652 cylinders
|
||||
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
|
||||
|
||||
Disk /dev/sdb doesn't contain a valid partition table
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
新建分区
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
输入 n
|
||||
按提示操作
|
||||
|
||||
最后输入W 保存
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
格式化分区
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
格式化磁盘
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkfs.ext3 /dev/sdb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
格式化分区为XFS
|
||||
|
||||
使用mkfs.xfs命令。如果已有其他文件系统创建在此分区,必须加上"-f"参数来覆盖它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mkfs.xfs -f /dev/sdb1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
挂载 xfs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo mount -t xfs /dev/sdb1 /mnt
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 /storage xfs defaults 0 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
挂载分区
|
||||
|
||||
编辑文件
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
vim /etc/fstab
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 /opt ext4 defaults 0 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
临时挂载
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mount /dev/sdb1 /Public2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
174
linux/linux使用lvm.md
Normal file
174
linux/linux使用lvm.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
||||
# LVM
|
||||
|
||||
> LVM 是一种可用在 Linux 内核 的逻辑分卷管理器 ;可用于管理磁盘驱动器或其他类似的大容量存储设备。
|
||||
|
||||
## 结构和术语介绍
|
||||
|
||||
##### **物理卷 (PV)**
|
||||
|
||||
一个可供存储 LVM 的块设备. 例如: 一块硬盘, 一个 MBR 或 GPT分区 , 一个回环文件, 一个被内核映射的设备 (例如dm-crypt 它包含一个特殊的 LVM 头。
|
||||
|
||||
##### **卷组 (VG)**
|
||||
|
||||
物理卷的一个组,作为存放逻辑卷的容器。 PEs are allocated from a VG for a LV.
|
||||
|
||||
##### **逻辑卷 (LV)**
|
||||
|
||||
"虚拟 / 逻辑卷" 存放在一个卷组中并由物理块组成。是一个类似于物理设备的块设备,例如,你可以直接在它上面创建一个文件系统文件系统 。
|
||||
|
||||
##### **物理块 (PE)**
|
||||
|
||||
一个卷组中最小的连续区域 (默认为 4 MiB),多个物理块将被分配给一个逻辑卷。你可以把它看成物理卷的一部分,这部分可以被分配给一个逻辑卷。
|
||||
|
||||
逻辑结构大概像是这个样子
|
||||
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
graph TB
|
||||
A(逻辑卷 LV) --> B(卷组 VG)
|
||||
C(逻辑卷...) --> B
|
||||
B --> D[物理卷 PV]
|
||||
B --> E[物理卷...]
|
||||
D --> F[物理区域 PE]
|
||||
D --> G[物理区域...]
|
||||
E --> H[物理区域 PE]
|
||||
E --> I[物理区域...]
|
||||
|
||||
classDef node fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px;
|
||||
classDef pe fill:#6af,stroke:#333,stroke-width:1.5px,dashed;
|
||||
class F,G,H,I pe;
|
||||
```
|
||||
> 我们并不需要太过关心 PE
|
||||
|
||||
记好这三层的缩写 我们待会要把这三层定义和创建出来。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用 LVM
|
||||
|
||||
> 在继续配置 LVM 前,必须对设备进行 分区。
|
||||
|
||||
这里假设有两个硬盘 两个分区
|
||||
并且会同时演示如何拓展空间 所以有些命令不是最佳路径
|
||||
|
||||
- /dev/sdb1
|
||||
- /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建物理卷(PV)
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
pvcreate /dev/sdb1
|
||||
pvcreate /dev/sdc1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
***查看创建好的物理卷***
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
pvdisplay
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建卷组(VG)
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
vgcreate vg_demo /dev/sdb1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 这里 vg_demo 是你的卷组名
|
||||
> 后面的分区可以为多个 这里用一个方便后续演示扩容
|
||||
|
||||
***查看已创建好的卷组***
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
vgdisplay
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建逻辑卷
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
lvcreate -L 10G vg_demo -n lv_demo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 创建一个大小为 10G,名字为 lv_demo,所属 vg_demo 的逻辑卷。
|
||||
|
||||
***查看已创建的逻辑卷\***
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
lvdisplay
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 格式化并挂载逻辑卷
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
# 查看逻辑卷挂载位置
|
||||
vgscan
|
||||
|
||||
# 格式化逻辑卷
|
||||
mkfs -t ext4 /dev/vg_demo/lv_demo
|
||||
mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_demo/lv_demo
|
||||
|
||||
# 创建待挂载目录
|
||||
mkdir /demo
|
||||
|
||||
# 挂载
|
||||
mount /dev/vg_demo/lv_demo /demo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
用`df -hl` 就可以看到已经挂载的存储空间了
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们进行扩容
|
||||
|
||||
#### 对 VG 增加 PV
|
||||
|
||||
首先 需要创建好 PV
|
||||
|
||||
> 步骤在上面 不再重复写了
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
vgextend vg_demo /dev/sdc1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 调整 LV 大小
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
lvresize -l 102398 /dev/vg_demo/lv_demo
|
||||
|
||||
#or
|
||||
|
||||
lvresize -L +20G /dev/vg_demo/lv_demo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> 102398 是扩容后的 PE 总大小
|
||||
> PE 大小通过 pvdisplay 查看
|
||||
|
||||
#### 调整分区大小
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
# 扩展文件系统(根据实际文件系统类型选择命令)
|
||||
resize2fs /dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-ubuntu--lv # ext4
|
||||
# 或
|
||||
xfs_growfs /dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-ubuntu--lv # XFS
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### lsblk 命令
|
||||
|
||||
查看硬盘信息
|
||||
```
|
||||
lsblk
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
lsblk -f
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
[root@worker ~]# lsblk
|
||||
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
|
||||
sda 8:0 0 30G 0 disk
|
||||
├─sda1 8:1 0 200M 0 part /boot/efi
|
||||
├─sda2 8:2 0 1G 0 part /boot
|
||||
└─sda3 8:3 0 28.8G 0 part
|
||||
├─centos-root 253:0 0 27G 0 lvm /
|
||||
└─centos-swap 253:1 0 1.8G 0 lvm [SWAP]
|
||||
sdb 8:16 0 1T 0 disk
|
||||
└─sdb1 8:17 0 1024G 0 part /opt
|
||||
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,6 @@ s :取代,可以直接进行取代的工作哩!通常这个 s 的动作可
|
||||
可以使用正则 特殊字符\转义
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sed ”s/要被取代的字串/新的字串/g“ fileName
|
||||
sed "s/要被取代的字串/新的字串/g" fileName
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 二、ssh免密登录原理
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
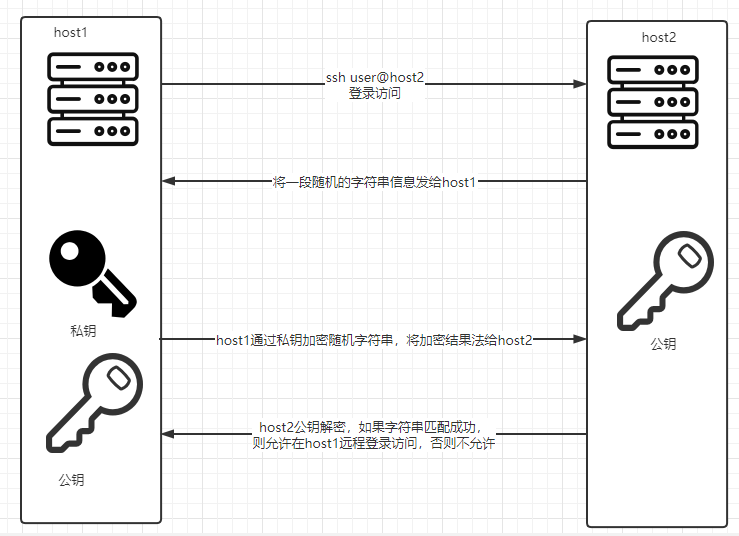
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果host1希望免密登录host2,那么密钥对是host1发布的。
|
||||
- 让host2信任host1的公钥,host1即可免密登录host2。所以host1需要将自己的公钥,在host2服务器上保存一份(复制密钥)
|
||||
@ -108,5 +108,4 @@ chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> 字母歌-kafka修炼之道
|
||||
> https://www.kancloud.cn/hanxt/kafka/2588987
|
||||
>
|
||||
> https://www.kancloud.cn/hanxt/kafka/2588987
|
||||
38
linux/linux分析进程内存占用.md
Normal file
38
linux/linux分析进程内存占用.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
### 寻找 内存orCPU 占用最高的程序
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
查看内存最多的进程
|
||||
|
||||
方法1
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ps -aux | sort -k4nr | head -10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
命令解释:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `ps`:参数a指代all——所有的进程,u指代userid——执行该进程的用户id,x指代显示所有程序,不以终端机来区分。ps -aux的输出格式如下:
|
||||
2. sort -k4nr中(k代表从根据哪一个关键词排序,后面的数字4表示按照第四列排序;n指代numberic sort,根据其数值排序;r指代reverse,这里是指反向比较结果,输出时默认从小到大,反向后从大到小。)。本例中,可以看到%MEM在第4个位置,根据%MEM的数值进行由大到小的排序。-k3表示按照cpu占用率排序。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
方法2:
|
||||
|
||||
top (然后按下M,注意大写)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
查看CPU 占用最多的进程
|
||||
|
||||
方法1
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ps -aux | sort -k3nr | head -3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
方法2
|
||||
|
||||
top (然后按下P,注意大写)
|
||||
15
linux/ntp.md
Normal file
15
linux/ntp.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
```
|
||||
根据您提供的ntpq -p命令输出结果,可以看到以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
remote列显示了NTP服务器的名称或IP地址。
|
||||
refid列显示了NTP服务器的参考标识。
|
||||
st列显示了NTP服务器的时钟层级。
|
||||
t列显示了NTP服务器的时钟类型。
|
||||
when列显示了最后一次成功与NTP服务器通信的时间(以秒为单位)。
|
||||
poll列显示了NTP客户端与NTP服务器之间的轮询间隔。
|
||||
reach列显示了NTP客户端与NTP服务器之间的成功通信次数。
|
||||
delay列显示了NTP客户端与NTP服务器之间的延迟(以毫秒为单位)。
|
||||
offset列显示了NTP客户端与NTP服务器之间的时钟偏移(以毫秒为单位)。
|
||||
jitter列显示了NTP客户端与NTP服务器之间的时钟抖动(以毫秒为单位)。
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
164
nginx启用njs动态修改请求.md
Normal file
164
nginx启用njs动态修改请求.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
|
||||
### nginx 使用njs模块动态修改请求
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 安装编译环境
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#GCC
|
||||
apt install -y build-essential
|
||||
|
||||
#安装正则库
|
||||
apt install -y libpcre3 libpcre3-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#安装zlib库
|
||||
apt install -y zlib1g-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#openssl
|
||||
apt install -y openssl libssl-dev
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 下载源码
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# 创建源码目录
|
||||
mkdir -p ~/build && cd ~/build
|
||||
|
||||
# 下载最新稳定版 Nginx
|
||||
wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.24.0.tar.gz
|
||||
tar -zxvf nginx-1.24.0.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
# 下载 njs 模块
|
||||
wget https://github.com/nginx/njs/archive/refs/tags/0.7.11.tar.gz -O njs-0.7.11.tar.gz
|
||||
tar -zxvf njs-0.7.11.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 编译
|
||||
这里采用最小化 默认配置编译
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd ~/build/nginx-1.24.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
./configure \
|
||||
--with-http_ssl_module \
|
||||
--with-http_v2_module \
|
||||
--with-http_realip_module \
|
||||
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
|
||||
--add-module=../njs-0.7.11/nginx
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
make && make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 配置
|
||||
|
||||
编辑conf/nginx.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
worker_processes 1;
|
||||
events {
|
||||
|
||||
worker_connections 1024;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
http {
|
||||
|
||||
include mime.types;
|
||||
default_type application/octet-stream;
|
||||
|
||||
sendfile on;
|
||||
|
||||
keepalive_timeout 65;
|
||||
|
||||
include /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
|
||||
include /usr/local/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建子配置目录
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mkdir /usr/local/nginx/{conf.d,sites-enabled}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
编辑子配置
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
js_import /usr/local/nginx/test.js;
|
||||
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 80;
|
||||
location / {
|
||||
root html;
|
||||
index index.html index.htm;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location /njs {
|
||||
return 200 test.version;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
location /hello {
|
||||
js_content test.hello;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
|
||||
location = /50x.html {
|
||||
|
||||
root html;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
编辑js 脚本
|
||||
```
|
||||
function hello(r) {
|
||||
r.return(200, "Hello from njs!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default {hello, version: "1.0.0"};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 访问测试
|
||||
|
||||
测试配置是否正确
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sbin/nginx -t
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动nginx
|
||||
```
|
||||
sbin/nginx
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
访问测试
|
||||
```
|
||||
[root@cdh-node-3 nginx]# curl 127.0.0.1:80/njs
|
||||
test.version[root@cdh-node-3 nginx]# curl 127.0.0.1:80/hello
|
||||
Hello from njs!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
9
npm镜像源.md
Normal file
9
npm镜像源.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
## NPM 镜像源
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
http://npm.taobao.org => http://npmmirror.com
|
||||
http://registry.npm.taobao.org => http://registry.npmmirror.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
307
openwrt/frr-动态路由.md
Normal file
307
openwrt/frr-动态路由.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,307 @@
|
||||
## FRR 动态路由
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
FRR 动态路由软件包 组件
|
||||
|
||||
这些配置行似乎来自于某种网络服务或路由器的配置文件,每一行都代表对一个特定的网络守护进程(daemon)的启用(yes)或禁用(no)设置。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### FRR 支持的协议
|
||||
|
||||
1. `frr`
|
||||
|
||||
这是 FRRouting 的核心包,包含了 FRR 的基础框架和多个路由协议守护进程(如 RIP、OSPF、BGP 等)。安装该包后,你可以运行 FRR 的所有路由协议服务和工具。
|
||||
|
||||
2. `frr-babeld`
|
||||
|
||||
Babel 是一种适用于 IP 网络的动态路由协议。这个包安装的是 **Babel 路由协议守护进程**,它用于支持 Babel 协议。Babel 是一种自适应的距离矢量协议,适用于小型到中型的网络。
|
||||
|
||||
用于动态路由发现和更新,特别适用于无线网络和 ad-hoc 网络。
|
||||
|
||||
3. `frr-bfdd`
|
||||
|
||||
BFDD(BFD:Bidirectional Forwarding Detection)是一种快速检测路径故障的协议。这个包提供了 **BFD 守护进程**,可以帮助快速发现路由器之间的连接故障,并根据路由协议快速进行故障恢复。
|
||||
|
||||
用于加速故障检测,并使路由协议更快地重新计算路径。
|
||||
|
||||
4. `frr-bgpd`
|
||||
|
||||
BGP(Border Gateway Protocol)是 Internet 上主要的外部网关协议。该包安装的是 **BGP 路由协议守护进程**,用于 BGP 配置和管理,支持 IPv4 和 IPv6 的路由交换。
|
||||
|
||||
用于与其他自治系统(AS)交换路由信息,常用于大规模网络(如互联网骨干网络)中的路由控制。
|
||||
|
||||
5. `frr-eigrpd`
|
||||
|
||||
EIGRP(Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)是 Cisco 开发的一种内部网关协议(IGP)。这个包安装的是 **EIGRP 路由协议守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
用于在同一自治系统内交换路由信息,EIGRP 是 Cisco 特有的协议,适用于企业网络。
|
||||
|
||||
6. `frr-fabricd`
|
||||
|
||||
这是 **Fabric 路由协议守护进程**,用于支持 **数据中心网络中的 Fabric 路由协议**,主要用于网络设备间的直接连接,简化网络架构和拓扑管理。
|
||||
|
||||
通常用于大型数据中心的网络结构中,提供更高效的流量路由和管理。
|
||||
|
||||
7. `frr-isisd`
|
||||
|
||||
IS-IS(Intermediate System to Intermediate System)是一种内部网关协议(IGP),主要用于大规模的服务提供商网络。这个包安装的是 **IS-IS 路由协议守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
用于在大型网络中进行高效的路由选择,IS-IS 主要在运营商和大规模网络中使用。
|
||||
|
||||
8. `frr-ldpd`
|
||||
|
||||
LDP(Label Distribution Protocol)用于 MPLS 网络中,帮助路由器之间分配标签。该包安装的是 **LDP 守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
在 MPLS 网络中,帮助管理标签分发和路由决策,优化数据包的转发路径。
|
||||
|
||||
9. `frr-libfrr`
|
||||
|
||||
这是 **FRR 的库包**,它提供了 FRR 所需的共享库。安装该包可以为其他 FRR 组件提供支持。
|
||||
|
||||
作为 FRR 的核心库文件,其他 FRR 组件依赖于它来提供基本的路由处理功能。
|
||||
|
||||
10. `frr-nhrpd`
|
||||
|
||||
NHRP(Next Hop Resolution Protocol)是用于 IP 网络中查找下一跳信息的协议,特别适用于 VPN 和 IP 网络互联。这个包安装的是 **NHRP 守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
用于基于 NHRP 协议查找 IP 地址的下一跳,通常用于 VPN 和其他隧道协议中。
|
||||
|
||||
11. `frr-ospf6d`
|
||||
|
||||
OSPFv3(Open Shortest Path First version 3)是用于 IPv6 网络的路由协议。这个包安装的是 **OSPFv3 路由协议守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
提供对 IPv6 网络的路由支持,OSPFv3 是 OSPF 的扩展版本,支持 IPv6 地址族。
|
||||
|
||||
12. `frr-ospfd`
|
||||
|
||||
OSPF(Open Shortest Path First)是一个广泛使用的内部网关协议(IGP),它使用链路状态协议来计算最佳路径。这个包安装的是 **OSPF 路由协议守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
用于基于链路状态协议的路由计算,适用于大型企业网络中的路由配置。
|
||||
|
||||
13. `frr-pbrd`
|
||||
|
||||
PBR(Policy-Based Routing)是基于策略的路由协议,允许根据数据包的内容(如源 IP、目标 IP 等)决定路由路径。这个包安装的是 **PBR 守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
提供基于策略的路由决策,允许对流量进行更细粒度的控制。
|
||||
|
||||
14. `frr-pimd`
|
||||
|
||||
PIM(Protocol Independent Multicast)是用于组播路由的协议,适用于需要多播的应用。这个包安装的是 **PIM 守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
为网络提供组播支持,适用于需要组播(如视频流、广播等)的网络应用。
|
||||
|
||||
15. `frr-ripd`
|
||||
|
||||
RIP(Routing Information Protocol)是一个距离矢量协议,适用于小型或中型的网络。这个包安装的是 **RIP 路由协议守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
实现 RIP 协议,进行路由信息的传播,适用于简单的内部网络。
|
||||
|
||||
16. `frr-ripngd`
|
||||
|
||||
RIPng(RIP next generation)是 RIP 协议的扩展,支持 IPv6 网络。这个包安装的是 **RIPng 路由协议守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
提供 RIP 协议的 IPv6 支持,适用于 IPv6 网络中的动态路由。
|
||||
|
||||
17. `frr-staticd`
|
||||
|
||||
Staticd 组件用于管理 **静态路由**,这些路由是手动配置的,并不通过动态路由协议传播。这个包安装的是 **静态路由守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
管理静态路由的配置,适用于不需要动态路由的网络部分。
|
||||
|
||||
18. `frr-vrrpd`
|
||||
|
||||
VRRP(Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol)是一个用于提供虚拟网关冗余的协议。这个包安装的是 **VRRP 守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
提供网关冗余服务,保证网络的高可用性,当主网关故障时,自动切换到备用网关。
|
||||
|
||||
19. `frr-vtysh`
|
||||
|
||||
VTYSH 是 **FRR 的命令行界面工具**,用于与 FRR 进程进行交互,配置和管理各种路由协议。
|
||||
|
||||
提供一个统一的命令行界面(CLI)来管理 FRR 配置,包括所有路由协议和 Zebra。
|
||||
|
||||
20. `frr-watchfrr`
|
||||
|
||||
Watchfrr 组件是一个监控工具,用于检测 FRR 路由协议进程的健康状态并进行管理。
|
||||
|
||||
监控 FRR 各个路由协议守护进程的运行状态,确保路由协议的稳定性。
|
||||
|
||||
21. `frr-zebra`
|
||||
|
||||
Zebra 是 FRR 的核心组件之一,负责将路由协议的路由信息传递给内核,并管理网络接口和静态路由。这个包安装的是 **Zebra 路由守护进程**。
|
||||
|
||||
与操作系统内核进行交互,管理路由表、接口配置等。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### rip 配置
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#协议
|
||||
router rip
|
||||
#在这个网段上广播
|
||||
network 192.168.123.0/24
|
||||
network 192.168.192.0/24
|
||||
|
||||
#将这个路由广播出去
|
||||
route 192.168.1.0/24
|
||||
|
||||
no passive-interface eth0 # 启用 eth0 接口的 RIP 收发
|
||||
passive-interface br-lan # 禁用 br-lan 接口上的 发送,可以接收。
|
||||
|
||||
!
|
||||
|
||||
#指定这个接口上协议版本
|
||||
interface eth0
|
||||
# send 发送的协议
|
||||
ip rip send version 2
|
||||
# receive 接收的协议
|
||||
ip rip receive version 2
|
||||
!
|
||||
|
||||
#在这个接口上广播路由
|
||||
interface eth1
|
||||
ip rip send version 2
|
||||
ip rip receive version 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 常用命令
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
|
||||
# 全全局配置
|
||||
configure terminal
|
||||
|
||||
#在全局配置下进行RIP 配置
|
||||
route rip
|
||||
|
||||
#配置好后 输入 end 结束配置, write 保存配置
|
||||
end
|
||||
write
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#查看rip 状态
|
||||
show ip rip status
|
||||
|
||||
#查看路由
|
||||
show ip route
|
||||
|
||||
#查看RIP 路由
|
||||
show ip route rip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
`show ip rip` 命令输出的内容主要显示了 RIP 协议的路由表信息,包括每个网络的下一跳、度量值、路由来源等。下面是对输出的逐行解析:
|
||||
|
||||
**输出内容**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
Codes: R - RIP, C - connected, S - Static, O - OSPF, B - BGP
|
||||
Sub-codes:
|
||||
(n) - normal, (s) - static, (d) - default, (r) - redistribute,
|
||||
(i) - interface
|
||||
|
||||
Network Next Hop Metric From Tag Time
|
||||
C(i) 10.147.17.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 self 0
|
||||
C(i) 192.168.123.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 self 0
|
||||
R(n) 192.168.124.0/24 10.147.17.219 2 10.147.17.219 0 02:27
|
||||
C(i) 192.168.192.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 self 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Codes 和 Sub-codes 说明**
|
||||
|
||||
- **Codes**: 每条路由的类型。
|
||||
- `R`:RIP协议路由
|
||||
- `C`:连接路由(直接连接的路由)
|
||||
- `S`:静态路由
|
||||
- `O`:OSPF协议路由
|
||||
- `B`:BGP协议路由
|
||||
- **Sub-codes**: 路由的子类型。
|
||||
- `(n)`:正常路由
|
||||
- `(s)`:静态路由
|
||||
- `(d)`:默认路由
|
||||
- `(r)`:由其他协议重分发的路由
|
||||
- `(i)`:接口路由(指向接口的路由)
|
||||
|
||||
**路由信息解析**
|
||||
|
||||
**1. C(i) 10.147.17.0/24**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
C(i) 10.147.17.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 self 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **C(i)**:这是一条 "连接路由",即直接连接的网络。 `(i)` 表示它是一个通过接口直接连接的网络。
|
||||
|
||||
- **10.147.17.0/24**:这是网络地址,表示该设备有一个直接连接到 `10.147.17.0/24` 子网的接口。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Next Hop**:`0.0.0.0`,表示这是一个直接连接的网络,因此不需要下一跳地址。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Metric**:度量值为 `1`,表示该路由的度量值,这里是直接连接的网络,度量值是最小的。
|
||||
|
||||
- **From**:`self`,表示该路由是从本设备的接口直接学习到的。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Tag**:`0`,这是一个路由标签,用于标识或分类路由。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Time**:`0`,表示此路由是立即学习到的,没有过期时间。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**2. C(i) 192.168.123.0/24**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
C(i) 192.168.123.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 self 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 这条路由的解析与第一条相似,是一个直接连接的网络 `192.168.123.0/24`,度量值为 `1`,并且由本机接口学习到。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**3. R(n) 192.168.124.0/24**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
R(n) 192.168.124.0/24 10.147.17.219 2 10.147.17.219 0 02:27
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **R(n)**:这是一个由 RIP 协议学习到的路由,`(n)` 表示正常的 RIP 路由。
|
||||
|
||||
- **192.168.124.0/24**:目标网络是 `192.168.124.0/24`,这是一个通过 RIP 协议学到的路由。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Next Hop**:`10.147.17.219`,表示该路由的下一跳地址是 `10.147.17.219`,即该路由是通过 `10.147.17.219` 路由器到达的。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Metric**:度量值为 `2`,表示到达该网络的路径的跳数或成本,`2` 表示通过该路径的跳数为 2。
|
||||
|
||||
- **From**:`10.147.17.219`,表示该路由是从 `10.147.17.219` 路由器学到的。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Tag**:`0`,路由标签。
|
||||
|
||||
- **Time**:`02:27`,表示该路由自学习以来已经存在了 2 分 27 秒。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**4. C(i) 192.168.192.0/24**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
C(i) 192.168.192.0/24 0.0.0.0 1 self 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- 这条路由表示 `192.168.192.0/24` 是通过本机接口直接连接的网络,度量值为 `1`。
|
||||
-
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
- **C(i)** 类别的路由表示直接连接的子网,度量值为 `1`,即最佳路径。
|
||||
- **R(n)** 类别的路由表示通过 RIP 协议学到的路由。它是通过其他路由器 `10.147.17.219` 学到的,度量值为 `2`,表示该路径的跳数是 2。
|
||||
- 所有路由的下一跳信息和度量值都提供了路由信息的详细描述,表明如何到达不同的网络。
|
||||
|
||||
这些路由信息可以帮助你了解 FRR 当前的 RIP 路由表,具体到哪些路由是直接连接的(如 `C(i)` 路由)以及哪些路由是通过 RIP 协议学习到的(如 `R(n)` 路由)。
|
||||
29
openwrt/openVPN.md
Normal file
29
openwrt/openVPN.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
## openWrt 路由器中的 openVPN 组件
|
||||
|
||||
| **连接类型** | 配置文件说明 | **模式** | **网络类型** | **适用场景** | **对应配置文件示例** |
|
||||
| :-------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | :------- | :---------------- | :----------------------------------------------------------- | :------------------- |
|
||||
| **client_tap_bridge** | Client configuration for an ethernet bridge VPN | 客户端 | TAP(以太网桥接) | 客户端需完全接入服务器局域网(如访问 SMB 共享、网络打印机等) | `client-bridge.conf` |
|
||||
| **client_tun** | Client configuration for a routed multi-client VPN | 客户端 | TUN(IP 路由) | 标准多客户端 VPN,适用于远程办公、访问内网服务 | `client-routed.conf` |
|
||||
| **client_tun_ptp** | Simple client configuration for a routed point-to-point VPN | 客户端 | TUN(点对点路由) | 仅 1 对 1 连接,适合设备间专用加密隧道(如远程管理) | `client-p2p.conf` |
|
||||
| **server_tap_bridge** | Server configuration for an ethernet bridge VPN | 服务器 | TAP(以太网桥接) | 服务器提供桥接模式 VPN,客户端像本地设备一样访问整个 LAN | `server-bridge.conf` |
|
||||
| **server_tun** | Server configuration for a routed multi-client VPN | 服务器 | TUN(IP 路由) | 标准多客户端 VPN 服务器,适用于企业远程访问 | `server-routed.conf` |
|
||||
| **server_tun_ptp** | Simple server configuration for a routed point-to-point VPN | 服务器 | TUN(点对点路由) | 仅支持 1 对 1 连接的 VPN 服务器(如站点间 VPN) | `server-p2p.conf` |
|
||||
|
||||
### **关键说明**:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **配置文件名**:
|
||||
- 通常 OpenVPN 会根据 `option value` 生成对应的配置文件(如 `client_tun` → `client-routed.conf`)。
|
||||
- 实际文件名可能因系统不同有所变化,但逻辑一致。
|
||||
2. **TAP vs. TUN**:
|
||||
- **TAP(`tap_bridge`)**:模拟以太网设备,适合需要广播/组播的应用(如网络游戏、局域网发现)。
|
||||
- **TUN(`tun`)**:仅路由 IP 流量,更高效,适合大多数 VPN(如网页访问、SSH)。
|
||||
3. **多客户端 vs. 点对点(P2P)**:
|
||||
- **普通模式(`server_tun`/`client_tun`)**:支持多个客户端同时连接。
|
||||
- **点对点(`_ptp`)**:仅限两个节点直接通信,延迟更低。
|
||||
|
||||
### **典型应用**:
|
||||
|
||||
- **企业远程办公** → `server_tun` + `client_tun`
|
||||
- **家庭局域网扩展** → `server_tap_bridge` + `client_tap_bridge`
|
||||
- **服务器间加密通道** → `server_tun_ptp` + `client_tun_ptp`
|
||||
|
||||
307
openwrt/zeroTier结合rip动态路由协议实现互访.md
Normal file
307
openwrt/zeroTier结合rip动态路由协议实现互访.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,307 @@
|
||||
# ZeroTier 结合rip 实现局域网互访
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么选择 ZeroTier 与 rip
|
||||
|
||||
个人使用ZeroTier体验不错,
|
||||
|
||||
### 网络拓扑图
|
||||
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
graph TD;
|
||||
|
||||
LAN-124((LAN-124.0/24))
|
||||
ZT-17((zt-17.0/24))
|
||||
LAN-123((LAN-123.0/24))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
nx30pro(nx30pro)
|
||||
mi_4A(mi_4A)
|
||||
|
||||
ZT-192((zt-192.0/24))
|
||||
ZT-191((zt-191.0/24))
|
||||
|
||||
pro+(pro+)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
LAN-124-->|192.168.124.1|nx30pro
|
||||
nx30pro-->|192.168.124.100/24|LAN-124-pc1;
|
||||
nx30pro-->|192.168.124.120/24|LAN-124-pc2;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
LAN-123 -->|192.168.123.1|pro+
|
||||
|
||||
ZT-17 -.->|10.147.17.214/24| mi_4A;
|
||||
ZT-17 -.->|10.147.17.219/24| nx30pro;
|
||||
|
||||
ZT-192-.->|192.168.192.2|mi_4A;
|
||||
ZT-191-.->|192.168.191.2|mi_4A;
|
||||
|
||||
ZT-192-.->|192.168.192.2|zt-192-pc1;
|
||||
ZT-191-.->|192.168.191.2|zt-191-pc1;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pro+-->|192.168.123.100|LAN-123-PC;
|
||||
pro+-->|192.168.123.71|nas;
|
||||
pro+-->|192.168.123.10|mi_4A;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
LAN123 是本地局域网(租房) 路由器为中兴的 **PRO+** 网段为 `192.168.123.0/24`
|
||||
|
||||
LAN124 是本地局域网 (家) 路由器为h3c的 **nx30pro** 网段为 `192.168.124.0/24`
|
||||
|
||||
zt17 虚拟局域网 (用于动态路由通信) 网段为 `10.147.17.0/24`
|
||||
|
||||
zt192 虚拟局域网 (用于节点接入) 网段为 `192.168.192.0/24`
|
||||
|
||||
zt191 虚拟局域网 (用于节点接入) 网段为 `192.168.191.0/24`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
mi_4a 是刷了openWrt 固件的 小米4A路由器,
|
||||
|
||||
在次拓扑中 充当网段的中转节点
|
||||
|
||||
ip 如下
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
192.168.123.10/24 本地局域网
|
||||
192.168.192.2/24 zt节点接入
|
||||
192.168.191.2/24 zt节点接入
|
||||
10.147.17.214/24 动态路由互联
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
nx30pro 是刷了 openWrt 固件的新华三30pro路由器,在次拓扑中充当两个网段的中转节点
|
||||
|
||||
由于直接采用的nx30pro 拨号 ,本节点比上一个节点少一个路由。
|
||||
|
||||
ip如下
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
192.168.124.1/24 本地局域网
|
||||
10.147.17.219/24 动态路由互联
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
nas 是租房的nas 服务器 ip为 `192.168.123.71/24`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建ZeroTier
|
||||
|
||||
创建三个 zt-lan
|
||||
|
||||
网段分别为
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.192.0/24 zt节点接入
|
||||
192.168.191.0/24 zt节点接入
|
||||
10.147.17.0/24 动态路由互联
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在192.168.192.0/24 添加路由
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
192.168.191.0/24 via 192.168.192.2
|
||||
192.168.123.0/24 via 192.168.192.2
|
||||
192.168.124.0/24 via 192.168.192.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在192.168.191.0/24 添加路由
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
192.168.192.0/24 via 192.168.191.2
|
||||
192.168.123.0/24 via 192.168.191.2
|
||||
192.168.124.0/24 via 192.168.191.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如图
|
||||
|
||||
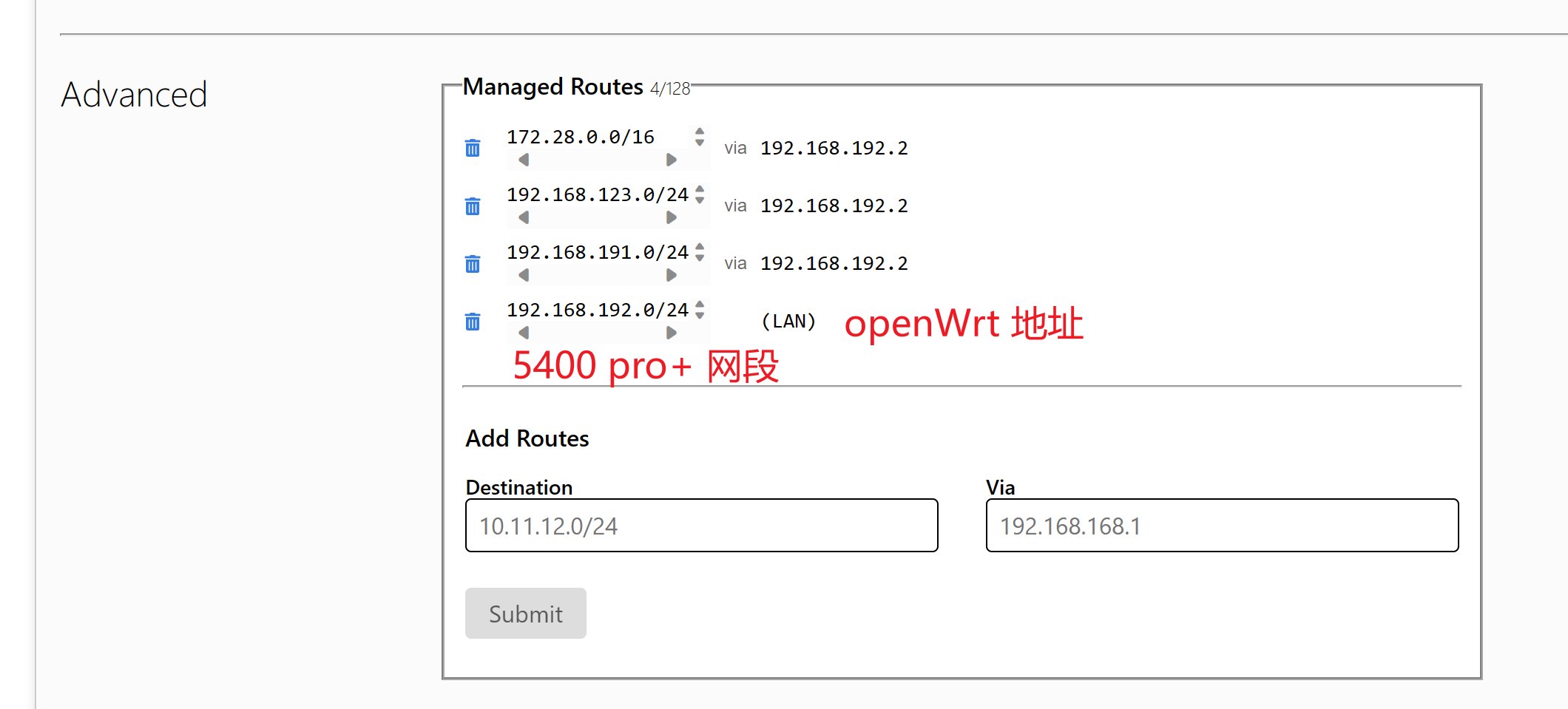
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 配置 openWrt
|
||||
|
||||
##### 安装 ZeroTier
|
||||
|
||||
在 mi_4a,nx30pro 中分别安装 ZeroTier
|
||||
|
||||
###### mi_4a
|
||||
|
||||
在mi_4a 中将三个zt-lan 添加至路由其中,
|
||||
|
||||
并为三个zt-lan 创建接口,按照规划设置静态ip,防火墙区域选择lan
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
###### nx30pro
|
||||
|
||||
在nx30pro中将zt-17的id 添加至路由其中,
|
||||
|
||||
并创建 接口按规划的设置IP,防火墙区域选择lan
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 安装 frr
|
||||
|
||||
**ssh 登录 openWrt 安装 以下软件包**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
opkg update
|
||||
opkg install frr frr-ripd frr-zebra frr-vtysh frr-watchfrr
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
说明:
|
||||
|
||||
frr frr-zebra frr-vtysh frr-watchfrr 必须装 其他的选配
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
完整版如下
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
opkg update
|
||||
opkg install frr frr-babeld frr-bfdd frr-bgpd frr-eigrpd frr-fabricd frr-isisd frr-ldpd frr-libfrr frr-nhrpd frr-ospf6d frr-ospfd frr-pbrd frr-pimd frr-ripd frr-ripngd frr-staticd frr-vrrpd frr-vtysh frr-watchfrr frr-zebra
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**编辑配置**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vi /etc/frr/daemons
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将 `ripd=no` 修改成 `ripd=yes` 保存
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vi /etc/frr/frr.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
添加网段 在图中红框位置 添加 (mi_4a)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
router rip
|
||||
route 10.147.17.0/24
|
||||
network 192.168.123.0/24
|
||||
network 192.168.192.0/24
|
||||
network 192.168.191.0/24
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
添加网段 在图中红框位置 添加 (华三)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
router rip
|
||||
route 10.147.17.0/24
|
||||
network 192.168.124.0/24
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
重启 frr
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/etc/init.d/frr restart
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
查看状态
|
||||
|
||||
等一两分钟后
|
||||
|
||||
执行以下命令可以看到 已经在交换路由了,也可以去openwrt 路由界面上观察 是否有rip 字样的路由
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vtysh
|
||||
show ip rip status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### pro+路由配置
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
登录本地 路由器 设置静态路由 将ZeroTier的网段指向 openWrt 在5400 pro+ 中的地址
|
||||
|
||||
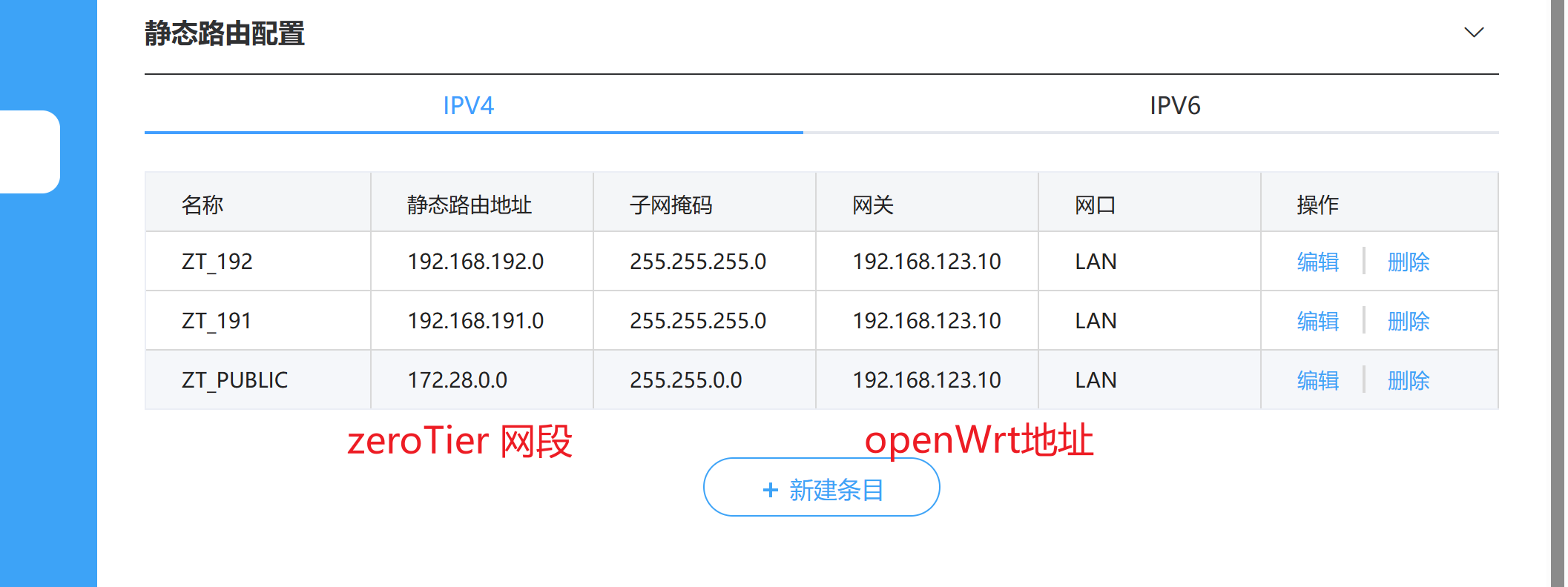
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 问题
|
||||
|
||||
- 在租房一侧 存在出入口不一致的情况, 因为在pro+ 上设置的路由 并没有下发到设备侧,
|
||||
|
||||
如图所示 去程经过mi_4a一个路由, 两跳 到达目的地。回程 经过pro+,mi_4a,两个路由 三跳 到达目的地
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
sequenceDiagram
|
||||
|
||||
zt_192_pc->>mi_4a: 192.168.192.3->192.168.192.2
|
||||
|
||||
mi_4a->>rdp远程桌面: 192.168.123.10->192.168.123.160
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
rdp远程桌面->> pro: 192.168.123.160->192.168.123.1
|
||||
pro->> mi_4a: 192.168.123.1->192.168.123.10
|
||||
mi_4a->> zt_192_pc: 192.168.192.2->192.168.192.3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
解决办法:在 rdp远程桌面 远程桌面上 添加静态路由
|
||||
|
||||
```cmd
|
||||
route ADD 192.168.192.0 MASK 255.255.255.0 192.168.123.10 METRIC 10 IF 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
命令解释
|
||||
|
||||
添加一条路由 匹配 192.168.192.0/24 的ip 下一跳 去往 192.168.123.10(mi_4a) 权重10 走序号为 2的网卡
|
||||
|
||||
网卡需要可以使用 route 命令查看,出来的网卡列表 前两个数字就是需要。
|
||||
|
||||
```cmd
|
||||
route print -4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
46
openwrt/小米4A刷入官方openWrt.md
Normal file
46
openwrt/小米4A刷入官方openWrt.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
# 小米4A千兆版刷入官方openWrt固件
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 刷入BREED
|
||||
|
||||
略
|
||||
|
||||
小米4AV1 用到的 breed 为 [ breed-mt7621-pbr-m1.bin](https://breed.hackpascal.net/breed-mt7621-pbr-m1.bin)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 刷入openWrt
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
本机 为 小米4AV1 千兆版 刷入的固件为 [ImmortalWrt](http://192.168.123.10/) 官网固件
|
||||
|
||||
首先进入 breed 刷入
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
immortalwrt-21.02.6-ramips-mt7621-xiaomi_mi-router-4a-gigabit-initramfs-kernel.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
内核文件
|
||||
|
||||
刷入完成后 检查 路由器是否正常启动 breed 是否丢失
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
确定无误后 在openWrt 的网页里刷入
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
immortalwrt-21.02.6-ramips-mt7621-xiaomi_mi-router-4a-gigabit-squashfs-sysupgrade.bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
升级包
|
||||
|
||||
刷机完成后 进入breed 新增环境变量
|
||||
在环境变量界面,增加**`autoboot.command`**字段,值设为 **`boot flash 0x180000`**
|
||||
即可,这就是告诉breed启动系统时,从0x180000处启动
|
||||
|
||||
因为小米4A 没有专用 breed 引导位置不正确 刷入官方 openWrt后无法正确进入系统
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
118
oracle/oracle.md
Normal file
118
oracle/oracle.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
|
||||
## oracle 数据库 job 操作
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**停止job** `force => TRUE` 不检查任务是否正在运行强制停止
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
BEGIN
|
||||
DBMS_SCHEDULER.STOP_JOB(job_name => 'TEST_JOB', force => TRUE);
|
||||
END;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**删除job** `force => TRUE` 不检查任务是否正在运行强制删除
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
BEGIN
|
||||
DBMS_SCHEDULER.DROP_JOB(job_name => 'TEST_JOB');
|
||||
END;
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**创建job**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
BEGIN
|
||||
DBMS_SCHEDULER.CREATE_JOB (
|
||||
job_name => 'MC_CH_ISSUE_INFO_CLEAN_NEW',
|
||||
job_type => 'PLSQL_BLOCK',
|
||||
job_action => 'BEGIN MC_CH_ISSUE_INFO_CLEAN_EVD; END;',
|
||||
start_date => SYSTIMESTAMP,
|
||||
repeat_interval => 'FREQ=DAILY; BYHOUR=8; BYMINUTE=25;',
|
||||
enabled => TRUE
|
||||
);
|
||||
END;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
停止执行计划
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
BEGIN
|
||||
DBMS_SCHEDULER.DISABLE('MC_CH_ISSUE_INFO_CLEAN');
|
||||
END;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
运行一个计划
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
BEGIN
|
||||
DBMS_SCHEDULER.RUN_JOB('test_job');
|
||||
END;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 关闭sesseion
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
SELECT
|
||||
s.sid,
|
||||
s.serial#,
|
||||
s.username,
|
||||
s.osuser,
|
||||
s.machine,
|
||||
s.program,
|
||||
s.sql_id,
|
||||
l.type,
|
||||
l.lmode,
|
||||
l.request
|
||||
FROM
|
||||
v$session s
|
||||
JOIN v$lock l ON s.sid = l.sid
|
||||
WHERE
|
||||
l.id1 = (SELECT object_id FROM dba_objects WHERE object_name = 'MKT_TEST')
|
||||
AND l.type = 'TM'; -- TM 锁表示表锁
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
SELECT
|
||||
s.sid,
|
||||
s.serial#,
|
||||
s.username,
|
||||
s.osuser,
|
||||
s.machine,
|
||||
s.program,
|
||||
s.sql_id,
|
||||
q.sql_text
|
||||
FROM
|
||||
v$session s
|
||||
JOIN v$sql q ON s.sql_id = q.sql_id
|
||||
WHERE
|
||||
s.sid =250 -- 替换为实际的 SID
|
||||
AND s.serial# = 53879; -- 替换为实际的 SERIAL#
|
||||
|
||||
--关闭
|
||||
ALTER SYSTEM KILL SESSION '250,53879';
|
||||
--强制关闭
|
||||
ALTER SYSTEM DISCONNECT SESSION '250,53879' IMMEDIATE;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 数据库重启
|
||||
|
||||
sqlplus / as sysdba
|
||||
SQL> shutdown immediate;
|
||||
SQL> startup;
|
||||
@ -101,3 +101,53 @@ alter table t1 exchange partition p2 with table test_t1;
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
快速创建分区表
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
|
||||
--生成sql
|
||||
|
||||
select 'CREATE TABLE tcn_stat_algorithm_data_fltn_'||"FLT_NBR"|| ' PARTITION OF "TCN_STAT_ALGORITHM_DATA_FLTN" FOR VALUES IN (''' || "FLT_NBR"||''');'
|
||||
from (
|
||||
select distinct "FLT_NBR"::varchar from "TCN_STAT_ALGORITHM_DATA" where "FLT_DT" between '20190101' and '20191231'
|
||||
EXCEPT
|
||||
select high_value from all_tab_partitions where table_name = '"TCN_STAT_ALGORITHM_DATA_FLTN"'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
--将上述查询结果另外开一个窗口进行执行,重复 第一步 直至 第一步查询不出结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
-- 生成创建 分区的sql
|
||||
select 'CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t_icc_retail_price_' || LOWER(tirp.flight_no) ||
|
||||
' PARTITION OF t_icc_retail_price FOR VALUES IN (''' || tirp.flight_no || ''');'
|
||||
from (select distinct flight_no::varchar
|
||||
from t_icc_retail_price
|
||||
where batch_date >= '2023-01-01 00:00:00'
|
||||
and batch_date <= '2023-11-30 00:00:00'
|
||||
and deleted = 0) as tirp
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--执行该sql 进行数据导入 可以调整 FLT_DT 分批执行 (可以重复执行)
|
||||
|
||||
INSERT INTO "TCN_STAT_ALGORITHM_DATA_FLTN" ("BOOKING_DATE", "BOOKING_TIME", "RDCP", "CARRIER", "FLT_NBR", "FLT_DT", "ORIG_AIRPORT_CD", "STOPOVER", "DEST_AIRPORT_CD", "CABIN_CD", "SCLS", "ROUTE_AMOUNT", "FINAL_AMOUNT", "TICKET_NO", "TICKET_ID", "FLTN_YEAR")
|
||||
|
||||
SELECT "BOOKING_DATE", "BOOKING_TIME", "RDCP", "CARRIER", "FLT_NBR", "FLT_DT", "ORIG_AIRPORT_CD", "STOPOVER", "DEST_AIRPORT_CD", "CABIN_CD", "SCLS", "ROUTE_AMOUNT", "FINAL_AMOUNT", "TICKET_NO", "TICKET_ID", "FLTN_YEAR" FROM "TCN_STAT_ALGORITHM_DATA"
|
||||
|
||||
where "FLT_DT" between '20230101' and '20231231'
|
||||
|
||||
ON CONFLICT ("FLT_NBR","TICKET_ID") DO nothing
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
120
postgresql_and_edb/edb表空间查询.md
Normal file
120
postgresql_and_edb/edb表空间查询.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SELECT nspname || '.' || relname AS "relation",
|
||||
pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size(C.oid)) AS "total_size"
|
||||
FROM pg_class C
|
||||
LEFT JOIN pg_namespace N ON (N.oid = C.relnamespace)
|
||||
WHERE nspname NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema')
|
||||
AND C.relkind = 'r'
|
||||
ORDER BY pg_total_relation_size(C.oid) DESC;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
SELECT schemaname || '.' || relname AS "relation",
|
||||
pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size(relid)) AS "total_size",
|
||||
pg_size_pretty(pg_table_size(relid) - pg_indexes_size(relid)) AS "table_size",
|
||||
pg_size_pretty(pg_indexes_size(relid)) AS "index_size",
|
||||
n_dead_tup
|
||||
FROM pg_stat_user_tables
|
||||
WHERE n_dead_tup > 0
|
||||
ORDER BY n_dead_tup DESC;
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
|
||||
SELECT
|
||||
table_schema || '.' || table_name AS 完整表名,
|
||||
table_type AS 表类型,
|
||||
table_catalog AS 数据库名,
|
||||
-- 使用 format() 函数正确引用表名
|
||||
pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(format('%I.%I', table_schema, table_name))) AS 数据大小,
|
||||
pg_size_pretty(pg_indexes_size(format('%I.%I', table_schema, table_name))) AS 索引大小,
|
||||
pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size(format('%I.%I', table_schema, table_name))) AS 总大小,
|
||||
pg_total_relation_size(format('%I.%I', table_schema, table_name)) AS 总字节数
|
||||
FROM
|
||||
information_schema.tables
|
||||
WHERE
|
||||
table_type IN ('BASE TABLE', 'PARTITIONED TABLE')
|
||||
AND table_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema', 'edb_sys')
|
||||
ORDER BY
|
||||
总字节数 DESC;
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
|
||||
SELECT
|
||||
pid,
|
||||
relid::regclass AS table_name,
|
||||
phase,
|
||||
heap_blks_total,
|
||||
heap_blks_scanned,
|
||||
heap_blks_scanned/heap_blks_total rate,
|
||||
heap_blks_vacuumed,
|
||||
index_vacuum_count,
|
||||
max_dead_tuples,
|
||||
num_dead_tuples
|
||||
FROM
|
||||
pg_stat_progress_vacuum;
|
||||
|
||||
SELECT
|
||||
pid,
|
||||
usename,
|
||||
datname,
|
||||
query,
|
||||
state,
|
||||
query_start,
|
||||
now() - query_start AS running_time
|
||||
FROM
|
||||
pg_stat_activity
|
||||
WHERE
|
||||
query ILIKE '%VACUUM%'
|
||||
ORDER BY
|
||||
query_start;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
SELECT
|
||||
schemaname,
|
||||
relname,
|
||||
n_live_tup AS 活元组数量,
|
||||
n_dead_tup AS 死元组数量,
|
||||
round(100 * n_dead_tup / (n_live_tup + 1), 2) AS 死元组占比
|
||||
FROM pg_stat_user_tables
|
||||
WHERE n_live_tup > 0
|
||||
AND round(100 * n_dead_tup / (n_live_tup + 1), 2) > 20 -- 死元组占比超20%
|
||||
ORDER BY 死元组占比 DESC;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
SELECT
|
||||
schemaname,
|
||||
relname AS 索引名,
|
||||
pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(relid)) AS 索引大小,
|
||||
idx_scan AS 扫描次数, -- EDB 中直接通过 pg_stat_user_indexes 的 idx_scan 字段获取扫描次数
|
||||
-- 索引膨胀率(索引实际大小 / 有效数据大小,>1.5 表示碎片严重)
|
||||
round(
|
||||
pg_relation_size(relid)::numeric /
|
||||
pg_indexes_size(relid::regclass)::numeric, -- 修正类型转换,去掉多余的 text 转换
|
||||
2
|
||||
) AS 膨胀率
|
||||
FROM pg_stat_user_indexes
|
||||
WHERE
|
||||
pg_indexes_size(relid::regclass) > 0 -- 排除无效索引
|
||||
AND round(
|
||||
pg_relation_size(relid)::numeric /
|
||||
pg_indexes_size(relid::regclass)::numeric,
|
||||
2
|
||||
) > 1.5 -- 筛选膨胀率 >1.5 的索引
|
||||
ORDER BY 膨胀率 DESC;
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
### 数据库导出
|
||||
## 数据库导出
|
||||
|
||||
#### 链接信息
|
||||
|
||||
@ -365,10 +365,6 @@ pattern参数
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### psql
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### pg_restore
|
||||
@ -628,23 +624,37 @@ psql -Uicctestedb -dicctestedb -h192.168.53.123 -f ~/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 实操数据导入导出
|
||||
|
||||
### 整库导出
|
||||
|
||||
使用 pg_dump 与 pg_restore 完成数据转移,适合整表 整库 迁移
|
||||
|
||||
#### 数据导出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
#导出 iccedb库
|
||||
# -O 不设置表归属,
|
||||
# -F c 自定义压缩
|
||||
# -v 显示详情
|
||||
./pg_dump -Uenterprisedb -diccedb -h192.168.53.118 -O -v -F c -f ~/diccedb_202207_29.data.sql
|
||||
./pg_dump -Uenterprisedb -diccedb -h192.168.53.118 -O -v -F c -f ~/alg.da
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 数据导入
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
|
||||
#导入数据
|
||||
#-c 指定恢复过程中清空目标数据库中的现有表
|
||||
#--strict-names 指定严格遵守输入文件中的名称规范
|
||||
#~/icc_data_20220719_test.sql 指定要恢复的输入文件路径
|
||||
#-n revenue_mgt 恢复 revenue_mgt schema
|
||||
#-j 4 并行化操作
|
||||
|
||||
./pg_restore -Uenterprisedb -dtest2 -h10.23.101.119 -F c -c -v --strict-names ~/icc_data_20220719_test.sql
|
||||
./pg_restore -Uenterprisedb -dtest2 -h10.23.101.119 -j4 -nrevenue_mgt -F c -c -v --strict-names ~/icc_data_20220719_test.sql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -655,25 +665,23 @@ psql -Uicctestedb -dicctestedb -h192.168.53.123 -f ~/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 部分数据导出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### COPY 导出导出部分数据
|
||||
COPY
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
sudo su - enterprisedb
|
||||
psql edb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 导出
|
||||
#### COPY 导出
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
COPY (select * from icc.tcn_stat
|
||||
where afferent_date between to_date('20220701','yyyymmdd') and to_date('20220714','yyyymmdd') ) TO '/home/edbdata/test.csv' WITH csv;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 导入
|
||||
#### COPY 导入
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
COPY tcn_stat_sales_volume_total FROM '/home/edbdata/tcn_stat_sales_volume_total.csv' WITH csv;
|
||||
@ -681,3 +689,14 @@ COPY tcn_stat_sales_volume_total FROM '/home/edbdata/tcn_stat_sales_volume_total
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 手动创建分区
|
||||
|
||||
```sql
|
||||
select 'CREATE TABLE tcn_stat_algorithm_data_fltn_'||"FLT_NBR"|| ' PARTITION OF "TCN_STAT_ALGORITHM_DATA_FLTN" FOR VALUES IN (''' || "FLT_NBR"||''');'
|
||||
from (
|
||||
select distinct"FLT_NBR"::varchar from "TCN_STAT_ALGORITHM_DATA" where "FLT_DT" between '20190101' and '20191231'
|
||||
EXCEPT
|
||||
select high_value from all_tab_partitions where table_name = '"TCN_STAT_ALGORITHM_DATA_FLTN"'
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
129
postgresql_and_edb/psql_常用命令.md
Normal file
129
postgresql_and_edb/psql_常用命令.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
||||
连接数据库, 默认的用户和数据库是postgres
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
psql -U user -d dbname
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
切换数据库,相当于mysql的use dbname
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\c dbname
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
列举数据库,相当于mysql的show databases
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\l
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
列举表,相当于mysql的show tables
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\dt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
查看表结构,相当于desc tblname,show columns from tbname
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\d tblname
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
查看索引
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\di
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建数据库:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
create database [数据库名];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
删除数据库:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
drop database [数据库名];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重命名一个表:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alter table [表名A] rename to [表名B];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
删除一个表:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
drop table [表名];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在已有的表里添加字段:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alter table [表名] add column [字段名] [类型];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
删除表中的字段:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alter table [表名] drop column [字段名];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重命名一个字段:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alter table [表名] rename column [字段名A] to [字段名B];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
给一个字段设置缺省值:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alter table [表名] alter column [字段名] set default [新的默认值];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
去除缺省值:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alter table [表名] alter column [字段名] drop default;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在表中插入数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
insert into 表名 ([字段名m],[字段名n],......) values ([列m的值],[列n的值],......);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
修改表中的某行某列的数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
update [表名] set [目标字段名]=[目标值] where [该行特征];
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
删除表中某行数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
delete from [表名] where [该行特征];
|
||||
delete from [表名];--删空整个表
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建表:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
create table ([字段名1] [类型1] <references 关联表名(关联的字段名)>;,[字段名2] [类型2],......<,primary key (字段名m,字段名n,...)>;);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\copyright 显示 PostgreSQL 的使用和发行条款
|
||||
\encoding [字元编码名称]
|
||||
显示或设定用户端字元编码
|
||||
\h [名称] SQL 命令语法上的说明,用 * 显示全部命令
|
||||
\prompt [文本] 名称
|
||||
提示用户设定内部变数
|
||||
\password [USERNAME]
|
||||
securely change the password for a user
|
||||
\q 退出 psql
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
68
postgresql_and_edb/一次数据库硬盘扩容.md
Normal file
68
postgresql_and_edb/一次数据库硬盘扩容.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
## 数据库硬盘扩容
|
||||
|
||||
### 前言
|
||||
|
||||
数据库硬盘不够用了 ,数据分区使用的普通分区,
|
||||
|
||||
新加一块硬盘 和原来的一块硬盘 组成lvm 分区
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 备份数据
|
||||
|
||||
1. 停机数据
|
||||
|
||||
2. 备份数据库文件,这里采用tar 配合zstd 压缩归档
|
||||
|
||||
`tar -I zstd -cvf archive.tar.zst /data/`
|
||||
|
||||
### lvm卷组创建
|
||||
|
||||
#### 一、卸载相关操作
|
||||
|
||||
1. `lsof +D /data` # 查看/data目录下打开的文件
|
||||
2. `umount /data` # 卸载/data挂载点
|
||||
3. `df -hT /data` #确定卸载情况
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 二、磁盘及分区查看
|
||||
1. `df -lh` # 查看磁盘分区的使用情况
|
||||
2. `fdisk /dev/nvme0n1p1` # 对nvme0n1p1分区进行操作(如查看、分区等)
|
||||
3. 使用 fdisk 删除 原有分区(备份好数据)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 三、LVM相关配置([详情看](/linux/linux使用lvm.md))
|
||||
1. `pvcreate /dev/nvme0n1 /dev/sdb` # 创建物理卷(可以为分区)
|
||||
2. `pvdisplay` # 显示物理卷的信息
|
||||
3. `vgcreate vg_data /dev/nvme0n1 /dev/sdb` # 创建卷组vg_data
|
||||
4. `vgdisplay` # 显示卷组的信息
|
||||
5. `lvcreate -l 100%FREE -n lv_data_all vg_data` # 在vg_data卷组上创建逻辑卷lv_data_all,使用全部空闲空间
|
||||
6. `lvdisplay /dev/vg_data/lv_data_all` # 显示vg_data卷组下lv_data_all逻辑卷的信息
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 四、文件系统及挂载配置
|
||||
1. `mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_data/lv_data_all` # 为逻辑卷创建xfs文件系统
|
||||
3. `mkdir /data` # 创建/data目录作为挂载点(原有目录存在则不创建)
|
||||
4. `mount /dev/vg_data/lv_data_all /data` # 将逻辑卷挂载到/data目录
|
||||
5. `df -lh` # 查看挂载后的磁盘使用情况( 如不生效则配置fstab重启)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 五、自动挂载配置及重启
|
||||
1. `vim /etc/fstab` # 编辑fstab文件,配置开机自动挂载
|
||||
2. `/dev/vg_data/lv_data_all /data xfs defaults 0 0 `
|
||||
3. `mount -a` # 挂载fstab文件中所有未挂载的文件系统,验证配置是否正确
|
||||
4. `reboot` # 重启系统
|
||||
|
||||
### 数据恢复
|
||||
|
||||
提供两种方法 恢复文件
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
zstd -d archive.tar.zst && tar -xvf archive.tar -C /path/to/extract
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
zstd -dc archive.tar.zst | tar -xvf -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
启动数据库
|
||||
214
redis/redis-3.0.3,哨兵集群.md
Normal file
214
redis/redis-3.0.3,哨兵集群.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
|
||||
## redis-v3.0.3哨兵集群搭建文档
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备工作
|
||||
|
||||
### 主机
|
||||
|
||||
准备三台全新 centos linux 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
固定IP
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
192.168.1.11
|
||||
192.168.1.12
|
||||
192.168.1.13
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**以下命令如无特殊说明 在三台主机中均要执行**
|
||||
|
||||
准备环境
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yum install make gcc wget
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建用户
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
useradd redis
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
创建相关目录
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir -p /opt/{app/redis,applog}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
授权
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
chown -R redis:redis /opt/app/redis/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
chown -R redis:redis /opt/applog/redis/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 编译源码
|
||||
|
||||
切换用户
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
su - redis
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下载源码
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd /opt/app/redis/
|
||||
wget https://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.0.3.tar.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
解压源码
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
tar -zxvf redis-3.0.3.tar.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
编译源码 这里为了和生产一致 使用libc 内存分配器
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd redis-3.0.3
|
||||
make MALLOC=libc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make PREFIX=/opt/app/redis/ install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
配置 path
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/opt/app/redis/bin' >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
source ~/.bashrc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置redis
|
||||
|
||||
复制配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cp /opt/app/redis/redis-3.0.3/src/redis.conf /opt/app/redis/
|
||||
|
||||
cp /opt/app/redis/redis-3.0.3/src/sentinel.conf /opt/app/redis/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
编辑配置文件 redis.conf
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sed -i 's/daemonize no/daemonize yes/g' redis.conf
|
||||
|
||||
sed -i 's|^logfile ""$|logfile "/opt/applog/redis/redis.log"|g' redis.conf
|
||||
|
||||
sed -i 's|^dir "./"$|dir "/opt/app/redis/"|g' redis.conf
|
||||
|
||||
sed -i 's/appendonly no/appendonly yes/g' redis.conf
|
||||
|
||||
sed -i 's/^# cluster-node-timeout 15000$/cluster-node-timeout 5000/g' redis.conf
|
||||
#设置主从复制密码
|
||||
sed -i 's/^# masterauth <master-password>$/masterauth dUw~7a)6/g' redis.conf
|
||||
#设置 节点密码
|
||||
sed -i 's/^# requirepass foobared$/requirepass dUw~7a)6/g' redis.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
配置主从节点
|
||||
|
||||
在 192.168.1.12,192.168.1.13 两台机子中执行
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
echo "slaveof 10.23.101.3 6379" >> redis.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
编辑配置文件 sentinel.conf
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sed -i 's|^\(sentinel monitor mymaster\) 127.0.0.1|\1 181.168.1.11|' sentinel.conf
|
||||
|
||||
#设置哨兵密码
|
||||
sed -i 's/^#sentinel auth-pass <master-name> <password>/sentinel auth-pass mymaster HmpYZ2KB/g' sentinel.conf
|
||||
|
||||
echo "daemonize yes" >> sentinel.conf
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
编写动脚本
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
echo "bin/redis-server redis.config">/opt/app/redis/start.sh
|
||||
chmod 775 start.sh
|
||||
|
||||
echo "bin/redis-sentinel sentinel.config">/opt/app/redis/start-sentinel.sh
|
||||
chmod 775 start.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
指定用户启动
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
su -s /bin/bash -c "$(pwd)/bin/redis-sentinel $(pwd)/sentinel.conf " redis
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动
|
||||
|
||||
先启动三个redis节点
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash start.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
再启动 sentinel j节点
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash start-sentinel.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
登录三个redis节点 分别写入key
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.1.11 成功写入 并同步至 192.168.1.12,192.168.1.13
|
||||
192.168.1.12 写入失败
|
||||
192.168.1.13 写入失败
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
登录哨兵节点 查看哨兵信息
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
redis-cli -p 26379
|
||||
|
||||
sentinel sentinels mymaster
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
杀死 主节点
|
||||
|
||||
分别查看 另外两台redis 的info 信息 是否发生切换
|
||||
BIN
resources/java/oauth2-server.assets/PhquBVnerb.webp
(Stored with Git LFS)
Normal file
BIN
resources/java/oauth2-server.assets/PhquBVnerb.webp
(Stored with Git LFS)
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
184
zeroTier/zerotier异地组网.md
Normal file
184
zeroTier/zerotier异地组网.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
||||
## ZeroTier 异地组网
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
异地组网 路由器类型 不同的类型组网方式不一样 这里介绍硬路由组网方式
|
||||
|
||||
- 路由器是硬路由 不能装插件
|
||||
|
||||
- 路由器是软路由
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 前置准备工作
|
||||
|
||||
- 需要一台在局域网里正常运行的linux主机
|
||||
- 一个能 添加静态路由的 硬路由
|
||||
- 一个 zeroTier账号
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 硬路由准备
|
||||
|
||||
##### 设置linux 主机mac地址绑定
|
||||
|
||||
防止断电重启后linux 主机地址发生变化 我这里绑定的 `192.168.123.119`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 添加静态路由
|
||||
|
||||
如图所示,路由地址 为 zerotier的网段 这里我们设置为 `192.168.191.0/24` 网关为 linux 主机地址
|
||||
|
||||
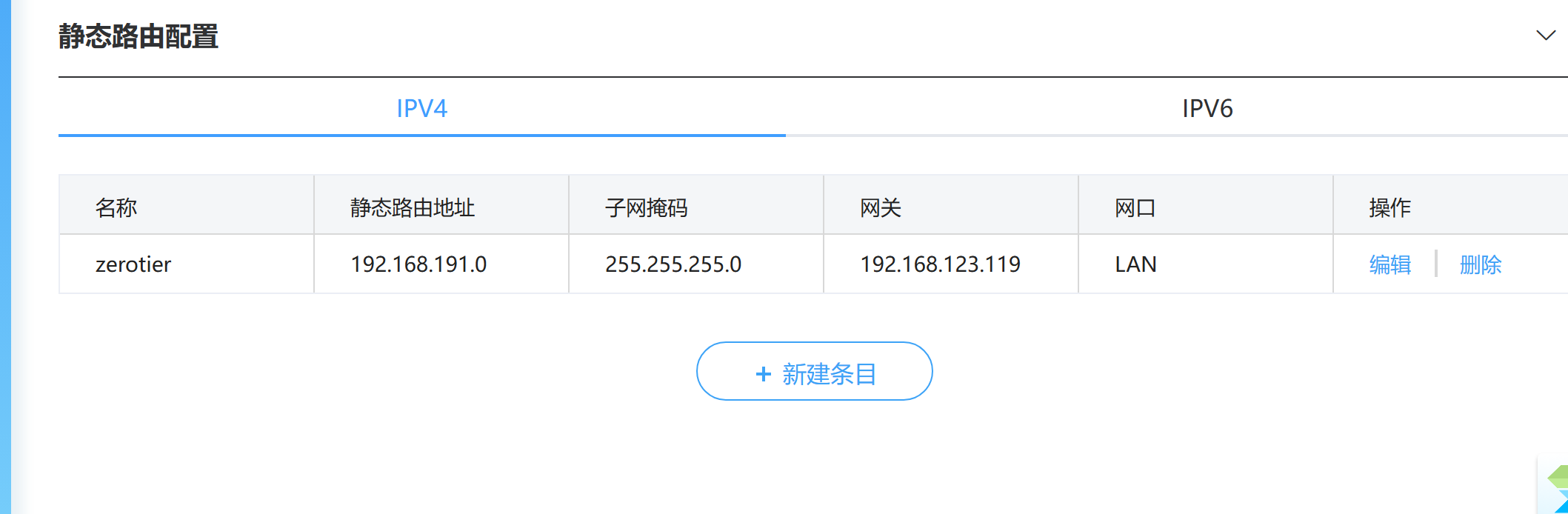
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### ZeroTier
|
||||
|
||||
##### 准备工作
|
||||
|
||||
- 登录 ZeroTier 控制台创建一个网络 网络类型私有 得到网络id
|
||||
|
||||
- 设置 zerotier的网段为 上述静态路由的地址 `192.168.191.0/24`
|
||||
- [添加路由](#添加路由跳转)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 安装 zerotier
|
||||
|
||||
在之前准备的内网linux上 安装 zerotier,脚本适用于 centos ,debian
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -s https://install.zerotier.com/ | sudo bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 加入网络
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
zerotier-cli join id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 授权节点、固定Ip
|
||||
|
||||
在zerotier控制台找到 Members 节点 ,找到加入网络的linux 主机
|
||||
|
||||
在AUTH 选项下打勾,禁止自动分配IP, 将节点IP 设置一个固定的值。
|
||||
|
||||
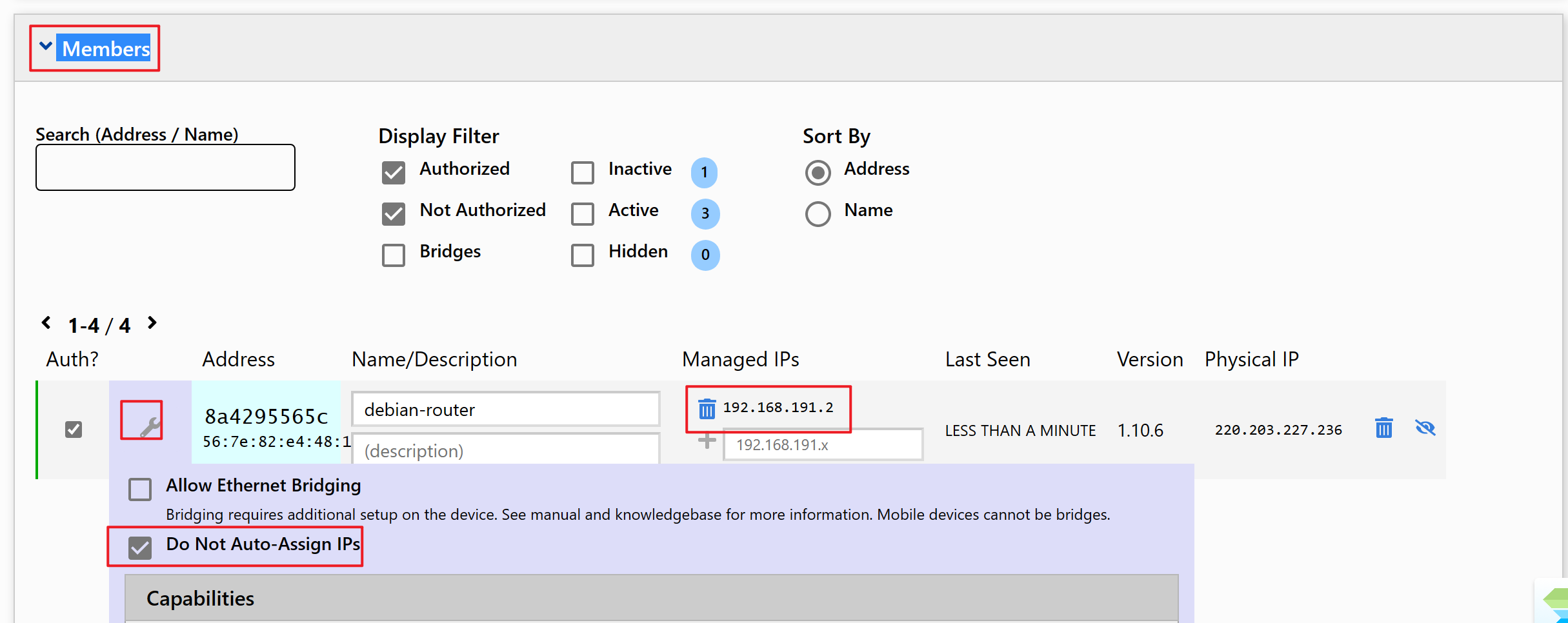
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 添加路由跳转
|
||||
|
||||
在高级选项中添加路由
|
||||
|
||||
第一个框是 你硬路由的局域网,我这里是 `192.168.123.0/24`
|
||||
|
||||
第二个框是 网关 填写上一步设置的ip ,我这里是 `192.168.191.2`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
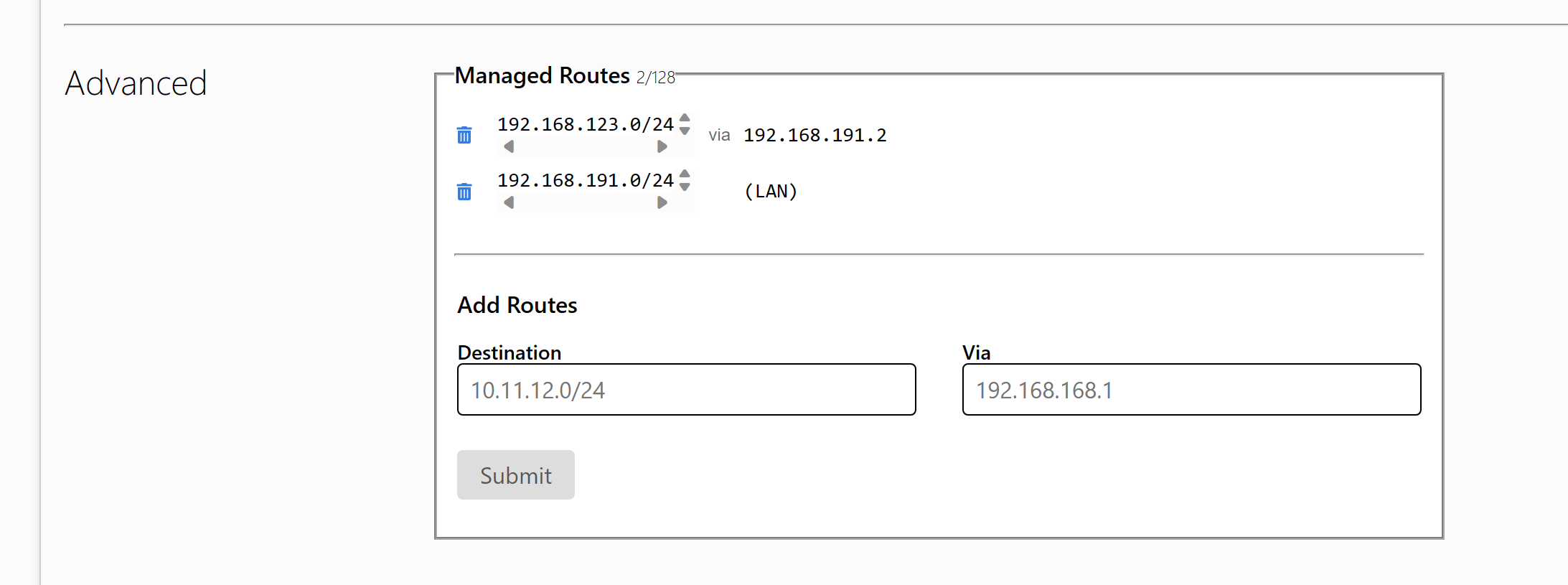
|
||||
|
||||
完成这两步后
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 附:zerotier 基本命令
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
Usage: zerotier-cli [-switches] <command/path> [<args>]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
switches:
|
||||
-h - 显示此帮助
|
||||
-v - 显示版本
|
||||
-j - 显示完整原始 JSON 输出
|
||||
-D<path> - ZeroTier 主目录路径,用于参数自动检测
|
||||
-p<port> - HTTP 端口 (默认: 自动)
|
||||
-T<token> - 认证令牌 (默认: 自动)
|
||||
|
||||
可用的命令:
|
||||
info - 显示状态信息
|
||||
listpeers - 列出所有对等节点
|
||||
peers - 列出所有对等节点(更美观)
|
||||
listnetworks - 列出所有网络
|
||||
join <network ID> - 加入网络
|
||||
leave <network ID> - 离开网络
|
||||
set <network ID> <setting> - 设置网络配置
|
||||
get <network ID> <setting> - 获取网络配置
|
||||
listmoons - 列出 moons (联邦根集)
|
||||
orbit <world ID> <seed> - 通过任何成员根加入 moon
|
||||
deorbit <world ID> - 离开 moon
|
||||
dump - 调试设置转储以供支持
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### LINUX 设置
|
||||
|
||||
这里使用的debian 系统 Debian系统使用的 ufw 防火墙
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 获取 网卡名字
|
||||
|
||||
记录 zerotier 网卡名字 `ztyqbub6jp `
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ip addre
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 开启nat 转发
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
echo "net/ipv4/ip_forward=1" >> /etc/ufw/sysctl.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 接收转发数据
|
||||
|
||||
打开UFW配置文件`/etc/default/ufw`。找到`DEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICY`键,然后将值从`DROP`更改为`ACCEPT`。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/default/ufw
|
||||
DEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICY="ACCEPT"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 设置ip伪装
|
||||
|
||||
在`nat`表中设置`POSTROUTING`链的默认策略和伪装规则。
|
||||
|
||||
打开`/etc/ufw/before.rules`文件。追加以下几行到文件.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/ufw/before.rules
|
||||
#NAT table rules 启用nat 表
|
||||
*nat
|
||||
# 允许POSTROUTING 链
|
||||
:POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0]
|
||||
|
||||
# 转发eth0接口的数据包,请将eth0更改为
|
||||
-A POSTROUTING -o ztyqbub6jp -j MASQUERADE
|
||||
|
||||
# don't delete the 'COMMIT' line or these rules won't be processed
|
||||
COMMIT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
最后,通过命令`sudo ufw reload`加载规则。
|
||||
85
模组电源/模组电源材料及工具.md
Normal file
85
模组电源/模组电源材料及工具.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
## 制作模组电源用到的材料工具
|
||||
|
||||
### 端子
|
||||
|
||||
##### 5557端子
|
||||
|
||||
5557端子 也叫**5557母端子** 规格为**4.2mm** ,是制作电源模组线的端子。
|
||||
|
||||
有高脚和低脚端子两种
|
||||
|
||||
高脚端子主要用于两根线的组合压制,也可以用来压制更粗直径的模组线。低脚端子用于单根线的压制。
|
||||
|
||||
端子的材料主要有黄铜的。磷铜的,半镀金的等等,不同的材料有不同的价格。低脚一般为3到3.5元100个,高脚4到6元100个。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 5559端子
|
||||
|
||||
5559端子,也叫5559公端子。在制作模组线延长线时我们可以用到。
|
||||
|
||||
价格一般也是3到3.5元100个,材料不同,价格可能也有所不同
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Sata端子**
|
||||
|
||||
sata端子 是制作sata供电线时需要用到的端子,有公端子和母端子之分,价格从几分钱到几毛钱一个不等。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 大4pin端子
|
||||
|
||||
大4p端子 是制作大4pin模组线用到的端子,规格为**5.08mm**。有公端子和母端子之分。价格一般为50个2到3元左右,不同材料价格不同。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 2510端子
|
||||
|
||||
风扇用端子 分为2510母端子和2510公端子 。规格为**2.54mm**。价格一般为2元左右100个。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 胶壳
|
||||
|
||||
胶壳主要分为公胶壳和母胶壳,公胶壳和母端子搭配使用,母胶壳和公端子搭配使用,大家千万不要买错了。我们模组线用的是公头胶壳线材,规格
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 线材
|
||||
|
||||
制作模组线一般为硅胶线和特氟龙镀银线
|
||||
|
||||
##### 硅胶线
|
||||
|
||||
硅胶线质地柔软,可以任意弯折。
|
||||
但是外皮比较容易破。所以可以搭配尼龙网套管配合使用,从而达到美观坚韧的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
##### 特氟龙镀银线
|
||||
|
||||
特氟龙镀银线,外观漂亮。质地比较坚硬。有一定的塑形性。
|
||||
接下来我们说一下规格,制作电源模组线一般的线材规格为18AWG,这是美国的线材标准。换算成公制标准大概是1平方毫米,如果有大功率需求,也可以买16AWG规格的
|
||||
|
||||
### 工具
|
||||
|
||||
##### 剥线钳
|
||||
|
||||
选择带18AWG或者1.0平方mm的即可,那个便宜买那个
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
##### 端子压线钳
|
||||
|
||||
选择带棘轮的,在压制端子时比较省力。我买的是SFN58b大家可以参考一下 价格在30到40元价位的即可。
|
||||
|
||||
##### 退针器
|
||||
|
||||
一般退端子的时候可以用到,可以不买。用卡针,曲别针都可以。
|
||||
|
||||
##### 万用表
|
||||
|
||||
测线序用。买蜂鸣的就可以,那个便宜买哪个。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1SY4y1S7ep
|
||||
414
私有CA.md
Normal file
414
私有CA.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,414 @@
|
||||
### 一、安装CFSSL工具
|
||||
|
||||
CFSSL(CloudFlare's PKI Toolkit)是一个开源的PKI工具集,可用于创建私有CA和证书。
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Linux/macOS**:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 下载cfssl和cfssljson工具
|
||||
curl -o cfssl https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssl_linux-amd64
|
||||
curl -o cfssljson https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssljson_linux-amd64
|
||||
chmod +x cfssl cfssljson
|
||||
sudo mv cfssl cfssljson /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Windows**:
|
||||
- 从 [CFSSL Releases](https://github.com/cloudflare/cfssl/releases) 下载对应版本的 `cfssl.exe` 和 `cfssljson.exe`
|
||||
- 将可执行文件添加到系统PATH路径
|
||||
|
||||
### 二、创建私有CA
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 配置CA证书
|
||||
创建一个名为 `ca-config.json` 的文件,定义证书的有效期和使用策略:
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"signing": {
|
||||
"default": {
|
||||
"expiry": "87600h" // 10年有效期
|
||||
},
|
||||
"profiles": {
|
||||
"server": {
|
||||
"expiry": "87600h",
|
||||
"usages": ["signing", "key encipherment", "server auth"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"client": {
|
||||
"expiry": "87600h",
|
||||
"usages": ["signing", "key encipherment", "client auth"]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"peer": {
|
||||
"expiry": "87600h",
|
||||
"usages": ["signing", "key encipherment", "server auth", "client auth"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 创建CA证书签名请求(CSR)配置
|
||||
创建 `ca-csr.json` 文件:
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"CN": "My Private CA",
|
||||
"key": {
|
||||
"algo": "rsa",
|
||||
"size": 4096
|
||||
},
|
||||
"names": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"C": "CN",
|
||||
"ST": "Shanghai",
|
||||
"L": "Shanghai",
|
||||
"O": "My Organization",
|
||||
"OU": "IT Department"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"ca": {
|
||||
"expiry": "87600h" // CA证书有效期10年
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. 生成CA证书和私钥
|
||||
执行以下命令生成自签名CA证书:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cfssl gencert -initca ca-csr.json | cfssljson -bare ca
|
||||
```
|
||||
这将生成三个文件:
|
||||
- `ca.pem`:CA公钥证书
|
||||
- `ca-key.pem`:CA私钥(妥善保管,不要泄露)
|
||||
- `ca.csr`:CA证书签名请求
|
||||
|
||||
### 三、使用CA签署服务器证书
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 创建服务器证书CSR配置
|
||||
创建 `server-csr.json` 文件:
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"CN": "server.example.com",
|
||||
"hosts": [
|
||||
"server.example.com",
|
||||
"192.168.1.100",
|
||||
"localhost",
|
||||
"127.0.0.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"key": {
|
||||
"algo": "rsa",
|
||||
"size": 2048
|
||||
},
|
||||
"names": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"C": "CN",
|
||||
"ST": "Shanghai",
|
||||
"L": "Shanghai",
|
||||
"O": "My Organization",
|
||||
"OU": "IT Department"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
> 注意:`hosts` 字段必须包含服务器的域名、IP地址以及任何需要访问的别名
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 生成服务器证书和私钥
|
||||
使用CA直接签署服务器证书:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cfssl gencert \
|
||||
-ca=ca.pem \
|
||||
-ca-key=ca-key.pem \
|
||||
-config=ca-config.json \
|
||||
-profile=server \
|
||||
server-csr.json | cfssljson -bare server
|
||||
```
|
||||
这将生成:
|
||||
- `server.pem`:服务器公钥证书
|
||||
- `server-key.pem`:服务器私钥
|
||||
|
||||
### 四、使用CA签署客户端证书
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 创建客户端证书CSR配置
|
||||
创建 `client-csr.json` 文件:
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"CN": "client.example.com",
|
||||
"hosts": [], // 客户端证书通常不需要指定hosts
|
||||
"key": {
|
||||
"algo": "rsa",
|
||||
"size": 2048
|
||||
},
|
||||
"names": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"C": "CN",
|
||||
"ST": "Shanghai",
|
||||
"L": "Shanghai",
|
||||
"O": "My Organization",
|
||||
"OU": "IT Department"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 生成客户端证书和私钥
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cfssl gencert \
|
||||
-ca=ca.pem \
|
||||
-ca-key=ca-key.pem \
|
||||
-config=ca-config.json \
|
||||
-profile=client \
|
||||
client-csr.json | cfssljson -bare client
|
||||
```
|
||||
这将生成:
|
||||
- `client.pem`:客户端公钥证书
|
||||
- `client-key.pem`:客户端私钥
|
||||
|
||||
### 五、证书验证
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 验证服务器证书
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
openssl verify -CAfile ca.pem server.pem
|
||||
```
|
||||
如果输出 `server.pem: OK`,则证书有效
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 验证客户端证书
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
openssl verify -CAfile ca.pem client.pem
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 六、证书使用示例
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 在HTTPS服务器中使用
|
||||
将 `server.pem` 和 `server-key.pem` 配置到你的Web服务器(如Nginx、Apache):
|
||||
```nginx
|
||||
server {
|
||||
listen 443 ssl;
|
||||
server_name server.example.com;
|
||||
|
||||
ssl_certificate /path/to/server.pem;
|
||||
ssl_certificate_key /path/to/server-key.pem;
|
||||
ssl_client_certificate /path/to/ca.pem; # 客户端证书验证(可选)
|
||||
ssl_verify_client on; # 启用客户端证书验证(可选)
|
||||
|
||||
# 其他配置...
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 在客户端应用中使用
|
||||
在需要验证服务器证书的客户端应用中,导入 `ca.pem` 作为信任的根证书。例如,使用curl访问HTTPS服务器:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl --cacert ca.pem https://server.example.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 七、安全注意事项
|
||||
|
||||
1. **私钥保护**:
|
||||
- `ca-key.pem`、`server-key.pem` 和 `client-key.pem` 是敏感文件,应存储在安全位置
|
||||
- 限制访问权限:`chmod 400 *.key.pem`
|
||||
|
||||
2. **证书备份**:
|
||||
- 定期备份CA证书和私钥
|
||||
- 考虑使用硬件安全模块(HSM)存储CA私钥
|
||||
|
||||
3. **证书撤销**:
|
||||
- 如需撤销证书,可使用CFSSL生成证书撤销列表(CRL)
|
||||
- 更新 `ca-config.json` 添加CRL配置
|
||||
|
||||
通过以上步骤,你已成功创建了一个有效期10年的私有CA,并使用它签署了服务器和客户端证书。
|
||||
|
||||
### 八、附快速签发脚本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# 证书快速签发脚本
|
||||
# 依赖: cfssl, cfssljson 已安装并初始化好CA证书
|
||||
|
||||
# 颜色定义
|
||||
RED='\033[0;31m'
|
||||
GREEN='\033[0;32m'
|
||||
YELLOW='\033[0;33m'
|
||||
NC='\033[0m' # No Color
|
||||
|
||||
# 默认配置
|
||||
CA_KEY="/root/ckw/cfssl/ca/ca-ecdsa-key.pem"
|
||||
CA_CERT="/root/ckw/cfssl/ca/ca-ecdsa.pem"
|
||||
CA_CONFIG="/root/ckw/cfssl/ca/ca-config.json"
|
||||
OUTPUT_DIR="certs"
|
||||
MERGE_CA="true" # 默认合并根证书
|
||||
|
||||
# 使用帮助
|
||||
function show_help {
|
||||
echo -e "${GREEN}证书快速签发脚本${NC}"
|
||||
echo "用法: $0 [选项]"
|
||||
echo "选项:"
|
||||
echo " -h, --help 显示此帮助信息"
|
||||
echo " -n, --name NAME 证书名称 (必填)"
|
||||
echo " -t, --type TYPE 证书类型: server, client, peer (默认: server)"
|
||||
echo " -c, --ca CA_CERT CA证书路径 (默认: $CA_CERT)"
|
||||
echo " -k, --ca-key CA_KEY CA私钥路径 (默认: $CA_KEY)"
|
||||
echo " -C, --ca-config CONF CA配置文件路径 (默认: $CA_CONFIG)"
|
||||
echo " -o, --output DIR 输出目录 (默认: $OUTPUT_DIR)"
|
||||
echo " -d, --domains LIST 域名列表 (逗号分隔)"
|
||||
echo ""
|
||||
echo "示例:"
|
||||
echo " $0 -n server1 -d example.com,www.example.com "
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 参数解析
|
||||
NAME=""
|
||||
TYPE="server"
|
||||
DOMAINS=""
|
||||
|
||||
while [[ $# -gt 0 ]]; do
|
||||
case $1 in
|
||||
-h|--help)
|
||||
show_help
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
;;
|
||||
-n|--name)
|
||||
NAME="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
;;
|
||||
-t|--type)
|
||||
TYPE="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
;;
|
||||
-c|--ca)
|
||||
CA_CERT="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
;;
|
||||
-k|--ca-key)
|
||||
CA_KEY="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
;;
|
||||
-C|--ca-config)
|
||||
CA_CONFIG="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
;;
|
||||
-o|--output)
|
||||
OUTPUT_DIR="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
;;
|
||||
-d|--domains)
|
||||
DOMAINS="$2"
|
||||
shift 2
|
||||
;;
|
||||
--no-merge-ca)
|
||||
MERGE_CA="false"
|
||||
shift
|
||||
;;
|
||||
*)
|
||||
echo -e "${RED}未知参数: $1${NC}" >&2
|
||||
show_help
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
;;
|
||||
esac
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
# 验证必填参数
|
||||
if [[ -z "$NAME" ]]; then
|
||||
echo -e "${RED}错误: 必须指定证书名称 (-n/--name)${NC}" >&2
|
||||
show_help
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# 验证证书类型
|
||||
if [[ "$TYPE" != "server" && "$TYPE" != "client" && "$TYPE" != "peer" ]]; then
|
||||
echo -e "${RED}错误: 证书类型必须是 server, client 或 peer${NC}" >&2
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# 验证文件是否存在
|
||||
for file in "$CA_CERT" "$CA_KEY" "$CA_CONFIG"; do
|
||||
if [[ ! -f "$file" ]]; then
|
||||
echo -e "${RED}错误: 文件 $file 不存在${NC}" >&2
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
# 当类型为server且未指定域名时,默认将name作为域名
|
||||
if [[ "$TYPE" == "server" && -z "$DOMAINS" ]]; then
|
||||
DOMAINS="$NAME"
|
||||
echo -e "${YELLOW}注意: 证书类型为server且未指定域名,默认添加 ${NAME} 作为域名${NC}"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# 创建证书单独目录
|
||||
CERT_DIR="$OUTPUT_DIR/$NAME"
|
||||
mkdir -p "$CERT_DIR" || { echo -e "${RED}无法创建证书目录: $CERT_DIR${NC}"; exit 1; }
|
||||
|
||||
# 生成证书签名请求配置
|
||||
CSR_CONFIG="$CERT_DIR/${NAME}-csr.json"
|
||||
cat > "$CSR_CONFIG" <<EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"CN": "$NAME",
|
||||
"key": {
|
||||
"algo": "ecdsa",
|
||||
"size": 256
|
||||
},
|
||||
"names": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"C": "CN",
|
||||
"ST": "Beijing",
|
||||
"L": "Beijing",
|
||||
"O": "CUA",
|
||||
"OU": "IT"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
# 生成SAN列表
|
||||
SAN_LIST=""
|
||||
if [[ -n "$DOMAINS" ]]; then
|
||||
SAN_LIST+="$DOMAINS,"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# 移除末尾逗号
|
||||
SAN_LIST="${SAN_LIST%,}"
|
||||
|
||||
# 根据证书类型选择profile
|
||||
case "$TYPE" in
|
||||
server)
|
||||
PROFILE="server"
|
||||
;;
|
||||
client)
|
||||
PROFILE="client"
|
||||
;;
|
||||
peer)
|
||||
PROFILE="peer"
|
||||
;;
|
||||
esac
|
||||
|
||||
# 生成证书
|
||||
echo -e "${YELLOW}正在生成 $TYPE 证书: $NAME${NC}"
|
||||
echo -e "${YELLOW}SAN列表: $SAN_LIST${NC}"
|
||||
|
||||
cfssl gencert \
|
||||
-ca="$CA_CERT" \
|
||||
-ca-key="$CA_KEY" \
|
||||
-config="$CA_CONFIG" \
|
||||
-profile="$PROFILE" \
|
||||
${SAN_LIST:+-hostname="$SAN_LIST"} \
|
||||
"$CSR_CONFIG" | cfssljson -bare "$CERT_DIR/$NAME"
|
||||
|
||||
# 验证生成结果
|
||||
if [[ -f "$CERT_DIR/${NAME}.pem" && -f "$CERT_DIR/${NAME}-key.pem" ]]; then
|
||||
echo -e "${GREEN}证书生成成功!${NC}"
|
||||
echo -e "${GREEN}证书路径: ${CERT_DIR}/${NAME}.pem${NC}"
|
||||
echo -e "${GREEN}私钥路径: ${CERT_DIR}/${NAME}-key.pem${NC}"
|
||||
echo -e "${GREEN}证书签名请求: ${CSR_CONFIG}${NC}"
|
||||
|
||||
# 合并根证书
|
||||
if [[ "$MERGE_CA" == "true" ]]; then
|
||||
FULL_CHAIN="${CERT_DIR}/${NAME}-fullchain.pem"
|
||||
cat "$CERT_DIR/${NAME}.pem" "$CA_CERT" > "$FULL_CHAIN"
|
||||
echo -e "${GREEN}合并后的完整证书链: ${FULL_CHAIN}${NC}"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# 显示证书信息
|
||||
echo -e "\n${YELLOW}证书信息:${NC}"
|
||||
openssl x509 -noout -text -in "$CERT_DIR/${NAME}.pem" | grep -A 5 "Subject Alternative Name"
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo -e "${RED}证书生成失败!${NC}"
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user